What is placenta previa and how does it affect pregnancy and childbirth?
Normal placement of placental tissue is an important condition for the physiological course of pregnancy. This article will tell about the placenta previa and how it affects pregnancy and childbirth.
Definition
The ancient doctors called the placenta "child's place." Even in Latin, the word "placenta" translates as "childish place", "afterbirth", "cake". All these comparisons quite clearly describe the placental tissue.
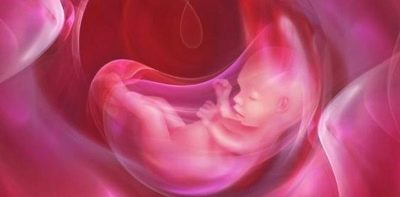
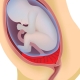
The placenta is formed only during pregnancy. Through it, the baby receives all the nutrients necessary for its growth and fetal development, as well as oxygen. Numerous blood vessels, which provide uninterrupted blood flow between mother and child, pass through the “children's place”. Such a unique circulatory system that occurs only in the period of carrying a baby is called the uteroplacental blood flow system.
The formation of the placenta involved the germ membranes of the chorion. They form dense fleecy processes that tightly penetrate the wall of the uterus. Such an attachment ensures the fixation of placental tissue. During birth, it is separated after the birth of a child and is called the "afterbirth."
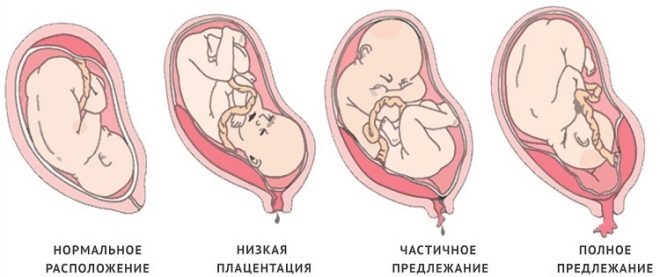
Normally, the placental tissue is formed slightly higher than the inner opening of the uterus. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the normal placenta should be 5 cm higher than the pharynx. If for some reason the placental tissue is located lower, then this is already a sign of a placental defect - low attachment of the placenta.
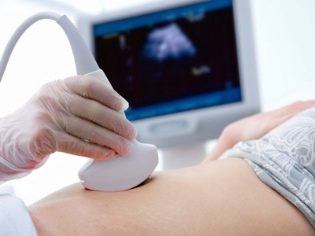
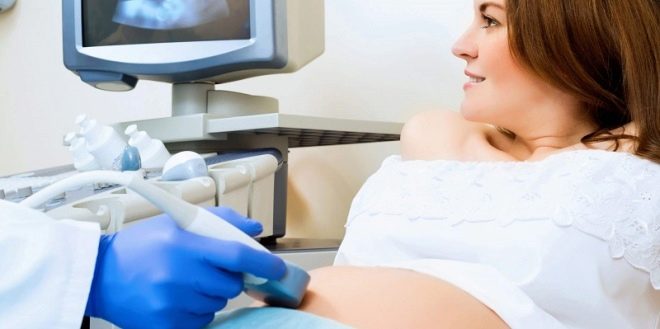
In the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, placental tissue is normally located at a distance of approximately 7 cm from the internal os. Determining the location of the placenta is quite simple. To do this, use ultrasound. Using such simple diagnostic procedures, doctors can quite accurately determine how high the placental tissue is located.
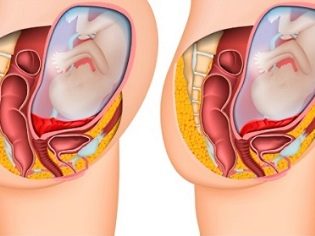
If the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus and even touches the internal os, this clinical condition is called previa. In such a situation, the placental tissue may partially “enter” the pharynx or even completely block it. According to statistics, this condition occurs in approximately 1-3% of all cases of pregnancy.
