Signs and causes of placental abruption, consequences for the fetus
Placental abruption is a serious complication of pregnancy and childbirth. Disconnecting the “baby site” from the uterine wall can be fatal to a child and his mother. According to statistics, such a violation occurs in 1.5% of cases of all pregnancies. Why is this happening, if there are chances for the salvation of the baby, and what the consequences may be at different times, will be discussed in this article.
What it is?
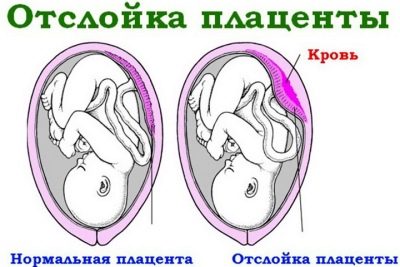
Placental abruption is considered normal only if it occurs after childbirth, after the baby is born. “Children's place”, having exhausted its resources and becoming unnecessary, is rejected, born. During pregnancy, first, the chorion, and then the placenta, formed on its basis, nourishes and supports the baby, supplies it with oxygen and all the substances necessary for growth and development.
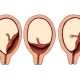
Premature detachment is called partial or complete detachment of the placenta from the uterine wall with vascular damage. The mechanism of development of detachment to the end of medicine is incomprehensible, but the processes that follow such detachment are obvious - bleeding of different intensity develops, comparable to the size of the detachment.
Most often, the pathology occurs in women who decide to become mothers for the first time. In addition, women during preterm birth are 3 times more likely to experience recession in the “baby seat” than women who give birth on time.
The condition and vitality of the baby, its development depends on the state of the placenta. The placenta not only participates in gas exchange (it supplies oxygen to the baby and removes carbon dioxide), it also nourishes it, protects and participates in the production of many of the hormones necessary for safe childbearing. "Baby seat" is usually quite tight to the wall of the uterus: from above it is pressed on the fruit and water, from below - the walls of the uterus. It is this double pressure that prevents the placenta from leaving its place before time.
Severe detachment, total detachment before childbirth leads to acute hypoxia - The baby loses oxygen, nutrients. In a pregnant woman’s body, hormones are disturbed. If emergency medical care is not provided, the child will die. If the baby is very premature at the time of detachment, it is more likely that he will also die.
With marginal, partial detachment, oxygen delivery will not stop completely, but will be insufficient. The consequences for the child will not be long in coming: the baby will receive less nutrients, will experience chronic hypoxia, and may slow down in development and growth. The state of chronic hypoxia is detrimental to all organs and systems of the child, but to a greater degree - to the nervous system and the brain and spinal cord, as well as the musculoskeletal system.
For a woman, detachment is dangerous if bleeding occurs. With prolonged bleeding, anemia occurs, the condition of the expectant mother worsens significantly. With abundant bleeding, typical of the total, large area detachment, the death of a woman from massive blood loss is possible. Even a small detachment of the placenta, which occurred at different times, creates huge risks of miscarriage or premature birth.
The reasons
The exact reasons that lead to the separation of the "children's place" from the uterine wall, science is still unknown. Doctors tend to believe that in each case, not even one role plays a role, but a combination of several risk factors.
- Pressure. High blood pressure can trigger the passage of the placenta. Half of the women who survived the detachment had hypertension. Approximately 10% of the detachment occurred against the background of a spontaneous jump in blood pressure to a higher or lower side. Often, blood pressure begins to "jump" under severe stress, in a threatening and unsuccessful psychological situation. Long lying on your back leads to a pressure disorder in the inferior vena cava, which can also lead to the detachment of the placenta from the uterine wall.
- Repeated pathology. If a woman has already had a detachment, the probability that she will repeat is above 70%.
- Multiple pregnancies and large families. Women who bear two or three babies are more susceptible to pathology than women who bear one child. Often the detachment is fixed in women who have given birth to many and often - their uterine walls are more flabby and stretched.
- The age of the pregnant. In future mothers older than 30 years, the risks of premature detachment are several times higher than among women 18-28 years old. If the expectant mother is more than 35 years old, then quite often the placenta “acquires” her additional lobule, and it is this lobe that comes off during the birth process, causing an automatic disconnection of the whole “baby seat”.
- Pregnancy after infertility, IVF. If pregnancy occurs after a long period of infertility, naturally or as a result of assisted reproductive methods, such as IVF, the probability of placental abruption increases, the risk is estimated at about 25%.
