Causes and effects of placental abruption in early pregnancy
Placental tissue is an important organ that appears in the female body only while carrying a baby. Pathology of attachment of the placenta can be very dangerous. This article will tell about the causes and consequences of placental abruption in early pregnancy.
What it is?
In normal placental tissue rather tightly attached to the walls of the uterus. Such a strong fixation is necessary for the unobstructed supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. Without placenta, physiological pregnancy is impossible.
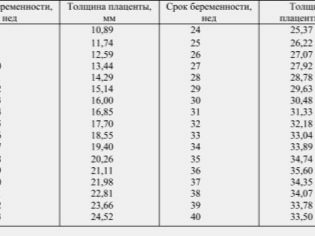
The placental tissue contains blood vessels. During pregnancy, the thickness of the placenta changes gradually. So, for childbirth, its thickness is usually 20-40 mm.
Unfortunately, in obstetric practice, there are cases when placental tissue is detached from the uterine walls. This pathology develops, according to statistics, in about 0.5-1.5% of cases.
Placental abruption in early pregnancy may be different. So, if the placental tissue is almost completely exfoliated, then this state means complete detachment. This pathology has, as a rule, an unfavorable prognosis for the further course of pregnancy.
Another clinical option is partial placental abruption. In this case, the placental tissue exfoliates from the uterine wall only in a specific area. In this case, as a rule, the forecast is already more favorable. In partial detachment of the placenta, adverse symptoms usually develop gradually.
What is happening?
A variety of causal factors can lead to detachment of the placental tissue. It also happens that some of them act simultaneously. In this case, the probability of developing pathology increases many times.
Doctors believe that various chronic diseases of the reproductive organs can lead to the development of placental abruption in the early stages. Quite often inflammatory pathologies contribute to the development of this pathology - endometritis, cercevitis and others. Typically, such diseases occur in women before pregnancy.
Dishormonal disorders can also lead to placental abruption. For the normal functioning of the placenta requires certain hormones. If for some reason they are few in organization, then in this case unfavorable pathologies develop.
Harmful habits can also cause the development of detachment of placental tissue from the walls of the uterus. Smoking and alcohol abuse can lead to the development of damage to the placenta.
Exfoliation of the placenta in early pregnancy may also occur in women who have a burdened obstetric and gynecological history. If a woman has previously had spontaneous miscarriages, then the risk of placental tissue detachment is also quite high. Antecedent abortions may also increase the risk of this pathology. Some scientists note that the risk of developing placental detachment is slightly higher in women who have given birth to several babies.
The presence of certain diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive and urinary systems can also contribute to the development of placental abruption in the early stages. Often, such pathologies significantly aggravate the course of pregnancy.
Allergic pathologies may also contribute to the development of placental tissue detachment. Impaired work of the immune system leads to an imbalance in the mother-fetus system. Autoimmune diseases can trigger the development of chorionic detachment. In this case, in order to prevent the development of complications, prescribing drugs is required.
Dishormonal disorders can also lead to placental abruption. For the normal functioning of the placenta requires certain hormones. If for some reason they are few in organization, then in this case unfavorable pathologies develop.
Harmful habits can also cause the development of detachment of placental tissue from the walls of the uterus. Smoking and alcohol abuse can lead to the development of damage to the placenta.
Traumatic injuries can also lead to placental abruption. Shocks, injuries, falls on the stomach contribute to the development of dangerous conditions. The danger of them is that not always adverse symptoms immediately appear. At first, clinical signs are usually minor. The more placental tissue exfoliates from the uterine wall, the more pronounced the symptoms.
Adverse symptoms of placental abruption can occur after intense exercise. Intense exercise in the gym can contribute to the development of microdamages in the placental tissue. This can cause the placenta to gradually flake off. Also, the development of this pathology may occur after lifting heavy objects.
If the course of pregnancy is aggravated by a number of other conditions, then the prognosis of the course of placental abruption changes and becomes less favorable. The combination of various pathologies contributes to the appearance of defects in the hemostatic system, the occurrence of vascular disorders and even the possible development of bleeding.
Symptoms
Unfavorable symptoms when exfoliating the placenta may appear differently. With partial detachment of placental tissue, symptoms develop gradually. In some cases, signs of pathology appear so slightly that the expectant mother does not attach importance to them. In such cases, the diagnosis of placental abruption may be delayed.