Normal location
In most cases, the placenta is formed on the back of the uterus. It can also move to the side walls - both on the right and on the left. In the area of the bottom of the uterus and posterior wall is a fairly good blood supply. The presence of blood supply vessels is necessary for the full intrauterine development of the fetus. The correct location of the placenta provides physiological growth developing in the womb of the baby.
Placental tissue is extremely rarely attached to the anterior wall of the uterus. The thing is that this zone is quite sensitive to various influences. Mechanical damage and injuries can damage the rather soft tissue of the placenta, which is an extremely dangerous condition.
The rupture of the placenta is dangerous complete cessation of blood supply to the fetus, and hence the development of acute oxygen deficiency.
If the pathology of the normal position of the placenta was detected at 18-20 weeks, then this is no reason to panic. The possibility of placental tissue displacement before the onset of labor is still quite high. This is influenced by a huge number of various factors. Detection of placenta previa at fairly early stages allows doctors to fully monitor the course of pregnancy, and therefore improves the potential prognosis.
Causes
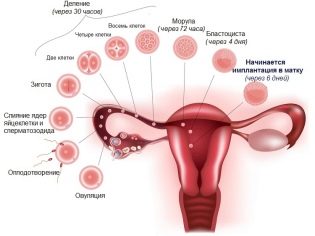
A number of different factors lead to a change in the place of attachment of placental tissue. In fact, the location of the placenta is determined after fertilization. The fertilized egg normally must be attached in the area of the bottom of the uterus.
In this case, the subsequent placental tissue will be attached correctly. If for some reason the implantation of the embryo does not occur in the area of the uterus bottom, then in this case the placenta will also be located nearby.
The most common and frequent cause leading to the development of placental presentation is the effects of various gynecological diseases, accompanied by inflammation of the inner wall of the uterus (endometrium). Chronic inflammatory process damages the delicate lining of the uterus, which can affect the attachment of placental tissue. In this case, the fertilized egg simply cannot fully attach (implant) into the wall of the uterus in the area of its bottom and begins to descend below. As a rule, it shifts to the lower parts of the uterus, where it attaches.
Also, the development of placenta previa can be facilitated by various gynecological surgeries performed before pregnancy. It can be curettage, cesarean section, myomectomy and many others. The risk of formation of placenta previa in this case is much higher in the first year after surgical treatment.
The more time passes since the gynecological operations were performed, the less likely it is that the woman will have placenta previa during the subsequent pregnancy.
Doctors note that in women with multiple flu the risk of developing previa is slightly higher than with nulliparous. Currently, scientists are conducting experiments aimed at studying the genetic factor of the possibility of developing placenta previa during pregnancy. So far, there are no reliable data on the influence of genetics on the development of this pathology among close relatives.
Studying the numerous cases of pregnancies that occur with the development of placenta previa, doctors have identified high-risk groups. They include women with a number of specific health features. In these women, the risk of developing placental tissue presentation or low location is quite high.
The high-risk group includes patients with:
- the presence of obstetric and gynecological history (previous abortions, surgical curettage, previous difficult labor, and much more);
- chronic gynecological diseases (endometriosis, salpingitis, vaginitis, myoma, endometritis, diseases of the cervix and others);
- hormonal pathologies associated with pathologies of the ovaries and accompanied by a violation of the regularity of the menstrual cycle;
- congenital anomalies of the structure of the female genital organs (hypoplasia of the uterus, hypoplasia of the uterus and others).
If a woman falls into the high-risk group, then the doctors watch her very closely during the course of her pregnancy. In such a situation, the number of vaginal examinations is minimized. Also, preference in diagnosis is given to transabdominal ultrasound, rather than transvaginal.Already in the early stages of pregnancy, the expectant mother will make individual recommendations aimed at minimizing the likelihood of the development of adverse symptoms of placenta previa.
