What does placental calcification mean and in what forms is it?
The normal structure of the placenta ensures the physiological intrauterine development of the fetus. The presence of structural defects and various anomalies of placental tissue significantly complicates the course of a healthy pregnancy.
This article will talk about what calcification of the placenta means, and also in what forms it occurs.
What it is?
It is possible to determine the structure of the placental tissue by conducting an ultrasound examination. During the ultrasound, the doctor assesses the density, thickness and other parameters of the placenta. Normally, placental tissue up to 30-32 weeks of gestation has a fairly smooth outer surface. At the same time, the placental tissue itself has a rather homogeneous (homogeneous) structure, in which there are no additional inclusions or definable formations.
If the placenta has an inhomogeneous structure, then in this case quite often various calcifications are found in it - compacted areas. Calcification of the placenta usually occurs in the third and final trimester of pregnancy. The closer to childbirth, the greater the likelihood of detecting various calcifications in the placental tissue.
If during the examination of the placenta in the earlier stages of pregnancy were found dense areas (calcinates), then this condition is called calcification by doctors. It is registered in obstetric practice often. With calcification, calcifications are usually found at 26-30 weeks of gestation, less often - at earlier periods.
Causes of development
For a long time, doctors studied the placenta only retrospectively - after its immediate “birth” during labor. The study of the structure of the placenta during pregnancy became possible only due to the introduction of ultrasound diagnostic devices into medical practice. During an ultrasound examination for pregnant women, doctors were able to study the structure of the placental tissue and got an objective idea of what the placenta should be during normal and complicated pregnancy.
The appearance of calcifications in the placenta at 34-36 weeks of pregnancy should not be a cause for concern for the future mother. At this time, even in a healthy placenta, certain structural changes begin to occur. This is a kind of preparation of the body for the upcoming birth.
If calcifications in the placental tissue were detected much earlier, in this situation, doctors try to identify a possible cause of the development of this condition. For the future mother, who has been identified such a condition, in this case, conduct a thorough medical observation.
The appearance of calcifications in the "young" placenta can lead a variety of reasons. Doctors now have not come to a common opinion about what ultimately affects the fact that the placenta begins to quickly "grow old", and in it appear multiple calcifications.
Doctors distinguish several conditions in which the prognosis of the development of calcification of the placenta increases:
- the presence of bad habits in a pregnant woman (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- sexually transmitted infections of the genitourinary system;
- some bacterial, viral and fungal diseases;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies of internal organs;
- severe preeclampsia;
- severe anemia;
- chronic diseases of the reproductive organs (endometriosis, fibroids, uterine malformations, and many others).
It is believed that The development of this condition is a consequence of any pathological process in which the blood supply to the placental tissue is disturbed. Severe narrowing of the blood capillaries can lead to disruption of nutrient and oxygen supply to certain areas of the placenta. A significant reduction in blood flow will lead to the development of functional disorders, which ultimately will contribute to the formation of compacted areas of the modified tissue - calcinates.
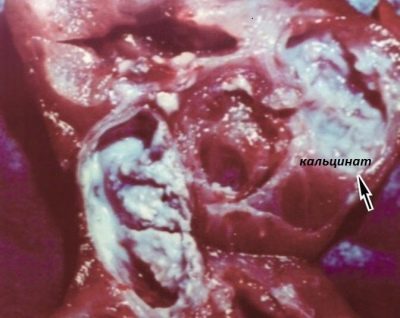
Quite a lot of calcium is deposited in the calcined area of placental tissue. It is because of this that calcinate has a characteristic appearance and density. The calcined areas of the placenta are much harder than the rest of the tissue, which is normally quite loose and soft.
What is the danger?
The appearance of multiple calcifications in the placental tissue much earlier than expected may indicate its early “aging”. In this case, as a rule, the prognosis of pregnancy may worsen. Calcification of the placenta may in this situation complicate the third trimester of pregnancy, and even be accompanied by the development of certain adverse effects.