With complete exfoliation of placental tissue from the uterine walls, adverse symptoms grow very quickly. In this situation, the general condition of the pregnant woman deteriorates so much that it requires emergency hospitalization in the hospital.
The most common sign of placental abruption from the uterine wall is the appearance of bleeding. The degree of severity may be different. It should be noted that bleeding can be both external and internal.
If as a result of exfoliation of placental tissue, the blood remains inside the uterus and does not immediately expire, then it is rather difficult to suspect pathology in early pregnancy.
If a pregnant woman in the early stages of blood appears from the genital tract, then she should not hesitate to seek medical help. The help of doctors is necessary. With the development of placental abruption, it is extremely important to assess the general condition of the expectant mother and her baby.
It should be noted that not all cases with placental abruption appear bleeding. Reviews of many women indicate that with this pathology they only had bleeding from the genital tract, and there was no bleeding. Such secretions can be both abundant and moderate. It depends on how much the placental tissue has exfoliated.
Another symptom that can occur with placental abruption is pain in the abdomen. In this situation, the pain is usually localized in the lower abdomen. With complete detachment of the placenta, pain syndrome usually appears suddenly, amid complete well-being. The intensity of the pain is very intense. Some women, experiencing such pain, may even lose consciousness.
With partial detachment of the placenta, pain in the abdomen usually develops gradually. It does not always develop, but only in 40-50% of cases. It usually appears after a fairly quick walk or weight lifting. The pain may be localized or even spread to the hips.
In some cases, with placental abruption, uterine hypertonus may also develop. This condition worsens during pregnancy. Pregnancy, aggravated by hypertonus and placental abruption, usually proceeds much harder.
With the development of this pathology, a woman may also have associated symptoms. So, the expectant mother may feel nausea, weakness, fatigue. In some cases, dizziness may occur.
It should be noted that in obstetric practice there are also cases when it is very difficult to suspect placental abruption. Asymptomatic variant of this pathology can only be determined by conducting an ultrasound examination.
How is the diagnosis?
Suspecting the exfoliation of placental tissue only on the emerging symptoms can be difficult. It usually happens that this pathology can be accurately determined only during ultrasound.
During this diagnostic procedure, the doctor may determine the extent of the detached area of the placenta, as well as identify the placental hematoma. Also during such a diagnosis, a specialist assesses the general condition of the fetus, as well as the presence of possible complications.
Effects
The detachment of placental tissue from the walls of the uterus is dangerous by the development of a number of dangerous complications. In each case, the course of pregnancy, they may be different.
Bleeding
Exfoliation of the placenta from the uterine walls can lead to bleeding. The appearance of blood from the genital tract may appear suddenly. This pathology is dangerous massive blood loss.
Severe blood loss leads to a decrease in circulating fluid volume. In this case, it is very important that medical care is provided in a timely manner. With the development of severe bleeding from the genital tract, a woman is hospitalized in the hospital.
Anemic condition
Bleeding from the genital tract leads to the fact that a pregnant woman can develop anemia. The anemic state is characterized by a decrease in the total number of red blood cells and (or) hemoglobin. It should be noted that the anemic state threatens with violation of the nutrient and oxygen supply to the embryo. In this situation, the children's body can not fully grow and develop.
To determine the anemia, the doctor must prescribe a future mother for a complete blood count. Through this simple laboratory test, it is easy to determine how much red blood cells and hemoglobin are reduced. For correction of the arisen violations, the future mother is prescribed iron-containing drugs. Apply these tools should be quite long.
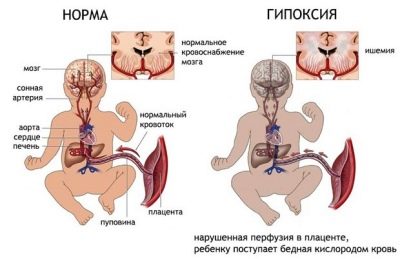
Intrauterine hypoxia
Oxygen deficiency in the blood is called hypoxia. If fetal hypoxia develops and persists in the first trimester of pregnancy, then this may impair the physiology of fetal development. In the early stages of pregnancy, the fetus is actively organogenesis - the process of formation of internal organs. Intrauterine hypoxia is a dangerous condition that can affect the development of various pathologies in a baby.