Clinical options
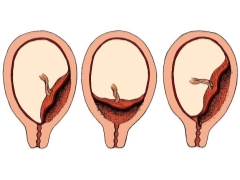
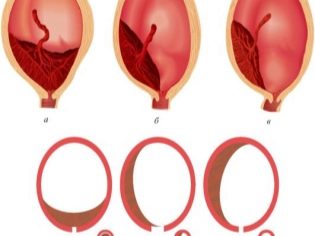
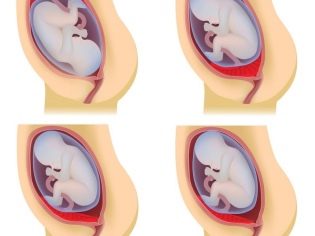
Experts identify several possible clinical situations, as it can be located placental tissue relative to the internal orifice of the uterus. These include:
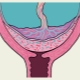
- full presentation;
- partial (incomplete) presentation.
With full previa placental tissue almost completely overlaps the area of the internal os. This situation, according to statistics, develops in 20-30% of all cases with placenta previa.
Obstetrician-gynecologists talk about partial presentation in the event that the placenta passes to the internal pharynx only partially. This pathology is already encountered somewhat more often - in about 70-80% of all pregnancies with placenta previa.
Classification
It is possible to assess the degree of overlap of the placental tissue of the internal pharynx through ultrasound. Doctors use a special classification, which provides for various clinical options. Taking into account the evaluated signs, this pathology can be:
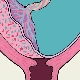
- 1 degree. In this case, the placental tissue is quite close to the opening of the cervix. Its edges are higher than the inner mouth, 3 cm.
- 2 degrees. In this case, the lower edge of the placenta is practically located at the entrance to the cervical canal, without overlapping it.
- 3 degrees. The lower edges of the placenta begin to overlap the inner uterus almost completely. In this situation, the placental tissue is usually located on the anterior or posterior uterine wall.
- 4 degrees. In this case, the placental tissue completely blocks the entrance to the cervical canal. The entire central part of the placenta “enters” at the same time on the area of the internal uterine throat. At the same time, both the anterior and posterior walls of the uterus contain separate areas of placental tissue.
In addition to ultrasound, obstetrician-gynecologists use the old proven methods of diagnosis of various options for the location of the placenta. These include vaginal examination. An experienced and qualified doctor can quickly and accurately determine where the "children's place" is located. It may have the following localizations:
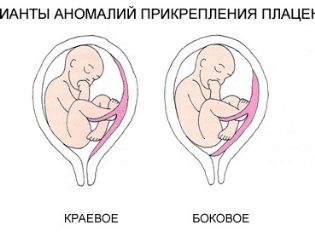
- In the center. This type of previa is called placenta praevia centralis.
- On the sides. This type of presentation is called lateral or placenta praevia lateralis.
- Around the edges. This option is also called edge or placenta praevia marginalis.
There is a series of correspondences between the ultrasound and the clinical classification. For example, the central presentation corresponds to 3 or 4 degrees by ultrasound. Its specialists are also called complete. 2 and 3 degree of ultrasound corresponds, as a rule, lateral presentation.
Regional presentation of placental tissue is usually equivalent to 1-2 degrees by ultrasound. Also, this clinical option can be called partial.
Some doctors use additional clinical classification. They share the presentation at the place of attachment of placental tissue to the uterine walls. So, it can be:
- In front of him. In such a situation, the placental tissue is attached to the anterior uterine wall.
- Rear. The placenta is mostly attached to the back of the uterus.
It is possible to determine exactly which wall the placental tissue is attached to, as a rule, up to 25-27 weeks of pregnancy. However, it is important to remember that the position of the placenta can change, especially if it is attached to the anterior wall of the uterus.
Symptoms
It should be noted that placenta previa is not always accompanied by the development of adverse clinical signs. With partial previa, the severity of symptoms may be quite insignificant.
