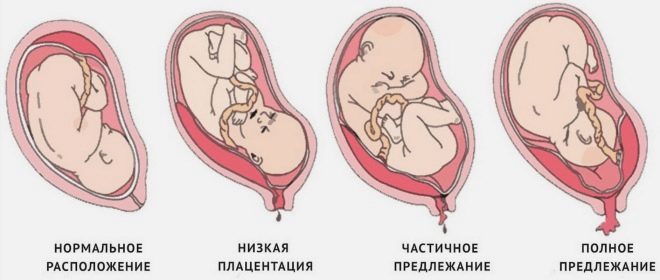
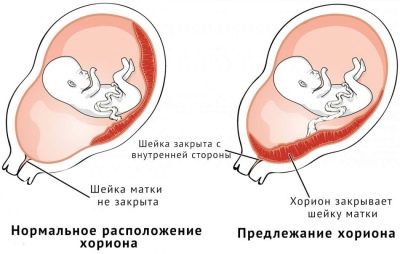
The position of the placenta in relation to the internal throat
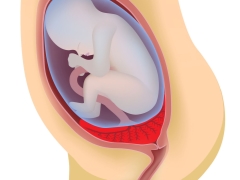
The intrauterine development of a baby is a rather complicated process. All the major nutrients the fetus receives through the placenta - a special organ, "children's place". The position of the placenta in relation to the internal pharynx may be different.
What it is?
Placental tissue appears at the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy. It is actively functioning during several months of pregnancy up to the very birth. The normal location of the placenta is an important clinical feature. If the placental tissue is located abnormally, then it can be dangerous by the development of pregnancy complications.
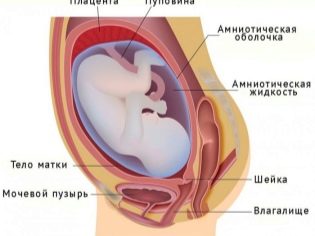
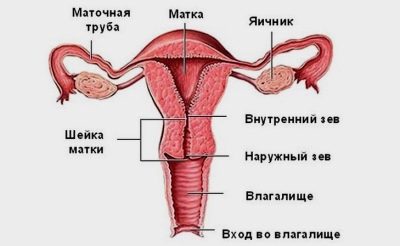
In order to understand how the placenta can be attached, you should touch the anatomy a little. The uterus is the main female genital organ in which the baby develops during pregnancy. Through its neck, it connects to the vagina. The outer boundary of such a connection is called an outer throat. The neck directly from the uterus itself is separated by an internal throat.
After the onset of pregnancy there are quite a lot of changes in the reproductive organs of women. After fertilization, the coloring of the mucous membranes of the cervix changes - it becomes more bluish. The mucous membranes also change their density - they become more dense, elastic.
Normally, the internal pharynx during pregnancy remains closed. It is necessary for the full intrauterine development of the baby. The closure of the inner throat also protects the fetal bladder from infection and keeps the fetus in the uterus.
If for some reason the tone of the internal pharynx changes, then dangerous pregnancy complications may occur. In such cases, as a rule, the risk of miscarriage increases many times over.
Location rate
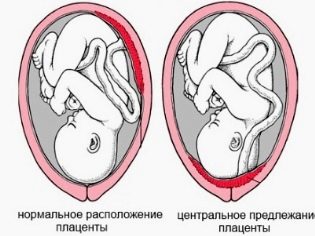
The formation and location of placental tissue depends largely on the initial site of attachment of the fertilized egg. Optimally, if it occurs near the bottom of the uterus. In this case, the placenta will be physiologically formed later. If for some reason the fertilized egg attaches low, closer to the neck, then the location of the placenta will be changed.
Doctors evaluate the location of the placental tissue at different stages of pregnancy. In this case, the rate of its location to the pharynx is determined by the weeks of pregnancy. So, in the 2nd trimester, the normal height of the location of the placenta from the internal os is 5 cm.
If at the same time the lower edge of the placenta is only 3 cm or less above the internal os, this is called a low attachment. As a rule, doctors diagnose it only by the 12th week of pregnancy.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, the distance from the placenta to the internal pharynx is normally 7 cm. If it is less than 5 cm, then this condition is defined as low attachment of the placenta.
A pregnant woman can carry out the baby with even a low attachment of placental tissue. In this situation, it is very important for her to monitor her state of health and closely monitor all the symptoms that occur. The appearance of sudden cramping pains in the lower abdomen and the appearance of bleeding should be a reason to immediately contact your obstetrician-gynecologist.