Risk of miscarriage
The prognosis of pregnancy during placental abruption, unfortunately, can be rather sad.
Exfoliation of placental tissue is accompanied by impaired uteroplacental blood flow. Without nutrients and especially oxygen for a long time, the fetus can not exist.
The development of spontaneous miscarriage in early pregnancy, unfortunately, occurs in gynecological practice quite often. The most dangerous in this case is complete detachment of the placenta. In such a situation, even the death of the fetus can occur.
How to prevent possible complications?
After the future mother was diagnosed with placental abruption, she should carefully monitor her well-being. Doctors make up a whole range of recommendations that should help avoid adverse effects. These recommendations include:
- strict adherence to the daily regimen;
- balanced diet, enriched with vitamins and microelements;
- full sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- restriction of classes in the gym and pool;
- ban on lifting heavy objects;
- stress reduction;
- regular observation by an obstetrician-gynecologist;
- restriction of sexual activity, and if necessary, even complete sexual rest;
- receiving individually selected medication.
If any adverse symptoms appear, the expectant mother should immediately see her doctor. These simple guidelines will help reduce the risk of developing dangerous complications in early pregnancy.
Treatment
The prognosis of the development of pregnancy in determining placental abruption depends largely on how timely the doctors determine this condition. Timely diagnosis can significantly reduce the possible complications, provided that a pregnant woman complies with all the recommendations that are made for her in this pathology.
Treatment of placental detachment complex. The choice of treatment tactics largely depends on the severity of the violations. For this, doctors necessarily evaluate both the condition of the future mother and her baby.
The degree of blood loss, which certainly develops with placental abruption, also significantly affects the choice of tactics for conducting such a complicated pregnancy in the future. Also, the doctor must evaluate the need for hospitalization in the hospital.
Drug therapy
Drugs used to treat placental abruption can be very diverse. So, in order to stop the developed bleeding, doctors resort to the appointment of hemostatic agents. One of these drugs is Tranexam. This tool contains tranexamic acid, which has a hemostatic effect.
Assigned to "Tranexam" for various bleeding, including those that occur during pregnancy. Before the appointment of this drug, as a rule, it is necessary to pass a biochemical analysis of blood clotting.
Take this tool yourself should not. Prior to admission, you should always consult with your doctor.
In some cases, doctors resort to prescribing drugs that help to cope with the adverse symptoms of placental insufficiency. One of such means is “Curantil”. It helps to normalize the reduced blood flow in the uteroplacental vessels and to improve the health of the fetus.
When placental abruption, which has developed due to dishormonal disorders caused by a decrease in progesterone in the blood, hormonal drugs are prescribed. So, to normalize the level of the main hormone of pregnancy in the blood, doctors quite often prescribe "Duphaston". Dosage and duration of use are determined by an obstetrician-gynecologist. While taking the drug, an assessment is made of the dynamics of the condition of the pregnant woman and baby.
If during bleeding, which develops with placental abruption, pain develops in the abdomen, then painkillers are prescribed for its relief. It is not necessary to use such means for a long time. They, as a rule, are used periodically only to relieve pain.
With a small exfoliation of the placenta, doctors can leave the expectant mother at home. Hospitalization in the hospital is carried out only with the threat of fetal life or decompensated state of the expectant mother. In this case, more careful and careful observation of doctors is required. During the hospital stay, a pregnant woman is given a number of medications that are necessary to improve her well-being.
In order to assess the dynamics of the pathology, doctors send the future mother, who has a placental abruption, to undergo various examinations. So, the woman is carried out ultrasound and cardiotocography. Also, the doctor may prescribe and dopplerography for the assessment of uteroplacental blood flow.
Drugs that have an antispasmodic effect are prescribed strictly according to indications. Their action is aimed at removing the spasm of the blood vessels. Drotaverine hydrochloride (“No-shpa"). Self uncontrolled use of antispasmodics at home to pregnant women who develop placental abruption during pregnancy is not worth it. In some cases, they can only increase bleeding.
The reasons for placental abruption will tell the obstetrician-gynecologist in the next video.