If the placental tissue significantly overlaps the inner throat of the uterus, then the pregnant woman begins to develop adverse manifestations of this pathology. One of the possible symptoms characteristic of presentation is bleeding. As a rule, it develops in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. However, some women develop bleeding from the genital tract and much earlier - in the earliest terms of carrying a baby.
In the final 3 trimester of pregnancy, the severity of bleeding may increase. This is largely facilitated by intensive contractions of the uterus, as well as the progress of the fetus down the genital tract. The closer the upcoming delivery, the higher the chance of developing severe bleeding.
Doctors believe that the main reason for the appearance of blood from the genital tract in this case is the inability of the placenta to stretch following the stretching of the uterine walls. The approaching onset of labor contributes to the fact that the placenta begins to exfoliate, which is manifested by the appearance of bleeding.
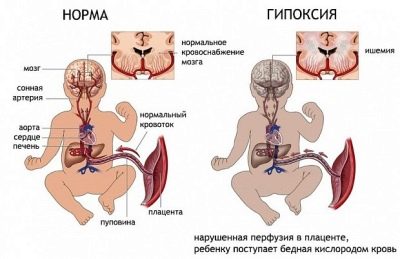
In this case, it is important to understand that the fetus does not lose its own blood. In this situation, only the breaks of the placental tissue itself occur. The danger of this condition is that the baby, "living" in my mother's tummy, can begin acute oxygen starvation - hypoxia.
The appearance of bleeding with the presentation of placental tissue, as a rule, contribute to any effects. So, it may develop after:
- lifting heavy objects;
- physical exertion and running;
- strong cough;
- reckless vaginal examination or transvaginal ultrasound;
- sex;
- thermal procedures (baths, saunas, baths).
With full previa, blood from the genital tract may appear suddenly. Usually it has an intense bright red color. A painful symptom may or may not be present. It depends on the individual condition of the pregnant woman. After some time, the bleeding usually stops.
In the case of incomplete previa, bleeding from the genital tract of a pregnant woman most often develops in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy and even with the immediate onset of labor. The severity of bleeding at the same time can be very different - from scarce to intense. It all depends on how much the placenta overlaps the inner uterine mouth.
Placenta migration
During pregnancy, the position of the placenta may change. This process is called migration. In many respects, it is caused by physiological changes in the lower parts of the uterus, which develop in different weeks of pregnancy.
The best prognosis is usually the migration of the placenta along the front wall. In this situation, the placental tissue moves up slightly, changing its original location. If the placenta is attached to the back wall, then its migration is usually difficult or extremely slow. In practice, there are cases when placental tissue, attached to the back wall of the uterus, has not shifted during pregnancy.
Placental migration is usually not a quick process. Optimally, if it occurs within 6-10 weeks. In this case, the pregnant woman does not experience any adverse symptoms. The migration of the placenta usually ends by 33-34 weeks of gestation of the baby.
If the placental tissue changes its position too quickly (in 1-2 weeks), then this can be a dangerous development of certain symptoms in the future mother. Thus, a pregnant woman may feel pain in the abdomen or notice the appearance of bleeding from the genital tract.
In this case, delay in seeking medical help is not worth it.
What can be complications?
The development of frequent bleeding is an unfavorable sign. Frequent blood loss threatens the development of an anemic condition in a pregnant woman, accompanied by a decrease in her blood iron and hemoglobin.Anemia of the mother is a dangerous condition for the developing fetus. A decrease in hemoglobin in the placental blood flow may contribute to a decrease in the intensity of the intrauterine development of a baby, which will adversely affect his health in the future.
Another possible complication of presentation may be the development of spontaneous unplanned birth. In this case, the fetus can be born much earlier. In this situation, the baby may be premature and incapable of independent living. If the placenta previa is too pronounced and proceeds rather unfavorably, then there is also a risk of spontaneous miscarriage.
Also, doctors note that patients who have placenta previa during pregnancy often have difficulty maintaining normal blood pressure numbers. A woman can develop hypotension - a condition in which the pressure drops below the age norm. According to statistics, this pathology develops in 20-30% of pregnancies occurring with placenta previa.
