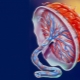
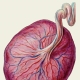
What does marginal placenta previa mean, what is it dangerous for and what does it affect?
During pregnancy can develop quite dangerous pathology associated with a violation of the normal location of the placenta. In this case, carrying a baby can be complicated by the development of certain adverse symptoms. It is necessary to consider in more detail what the regional presentation of the placenta means, as well as how it can be dangerous and what it affects during pregnancy.
What is it?
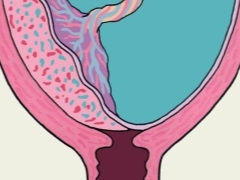
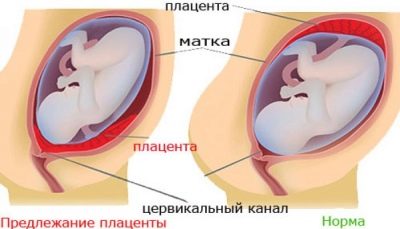
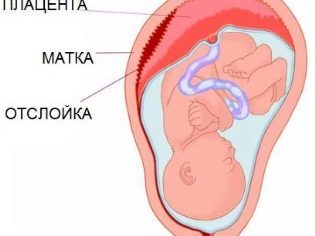
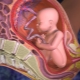
Doctors believe that placenta is a pathology in which the place of initial attachment of placental tissue is in close proximity to the internal uterine pharynx. Normally, a fertilized egg is attached during implantation in the area of the upper part of the uterus, which is called the bottom.
The location of the future chorion largely determines the initial location of the placental tissue. It is formed from fetal components, therefore it is located in close proximity with it. If for some reason the fertilized egg is displaced to the internal fallopian pharynx, then in this zone, placental tissue begins to form. This leads to the development of pathology - placenta previa.
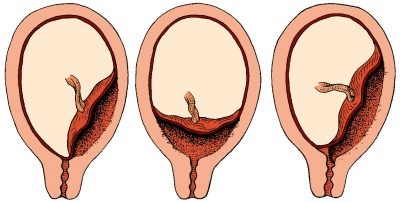
Doctors distinguish several clinical variants of this pathological condition. They determine them from how strongly the placental tissue is in contact with the internal uterine throat. One of these clinical options is the regional presentation. In this case, not the entire surface of the placental tissue, but only its individual sections are in contact with the uterine throat with their edges.
Causes
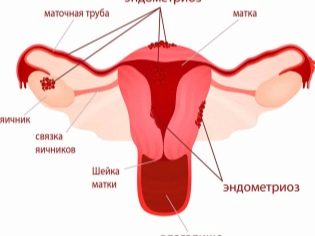
A variety of causal factors can lead to the development of this pathology. Quite often, this disease state is preceded by chronic diseases of the reproductive organs. Women suffering from endometriosis, adnexitis, cervicitis and other diseases of the genital organs before pregnancy are at increased risk for the development of this pathology.
The risk of developing regional presentation is also quite high in women who have undergone surgery on the uterus or its appendages. Doctors say that the development of regional presentation of the uterus can also contribute to, which appeared as a result of earlier caesarean section.
The development of regional presentation of the placenta can lead and the consequences of past infectious diseases. So, coccal flora, affecting the internal uterine walls, leads to changes in the mucous membranes, which contributes to implantation impairment. In this case, the normally fertilized egg descends to the lower sections of the uterus, where the endometrium is more functional.
Congenital anomalies of the female genital organs can also lead to the development of this pathology. So, with the double-horned uterus, the risk of developing placenta prevailing slightly increases. The presence of polyps and myomatous nodes, which are located in the uterine region, can also become a definite obstacle to the implantation of a fertilized egg in this zone.
To placenta previa can lead not only to the pathology of the woman.Some abnormalities of the chorion can also cause the development of this pathology. In some genetic pathologies, the trophoblast lacks certain enzymes necessary for implantation into the uterus wall. In this case, the attachment to the uterus does not occur, as a result, the pregnancy itself is interrupted almost at the very beginning of its development.
Doctors note that the risk of developing regional presentation of the placenta is somewhat higher in women who give birth to second and subsequent babies. If at the same time the previous pregnancy ended with a cesarean section, then the probability of the development of regional presentation increases.
Features of the course of pregnancy
Regional presentation of the placenta can significantly complicate the process of carrying a baby. Such a pregnancy is usually characterized by a restless course, as well as the periodic appearance of adverse symptoms. It is worth noting that with extreme previa, still carrying out is somewhat calmer than with full. In this case, the prognosis of the course of pregnancy is more favorable.
Unfavorable symptoms in this pathology usually appear after 16–20 weeks of pregnancy. By the third trimester, they can increase. In the very first weeks after fertilization, any significant discomfort in the expectant mother may be absent.
How to determine?
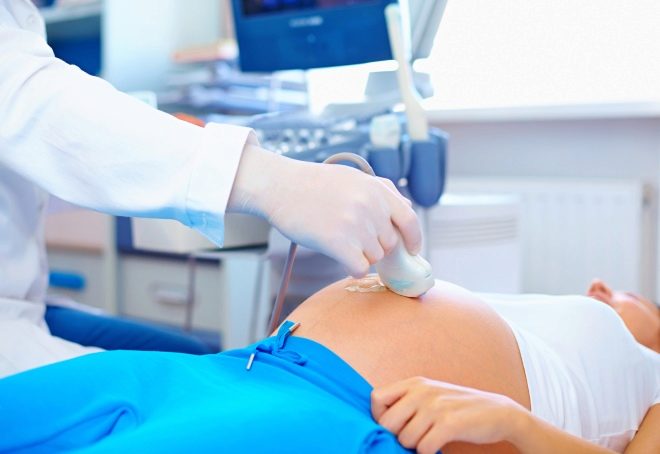
The location of the placental tissue is currently quite simple to determine. To do this, doctors resort to the appointment of ultrasound examinations. When regional presentation of the placenta is undesirable to conduct transvaginal ultrasound. In this case, the possibility of damage to the low-lying placental tissue is quite high. In this situation, it is better to choose transabdominal ultrasound.