The presence of multiple calcifications in the placenta is dangerous because its functioning is impaired. In this case, the fetus does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen. This generally negatively affects the entire process of intrauterine development.
A strong violation of the body’s development in the baby’s womb can be dangerous in the development of placental insufficiency - an extremely dangerous condition. If the pathological condition continues to progress, it may even contribute to premature labor.
Clinical options
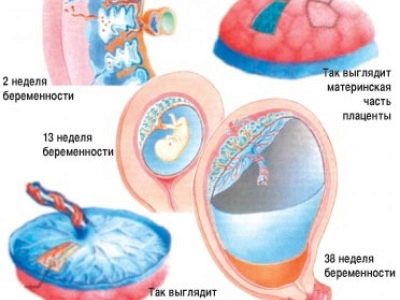
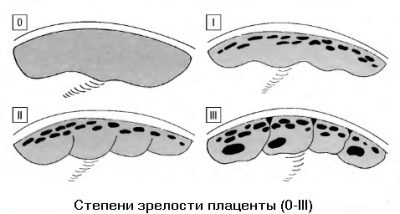
The appearance of compacted areas in the placenta also depends on its degree of maturity. The "older" placental tissue, the more it is changed. Placenta in its maturity can be of several types.
- Zero (0). Characteristic for placental tissue in the normal "younger" 30 weeks. The structure of the placental tissue is homogeneous with no extraneous inclusions.
- The first (1). It is characteristic in the normal course of pregnancy for 36-37 weeks. In the placenta of such maturity, single calcifications are usually found, the age-related changes are moderate.
- The second (2). Characterized for 34-39 weeks of pregnancy. The structure becomes less homogeneous, various indentations appear in it. Calcinates are usually multiple.
- The third (3). Characteristic for placental tissue "older" 37 weeks. The structure of the placental tissue becomes heterogeneous. On the outer surface of the placenta, many different dimples appear. Calcinations with multiple, located almost in the entire depth of the placental tissue, can merge with each other.
How does it manifest itself?
The course of calcification can be asymptomatic, as well as lead to the appearance of various clinical signs. It largely depends on what sizes calcinates are, as well as on their quantity.
So, if the compacted areas are multiple, then the prognosis of the course of pregnancy usually worsens. The more damaged tissue, the less the placenta performs its functions intended by nature.
Single small calcifications usually do not affect the course of developing pregnancy. They are detected, as a rule, by chance - during a planned ultrasound scan. In this case, the daily life of a pregnant woman is practically unchanged. She has no adverse symptoms characteristic of severe placental calcification. The general condition of the fetus is also not disturbed.
The presence in the placental tissue of multiple and rather large in size calcinates can lead to disruption of the functioning of the child's body. Usually, a child “manifests” this by changing his motor activity. So, a pregnant woman may feel that her baby has become too often and painfully pushed, or vice versa - has begun to move much less.
An unfavorable sign is the change in the heart rate of the fetus. This indicator of the heart allows doctors to assess the general condition of the fetus in the womb. A child may develop tachycardia or bradycardia. In this situation, the required intervention of doctors to compensate for the general condition of the baby.
If placental calcification is detected, and is still far from giving birth, then the expectant mother is prescribed therapy. It includes not only the use of drugs, but also implies the observance of strict recommendations on the management of the regime of the day and rest.
So, to correct the hemodynamic disturbances that have occurred, doctors may resort to prescribing medications that improve blood flow. It is possible to assess the dynamics through CTG. The normalization of the fetal heart rate and its motor activity indicate an improvement in its general well-being against the background of the prescribed therapy.
To achieve the complete disappearance of calcifications from placental tissue against the background of treatment is impossible, and is not required. The goal of therapy for calcification is the normalization of impaired functions performed by the placenta. Also, prescribing medications helps to reduce the risk of developing dangerous complications during pregnancy.
On the structure and function of the placenta, see the following video.