- Gestosis and toxicosis. In the early stages, a pronounced, painful toxicosis is considered a risk factor. Vomiting, nausea, metabolic disorders, pressure drops often lead to exfoliation in one degree or another. In the later stages dangerous preeclampsia.
When edema, excess weight, leaching protein from the body with urine and hypertension, the vessels suffer, which can also lead to the detachment of the placenta from its place.
- Features of the uterus and blood vessels. Some abnormalities in the structure of the main female reproductive organ, for example, the two-horned or saddle-shaped uterus, as well as abnormalities in the structure of the uterine vessels, can lead to habitual miscarriage due to permanent abnormalities.
- Placenta previa or low placentation. If for some reason the fetal egg stuck in the lower segment of the uterus, and subsequently the chorion, and the placenta behind it did not migrate higher, then the detachment becomes the main threat to this condition. Especially dangerous is the complete central presentation of the placenta when the baby seat closes the entrance to the cervical canal completely or almost completely.
- Hemostatic disorders. In women with bleeding disorders, detachment of the “children's place” during pregnancy and childbirth often occurs. Usually, hemostasis disorders are accompanied by other pathologies of pregnancy.
- Problems of generic activities. Often, a dangerous condition arises directly in childbirth - due to the pressure drop, during fast, rapid delivery, after the birth of the firstborn from twins, with untimely rupture of amniotic shells, as well as with a short umbilical cord.
- Injury. Unfortunately, this is also a common cause of serious complications. A woman can get a blunt abdominal trauma, fall on the stomach, get into an accident and hit the stomach. With such an injury, detachment of the “children's place” occurs in about 60% of cases.
- Bad habits. If the expectant mother cannot give up the habit of smoking or taking alcohol and drugs even while carrying her baby, then the probability of spontaneous sudden detachment increases tenfold.
- Autoimmune processes. Immunity of the pregnant woman can begin to produce specific antibodies to their own tissues. This happens in case of severe allergies, for example, on medications or in case of incorrect transfusion of blood, as well as in severe systemic diseases - lupus erythematosus, rheumatism.
- Mom's diseases. In terms of the probability of detachment, all chronic diseases of a pregnant woman are dangerous, but diabetes, pyelonephritis, thyroid problems, and obesity of a woman pose the greatest risks.
If, when registering, after examining the woman’s history, the doctor decides that this pregnant woman is at risk for the possible development of a detachment, he will more closely lead such a pregnancy. A woman will often have to visit a doctor, get tested, do an ultrasound scan, and she can also be recommended preventive stay in the day hospital several times during pregnancy.
Symptoms and signs
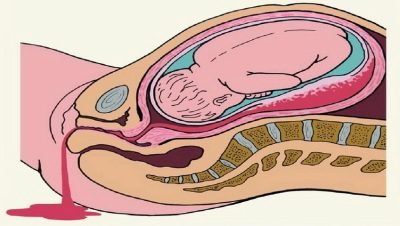
All signs of premature separation of the "children's place" are reduced to one manifestation - bleeding. The degree and severity of it depends on how extensive the detachment. Even a small detachment can lead to a large hematoma. It is a collection of blood released from the damaged vessels and accumulating between the uterus wall and the “children's place” itself. If there is no blood flow, the hematoma grows and increases, contributing to the detachment and death of all new areas of the placenta.
Symptoms can not be only with mild degree of pathology. Only a very attentive ultrasound doctor can notice a small detachment, as well as an obstetrician who will take birth - on the placenta, on the side where it adjoins the uterus, there will be small depressions, and, possibly, blood clots.
If a woman feels a slight nagging pain in the abdomen, accompanied by insignificant in volume brown or pink discharge, we are talking about a moderate degree of severity of the pathology. With the appearance of bloody "smears", the condition of the placenta on any term in any woman is necessarily examined.
The detachment of the average degree is much more dangerous than pregnant women used to think. It threatens to hypoxia for the baby, and often manifests itself a violation of the heart rhythm of the fetus.
Severe pathology is always characterized by an acute onset. A pregnant woman has a sharp, sudden, severe pain in the abdomen, a feeling of fullness from the inside, dizziness. Not excluded loss of consciousness. With this form of detachment, bleeding can be severe, intense. But also moderate bleeding is possible. A distinctive feature of the form - the color of blood. It is with severe detachment - scarlet, bright. The woman almost immediately develop shortness of breath, the skin becomes pale, she intensively sweats.