The low location of the placental tissue over a period of 20 weeks requires more careful observation of the pregnant patient. At this time, the risk of intrauterine hypoxia increases. This condition can be dangerous in the development of bleeding, placental abruption, as well as in-fetal development.
With a low position of the placental tissue, doctors recommend that patients carefully monitor their state of health. So, a pregnant woman with such an arrangement should not lift weights. This can provoke uterine bleeding.
With a low prevalence of placental tissue, a pregnant woman should also monitor her emotional state. Stress and anxiety can provoke a dangerous condition - hypertonicity of the uterus. In this case, the risk of miscarriage increases. To normalize the emotional background, the future mother is recommended to walk more often in the fresh air, as well as get enough sleep.
If the expectant mother, having a low prevalence of placental tissue, has uterine bleeding, then she should be hospitalized. If the bleeding has developed at a fairly early date, then in this case, the doctors make up the correct tactics for the further management of the pregnancy.
If necessary, a woman can be left in the hospital for several weeks "to save." After inpatient treatment, the expectant mother is prescribed medication as necessary and recommendations are made for changing the regimen of the day.
Clinical options
Placental tissue is usually located more often at the level of the anterior and posterior walls of the uterus. Also, in some cases, it reaches the side walls. Much less often, the placenta is attached directly to the bottom of the uterus or in the area of the tube corners.
Doctors believe that not all clinical options for attaching the placenta are favorable for the course of pregnancy. Less physiological cases of the location of the placental tissue can be dangerous by the development of complications.
To determine the exact location of the placenta can be using ultrasound. If the placental tissue overlaps the internal pharynx, then this is a very dangerous pathology. In this case, the risk of spontaneous birth increases significantly. Also, with this option, the risk of infection from the external genital tract to the uterus, where the fetus is located, is quite high.
Types of pathologies
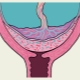
If placental tissue is determined directly at the site of the internal os, this clinical condition is defined as a presentation. It is partial, complete and marginal. Each type of presentation is determined by the location of the placenta relative to the internal os.
To determine the abnormal position of the placental tissue is necessary. This allows doctors to warn quite a lot of dangerous pathologies that may develop during pregnancy.
Obstetricians and gynecologists identify several clinical variants of this pathological condition:
- Central. In this situation, the placental tissue is located in the lower part of the uterus, and also covers the internal pharynx.
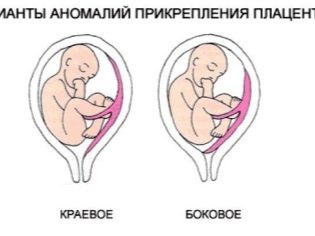
- Lateral. In this situation, the placental tissue is also located in the lower uterus, but the pharynx is not completely blocked.
- Regional. In this case, the placental tissue and the pharynx are practically in contact with their edges.
Placental tissue presentation can be dangerous development of very dangerous complications that occur during childbirth. They can be manifested by a weakening of labor, the growth of placental tissue, atonic uterine bleeding, various infections, and the possible development of septic pathologies.
With the central presentation of placental tissue, obstetrician-gynecologists are forced to resort to performing cesarean section.Quite often, in this case, a planned operative obstetrics is performed at the 37th week of pregnancy.
In medical practice, there are cases when the presentation of the chorion on the back wall overlaps the inner throat. Usually, in this case, doctors conduct more careful monitoring of the development of pregnancy. "Climb" on the back of the chorion can be quite difficult.
There are situations when he remains in this position and does not rise. In this case, it is very important to monitor the course of pregnancy, as well as to choose correctly the tactics of obstetric aid in the future. It may be that for the birth of a baby, a caesarean section will be required.
What is the migration of the placenta?
In some cases, when tracking the dynamics of the location of the placental tissue, doctors determine its movement. Also, this phenomenon experts call the migration of the placenta. In this case, the low-lying placenta begins to "rise."
Usually, the migration of placental tissue is completed by 32-35 weeks of pregnancy. As a rule, at this time a pregnant woman does not feel any significant changes in her body. Quite often, the placenta migrates, which is located on the anterior wall of the uterus.
For normal migration of the placenta may take about 6-10 weeks. In this case, the process proceeds slowly and gradually, without causing adverse symptoms in the future mother.
If the placental tissue migrates within 1-2 weeks, then in such a situation a bloody discharge from the genital tract may occur in a pregnant woman. In this case, the risk of developing undesirable complications is quite high.
The obstetrician-gynecologist Dyakova S. M. will tell you about the placenta previa in the next video.
About the anomalies of the location of the placenta can be found in the following video.