What does the third degree of maturity of the placenta mean and what week is it normal for pregnancy?
Pregnancy develops, but at the same time specific changes occur in the placenta. Each period of pregnancy is characterized by a certain degree of maturity of placental tissue. Our article will tell in more detail about what the third degree of maturity of the placenta means, and what week it is normal for pregnancy.
What does it mean?
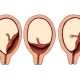
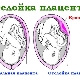
Experts distinguish several degrees of maturity of placental tissue. So, the placenta can be from zero to third degree of maturity. This indicator is determined during a planned ultrasound study, which is conducted by the expectant mother.
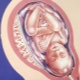
Placental tissue during pregnancy performs many very important functions. So, by means of the placenta and the blood vessels located in it, the baby developing in the uterus receives all the necessary nutrients and oxygen for its growth. With excessively early maturation of placental tissue, this balance is disturbed, and the fetal development of the fetus is not so physiological.
The reasons that can lead to excessively early maturation of the placenta, are very diverse. For example, vascular diseases with which the expectant mother suffers can lead to the appearance of specific changes characteristic of the 2 degree of maturity of the placenta.
Arterial hypertension or severe preeclampsia can lead to disruption of the functioning of the placenta and its early maturation, which may adversely affect the further course of pregnancy.
Norm
By the end of the third trimester of pregnancy, specific changes begin to occur in the placenta. They are quite normal and indicate that the female body is gradually beginning to prepare for the upcoming delivery. The closer the date of the birth of the baby, the more changes occur in the placenta. When the baby arrives, he will no longer need to receive nutrients and oxygen through the placenta. His body will already be able to breathe atmospheric air.
In the final trimester of pregnancy, the placenta begins to change its appearance. All characteristic changes indicate that placental tissue is already fully matured. Natural aging of placental tissue corresponds to 3 degrees of maturity of the placenta. This condition is usually diagnosed normal at 37 weeks of gestation and later.
Often in obstetric practice there are cases when the final maturation of the placental tissue occurs much earlier. So, 3 degree of maturity of the placenta can be detected in 35-36 weeks of pregnancy.
Future mother, in which this happens, should not panic. Small deviations maturation of the placenta in this situation are quite acceptable.
Matured placenta is almost unchanged before delivery. This means that all emerging changes in the structure of the placental tissue are preserved until the immediate birth of the afterbirth.
After it was born, doctors, using histological examination, can study the structure of the tissue and reveal various possible defects and abnormalities in the development of the organ, which were formed during the pregnancy.
How is it determined?
Determination of the degree of maturity of the placenta is carried out using ultrasound.This examination is painless and fairly informative. Using a special sensor, an ultrasound specialist examines the placenta in detail. It determines the thickness of the tissue, its size, the presence of compacted areas and cysts, and also assesses the presence of various anatomical defects.
The finally formed and mature placenta has a rather uneven surface. All of it is covered with grooves that penetrate deep into the placental tissue. Previously, the smooth and even surface of the fabric becomes bumpy and even rough by the 37th week of pregnancy.
Another characteristic feature for the placenta of 3 degrees of maturity is the presence of compacted areas in it - calcinates. In terms of their density, they are different from ordinary fabric. Calcifications appear in the placenta due to its physiological aging. This process is quite normal and indicates the imminent approach of childbirth.
In some cases, the maturation of the placenta occurs with pronounced calcification. The presence of calcium in the placental tissue in the early stages can be dangerous in the development of a number of complications, one of which is intrauterine hypoxia. A child who is hypoxia in the womb cannot fully exist. Oxygen deficiency, which occurs during intrauterine hypoxia, leads to increased stress on the heart and blood vessels of the baby. In this case, the fetus, as a rule, changes the work of all vital organs.
A change in the general condition leads to the fact that the baby in the womb changes the heart rate and increases physical activity. In this case, the required intervention of doctors. In such a situation, the expectant mother can be hospitalized in the hospital for treatment, aimed at correcting the violations.
If the placenta due to excessively early maturation does not function well enough, which leads to a deterioration in the general well-being of the baby, then in this case it is necessary to conduct the treatment.
In this situation, therapy is usually also carried out in the hospital. A pregnant woman is prescribed a complex drug therapy, bed rest is prescribed, as well as careful medical observation. If the placenta is too early to mature, the risk of preterm labor is high.. To give birth to a pregnant woman will be under the close supervision of doctors.
If during the ultrasound examination the degree of maturation of the placenta was detected much earlier than the 37th week of gestation, then additional research is required. Doppler sonography is one of them. Usually it is carried out immediately after performing the ultrasound, usually on the same day.
When carrying out Doppler ultrasound, doctors can evaluate the blood flow in the vessels that supply blood to the fetus. With early maturation of the placenta, its functioning may be impaired. One of the main functions of placental tissue is to provide the fetus with nutrients. Reduction of uteroplacental blood flow can lead to the threat of intrauterine hypoxia.
Another method of diagnosis, which is used for early detection of 3 degrees of the placenta, is cardiotocography. Through this simple examination, it is possible to estimate the basic vital signs of the fetus.
If they are violated, then the therapy and the choice of tactics for further management of pregnancy are required. In some cases, hospitalization may be required in the hospital, where, with certain indications, the expectant mother can be directly to the birth.
About premature maturation of the placenta, see the following video.