In severe and moderate form, tension of the smooth muscles of the uterus is always observed, and there is an increased tone; when examined, the doctor finds asymmetry of the reproductive female organ. By the nature of the bleeding, an experienced doctor can easily determine the type of detachment.
- No or minor bleeding. - central placental abruption is not excluded, in which all the blood accumulates between the uterus wall and the central part of the "children's place". This is the most dangerous form.
- Moderate vaginal bleeding - regional or partial detachment is not excluded, in which the blood leaves the space between the uterus and the “children's place” faster. Pathology of this kind has more favorable prognoses, since blood flow increases the probability of thrombosis of damaged vessels and healing of the area.
- No bleeding against the background of a noticeable deterioration of the condition of the pregnant woman and of the soreness of the uterus - the bleeding is latent, and it is a rather dangerous condition that can lead to total detachment.
The pain usually has a dull and aching character, but with acute and severe detachment, it can be sharp, spreading to the lower back, thigh. On palpation of the uterus by the doctor, the woman will experience severe pain. The baby's heartbeat is disturbed due to oxygen deficiency, which develops against the background of the discharge of the placenta.
The first signs of a violation of the condition of the fetus make themselves felt, if the “baby seat” has departed by about a quarter of its total area, with a threatening condition, which is manifested by a violation of the motor activity of the little ones, they say about 30% of the placenta is detached. With the discharge of an organ in 50% of its own area, the child usually dies.
In the diagnosis, the doctor will necessarily take into account the duration of pregnancy, because in different trimesters the symptoms and manifestations of the pathology may be different.
Detachment on different terms
In the early stages, the discharge of the placenta occurs most often, but you should not get upset, because if you go to a doctor in time, there are plenty of ways to save the pregnancy and prevent negative consequences for the mother and her baby. Usually in the first trimester, such a detachment manifests itself retrochorial hematoma, which is confirmed by the results of ultrasound. Allocations may be present, but may not appear at all.
In most cases, proper treatment at this stage allows the placenta to fully compensate for the loss of contact between a part of the area and the uterus in the future, and the pregnancy will develop quite normally.
If detachment occurs in the second trimester up to week 27 inclusive, then this is a more dangerous condition that threatens hypoxia to the baby. The crumb at the initial stage of oxygen starvation becomes more active, he is trying by all means to get himself additional oxygen.
If hypoxia becomes chronic, the movements of the child, on the contrary, slow down. Until the middle of the second trimester, the placenta can grow, then it loses this ability and can no longer compensate for the lost area. Therefore, the forecasts are more favorable if the detachment occurred before 20-21 weeks. After this period, the forecasts are not so bright.
In later periods, pathology is the greatest danger. "Children's place" can no longer grow, the compensation of part of the lost functions is physically impossible. Hypoxia of the fetus will only progress, the condition of the child may become critical. If the detachment continues to grow and increase in size, a woman will undergo a caesarean section to save the baby.
It is not always possible to save, because children can be deeply premature, and then death can occur as a result of acute respiratory failure due to the immaturity of the lung tissue or due to the inability of the child to maintain body temperature.
Only if the detachment does not progress in the third trimester, is there a chance to keep the pregnancy under strict bed rest under 24-hour observation in a gynecological hospital. At home, a woman's stay is impossible.
Placental abruption during childbirth can occur for a variety of reasons, most often this happens in pregnant twins or women with diagnosed polygamy. The walls of the uterus due to the abundant outpouring of blood can lose contractility. At any stage of the birth process in this situation, doctors use the stimulation of contractions, if this is unsuccessful, then an emergency cesarean section is performed.
Treatment
If there is quite a bit left before the date of birth, treatment of the detachment is impractical. Doctors recommend giving birth - to stimulate natural childbirth, or to conduct a cesarean section (depending on the time and situation). There is no point in waiting and delaying - delay can lead to tragedy.
But if the child is not yet considered viable, then the doctors will try to do everything to prolong the pregnancy, if the detachment does not progress. There is no single, ready-made solution — in each specific situation, the doctor and patient must carefully weigh the risks: give birth to a premature baby who may not survive, or take a risk and possibly face the critical state of the child due to detachment and hypoxia.