Localization of the placenta can be determined through a routine vaginal examination. However, in case of regional presentation of the placenta, it is often not necessary to resort to this technique. If carelessly conducting such an examination, the delicate tissue of the placenta can be damaged. That is why doctors give their preference more ultrasound techniques.
If during the diagnosis the regional presentation was determined, then the following additional studies are also assigned to the expectant mother. They are necessary in order to assess the dynamics of the current pathology.
If the pathology was discovered quite early - at 12–16 weeks of gestation, then in such a situation, the localization of the placental tissue may still change. The shift of the placenta up doctors call migration. It proceeds rather slowly and ends only by the 3rd trimester of pregnancy. That is why the localization of the placenta during its presentation is determined for the entire period of gestation of the baby several times. Unfortunately, the migration of the placenta does not occur in all cases.
Possible complications
The most striking sign that usually causes a pregnant woman with a regional placenta previa to seek advice from an obstetrician-gynecologist is the appearance of blood from the genital tract. In this pathology, blood usually appears after lifting heavy objects or after intense exercise. The appearance of blood in underwear can only be an isolated symptom. In some cases, it is combined with the appearance of pain in the abdomen.
If a pregnant woman has seen bleeding from the genital tract and at the same time she has a severe stomach ache, this means that she should not hesitate to seek medical help.
Bleeding from the genital tract with a very low position of the placenta may develop after sex. The possibility of having sex in the presence of such pathology is necessarily discussed with an obstetrician-gynecologist. Usually, nevertheless, doctors recommend their patients with regional placenta previa to limit sex and prescribe sexual rest.
Many pregnant women confuse pathology of the placenta and the umbilical cord. Thus, the marginal presentation of placental tissue has nothing to do with the marginal discharge of the umbilical cord. Placenta previa is a pathology, and the marginal discharge of the umbilical cord is only a physiological feature of the course of a particular pregnancy.
No less dangerous complication that can develop during pregnancy, complicated by regional placenta previa, is the development of placental abruption from the walls of the uterus. This pathology is usually found as a consequence of traumatic effects. The more placental tissue exfoliates from the uterine wall, the less favorable is the prognosis of pregnancy. To avoid the development of possible placental abruption, doctors make up a whole range of different recommendations. So, contraindications include intensive exercise and running. A pregnant woman whose pregnancy proceeds with the development of a regional presentation is prohibited from lifting too heavy objects. It is very important that the expectant mother rested more.
In addition to sports, a pregnant woman with a regional placenta previa, the doctor may prohibit and visit the pool. Reviews of many women who had this pathology during pregnancy confirm this. For extremely severe previa, any physical activity may be limited, and in some cases even bed rest is prescribed.
Strong stress can also make things worse. Future mother should strictly follow such recommendations.
Preventing infection of a low-lying placenta is another challenge during a complicated pregnancy. In this case, the disease-causing organisms most often enter the uterine cavity from the external genital organs. In order to prevent such an infection, a pregnant woman should carefully follow the rules of personal hygiene. The extreme position of the placenta relative to the uterine throat can also be dangerous for the fetus developing in the mother's womb.
Impaired uteroplacental blood flow can lead to the development of placental insufficiency. In this situation, the intensity of fetal development is significantly reduced.
How is the birth?
Pregnancy occurring with regional presentation of the placenta can have a highly unpredictable prognosis. At any stage of carrying a baby, there may be dangerous complications that contribute to the change of tactics originally chosen by the doctors. So, if severe bleeding occurs or the fetus is threatened, the doctor will have to resort to emergency surgical obstetric care.
Pregnant women with regional presentation of the placenta, as a rule, perform cesarean section. In this case, it is possible to minimize the risk of developing dangerous complications that occur during independent labor.
If, before giving birth, a woman had severe anemia, due to frequent previous bleeding from the genital tract, then in this situation she would be prescribed iron-containing drugs. For the most rapid compensation of the general condition, such drugs are administered by injection. Even during cesarean section during pregnancy, accompanied by regional placenta previa, there is a high risk of severe bleeding. During the operation, doctors must control the pulse and blood pressure of the woman.
With the development of severe bleeding and massive blood loss, these indicators begin to critically decrease. In such a situation, doctors usually resort to parenteral administration of oxytocin or hemostatic agents. The main goal of such drug therapy is to save the life of the mother and her baby.
After the baby was born, doctors must evaluate its overall condition. If necessary, the child is a complex resuscitation.Usually, their conduct is required if the baby was born much earlier. The neonatologist, who is in the delivery room during childbirth, conducts such medical manipulations. After giving birth, doctors must also monitor the condition of the parturient woman.
When placenta previa often happens so that when a baby is born, a woman loses quite a lot of blood. In order to quickly restore its condition, doctors resort to the management of medicinal solutions, and, if necessary, hemostatic drugs.
See what the dangerous placenta previa is in the next video.