What does the first stage of maturity of the placenta mean and what week is it normal for pregnancy?
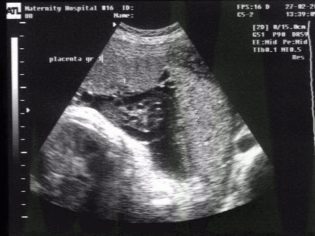
At 20 weeks and later, the doctors determine the degree of maturity of the placenta in an ultrasound woman. Until this time, the definition of this parameter is not considered informative, since the “children's place” has not yet been fully formed. That means 1 degree of maturity and how long it theoretically corresponds to the norm, we will tell in this material.
Special features
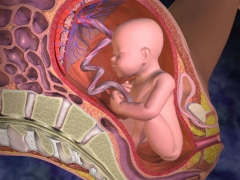
A “baby seat” or placenta is the most important organ, without which it would be absolutely impossible to carry a child. This discoid and slightly flattened organ is on one side adjacent to the uterus, growing into it by the network of blood vessels, and on the other side it is connected to the fetus via the umbilical cord.
The placenta feeds, protects and protects the growing baby. It takes over the tasks of the endocrine glands, producing the hormones necessary for the preservation of pregnancy. The placenta transfers to the child the necessary substances, oxygen and water and takes the products of its metabolism - urea, creatinine and carbon dioxide.
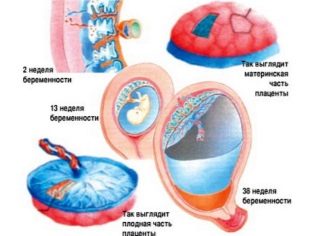
The formation of the placenta starts from the moment of implantation of the ovum into the uterus. Her predecessor is the chorion. Gradually, the chorion expands, forming a young placenta, which increases in thickness and area. Formation of the placenta is usually completed by 14-16 weeks of pregnancy. And from this moment begins its steady aging.
Gradually, the placenta gives the baby everything that can, is changing, and by the time the baby starts giving birth, it is already depleted and has exhausted its useful resource. The placenta is born after the baby within 20-50 minutes, because there is no longer any natural need in it.
The maturity levels of the “children's place” measure this irreversible process of maturation and aging of the placenta. Normally, each of the stages of aging should correspond to certain periods of gestation. If the “baby seat” is aging faster than normal, the baby will not receive enough oxygen and useful nutrients, it can develop hypoxia, hypotrophy, it can significantly lag behind in development. Sometimes, hypoxia can lead to fetal death.
Too slow maturation of the placenta also creates a threat, because the pathologically underdeveloped "children's place" can not cope with the significant and constantly increasing loads that the rapidly growing baby has on it.
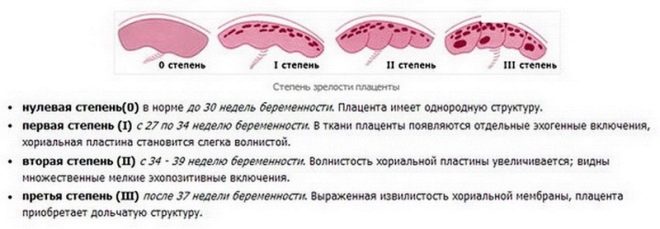
Degrees of maturity
Since the complete formation of the placenta and up to 30 weeks of gestation, zero maturity has been normal. This means that the temporary body is in its prime and is functioning at its full potential.
The first degree is considered normal for the period from 30 to 34 weeks of pregnancy. In practice, from about the 27th week of pregnancy, an ultrasound doctor can detect the first signs of an initial change in the placenta — its growth has stopped, the thickness has also practically become fixed. But the organ remains flat, on the monitor of the ultrasound scanner only small wavy changes of the membrane and single inclusions in the structure are noticeable. These inclusions are salt deposits, because we know that the “baby seat” accepts baby waste products.
If the signs of aging are still not obvious, then a borderline 0-1 degree can be set and for the duration of gestation from 26–27 weeks to 32 weeks this is quite normal. True, provided that the pregnancy proceeds without complications, there is no previa and regional location of the placenta. 0-1 degree before the 26th week is a dangerous sign of premature aging of the “children's place”.
From the 32nd week, another frontier degree of maturity can be set - 1-2. From the 35th week, the second degree is registered in the majority of future mothers, and from about the 38th week - the borderline 2-3 or 3. The third degree of maturity of the “children's place” indicates that the placenta has exhausted its possibilities. Normally, it is diagnosed immediately before childbirth, and if it occurs within the specified time, then such an adult, more precisely, the old placenta does not pose any danger to the child.
The aging process in this case is purely physiological in nature. They speak about pathology when the first degree of the “children's place” does not correspond to the periods at which it is considered normal, that is, from 27 to 34 weeks gestation.
Norm or deviation?
If the conclusion of the ultrasound doctor that the degree of maturity first sounded for up to 27 weeks, the woman will begin to observe with redoubled efforts. If necessary, the tactics of observation is replaced by the tactics of active medical intervention. If the baby develops normally, it does not show signs of trouble, the doctors limit themselves only to observing, prescribing vitamins to the expectant mother and recommending to walk more often in the fresh air.
If there are other problems, besides, the baby is lagging behind in development or shows signs of hypoxia, a woman is hospitalized to the department of pathology of pregnancy and prescribed drugs that improve uteroplacental blood flow and also reduce the tone of the uterus.
Determining the first degree of maturity in the period of 31-34 weeks is the norm and there is absolutely nothing to worry about. If the first degree is determined after 35 weeks of pregnancy, this may indicate developmental malformations of the baby, abnormal structures of the placenta itself, metabolic disorders between the fetus and the mother, and the presence of nodes on the umbilical cord. This condition necessarily requires additional examination and hospitalization.
The reasons
Most often, the placenta is aging earlier than the allotted time due to the bad habits of the future mother - smoking, alcohol, drugs. Also, earlier maturation is characteristic of women who live in ecologically polluted areas. Any infectious diseases such as influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections during pregnancy at any time increase the likelihood of pathologically rapid aging of the placenta.
The higher the body temperature during the illness, the greater the likelihood that unwanted and premature changes will occur in the “children's place”.
The first degree of maturity before normal periods can be diagnosed in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus or Rh negative blood if the woman bears a Rh-positive baby. Many medicines can affect the rate of “maturation” of the “children's place”, for example, antibiotics, painkillers.
Therefore, it is not recommended to drink pills during pregnancy without agreement with the attending doctor.
Early presence of the first degree of maturity is characteristic of women suffering from preeclampsia and high blood pressure, overweight, as well as women bearing double-triple.
Preservation of the first degree after 34 weeks of pregnancy may be more dangerous, doctors' forecasts are less optimistic. A baby may be born dead, because the state of hypoxia with an underdeveloped placenta becomes permanent for it. Such a violation is often found in women who carry a baby with chronic diseases or bleeding disorders. The fetus must be additionally examined for genetic pathologies and abnormalities of the development of organs.
The fact that such a placenta and what functions it performs, see the following video.