The detachment is always treated in stationary conditions. Therapy, which will include drugs - haemostatics, stopping bleeding, as well as drugs of other groups at the discretion of the doctor, is carried out only when the detachment is partial, the gestation period is less than 36 weeks, vaginal bleeding is absent or moderate, and there are no signs of severe fetal hypoxia and the progression of the detachment of the "children's place".
To remove the threat, antispasmodics are prescribed, which should keep the uterus muscles in a relaxed state, preventing even a short-term tone. The woman will be given medications that fill the baby with nutritional deficiencies and improve blood circulation between the uterus and the placenta. And she may also be recommended sedatives and iron supplements that will help get rid of the symptoms of anemia.
In the in-patient setting, women will do an ultrasound scan with a Doppler almost daily, and also do CTG to find out how the baby feels. Doctors will monitor laboratory tests for pregnant women, special attention will be paid to blood clotting factors. All measures will be aimed at avoiding repeated bleeding.
With the appearance of even the slightest signs of progression of the detachment of the “children's place”, the decision is made to stop waiting tactics and preserving therapy in favor of emergency delivery.
Prevention
Any pregnant woman should do everything possible to prevent such pathology. If there is at least minimal chances for detachment, the doctor will inform about it and give a number of important recommendations that will help protect the baby and their own health.
So, for women who have previously encountered this unpleasant complication, no one can offer any preventive treatment, because it does not exist in nature. But for the prevention of recurrence of the problem of a pregnant woman, it is recommended to contact the antenatal clinic for registration as early as possible.
Women with low placentation or placenta previa, as well as threatened abortion due to malformations of the “baby place” itself, do not recommend sex, excessive exercise and stress. It is impossible to neglect the visit of a doctor, the delivery of mandatory and additional tests during the carrying of a child.
If a woman suffers from high blood pressure, she must control her level and, if necessary, take medications that, if necessary, can effectively reduce the pressure without harming the child’s body. Women with a negative Rh factor during pregnancy from an Rh-positive man require the introduction of Rh immunoglobulin in the second trimester of pregnancy.
If a woman is at risk of detachment (and even if she does not belong to it), you should stop smoking during the gestation period and even avoid small doses of alcohol. Women should always wear a seat belt when traveling by car, and the belt should be held above or below the abdomen. In winter, when the stomach becomes quite large, you should move very carefully, because your own legs are not visible and the probability of falling and getting a blunt abdominal injury increases.
A woman should avoid contact with allergenic substances, do not take medicine without a doctor's prescription, since many drugs can provoke a detachment of the placenta and the occurrence of bleeding. In the presence of chronic diseases, two specialists must conduct a pregnancy with a woman - an obstetrician-gynecologist and a doctor of that specialty, in whose jurisdiction the future mother's disease belongs. Only a joint medical tandem will avoid complications.
When signs of preeclampsia appear (urinary protein appears, pressure increases, edema and abnormal weight gain), the expectant mother must comply with all prescriptions, and if necessary, go to hospital to be monitored by doctors and receive the necessary treatment.
Forecasts
Forecasts are more favorable if a woman asks for help from a doctor as soon as possible. With the appearance of bleeding, pain in the abdomen, deterioration of general well-being, you can not look for the answer to the question of what is happening on the Internet or with friends and girlfriends. It is important to call an ambulance as soon as possible. Spotting can not be considered normal during pregnancy, and in most cases they are an unambiguous sign of the problems with the integrity of the "children's place".
Every day, every hour is of great importance in predicting the outcome and consequences of placental abruption. The longer the gestational period, the more unfavorable the forecasts will be. The size of the detachment and the presence of its progression also affect the prognosis.
Reviews
Many women describe in their responses on the thematic forums that the placenta abruption was not preceded by any difficulties, diseases, problems with gestation. It all happened suddenly. In the early stages, most of the stories have a good ending - after a course of treatment in a gynecological hospital, the symptoms receded and the pregnancy was brought to a deadline. Unfortunately, in the later periods women often lose babies because of a sudden detachment of the “children's place”.
In severe cases, when the walls of the uterus are soaked with blood, neither the child nor the reproductive health of the woman can be saved - the uterus must be removed completely. After the death of the child due to the detachment of the “children's place”, it is especially difficult for women to plan the next pregnancy, both in terms of gynecological problems and psychologically.
There are groups on the Internet in which women who have survived this, but not losing hope of having children in the future, help each other with good advice and a supportive word. It is very important to overcome the fear of a new pregnancy.
About why premature placental abruption may occur, see below.