One of the serious complications of gestation is gestosis. This pathology is no exception for women who have placenta previa during pregnancy. Especially often in this case, late gestosis develops. It is accompanied by the development of the pathology of blood clotting, as well as disturbances in the work of the internal organs.
Fetal-placental insufficiency is another pathology that can develop during presentation. This condition is extremely dangerous for the fetus. It is characterized by a decrease in the oxygen supply to the children's organism, which negatively affects the development of the heart and brain of the child.
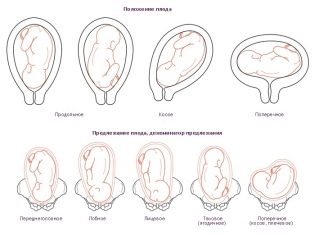
Experts have found that when the placenta prevails, abnormal fetal location in the uterus is often found. For normal physiological development, the baby should be in the head-down position.
However, with placenta previa, other clinical options may develop. Thus, the fetus may be located in an oblique, pelvic or transverse position. With such options for the location of the child in the uterus during pregnancy, various pathologies can occur. Also, the data previa can be an indication for obstetrics surgically. Quite often, future mothers in such situations performed a cesarean section.
How is the diagnosis?
Suspected placenta previa and tissue can be without ultrasound. The presence of this pathology may indicate repeated bleeding from the genital tract in a pregnant woman, usually developing in 2-3 trimesters of pregnancy.
With the appearance of blood from the genital tract it is very important to conduct a clinical vaginal examination. This excludes any other pathologies that could cause the development of similar symptoms. Also, with this pathology, the general condition of the fetus is necessarily evaluated. This is done through an ultrasound examination.
The basic method of diagnosis of placental tissue presentation today is ultrasound. An experienced doctor can easily determine the degree of overlap of the internal pharynx by the placenta. After the study, an ultrasound specialist gives the future mother a hand-drawn conclusion. It is necessarily invested in a medical card of a pregnant woman, as it is necessary for drawing up the correct tactics for managing pregnancy, as well as tracking it over time.
If, during an ultrasound examination, placental tissue is found in the region of the internal pharynx, then in this case it is undesirable to conduct further vaginal examinations in the future. If necessary, doctors resort to doing this examination, but they try to do it as carefully and carefully as possible.
If the placenta previa was established early enough, then in this case, the expectant mother will be assigned several additional ultrasounds.As a rule, they are carried out consistently at 16, 25-26 and 34-36 weeks of pregnancy.
Experts recommend an ultrasound when the bladder is full. In this case, it becomes much easier for the ultrasound doctor to see the pathology.
With the help of ultrasound, it is also possible to determine the accumulation of blood in a hematoma. At the same time, its quantity is necessarily estimated. So, if it is less than ¼ of the total area of the placenta, then this clinical condition has a rather favorable prognosis for the further course of pregnancy. If the hemorrhage is more than 1/3 of the total area of the placental tissue, then in such a situation the prognosis for the life of the fetus is rather unfavorable.
What measures should be taken?
When bleeding from the genital tract occurs, it is very important for a pregnant woman to immediately consult your obstetrician-gynecologist for advice. Only a doctor can fully assess the severity of the condition and make a plan for further pregnancy.
If the placenta previa is not accompanied by the development of adverse symptoms, then the expectant mother may be in such a situation in the dispensary observation. To hospitalize a pregnant woman in the hospital during the normal course of pregnancy will not. In this case, the future mother must be given recommendations that she should carefully monitor her state of health. Recommendations are also made that it is impossible to lift weights and intensive physical activities are limited. The future mother, who has placenta previa, should also carefully monitor her emotional state.
Strong stress and nervous shocks can cause a pronounced spasm of the uteroplacental vessels. The resulting blood flow disorders can be very dangerous for fetal development.
Treatment
As a rule, therapy for placenta previa after 24-25 weeks is carried out in stationary conditions. In this situation, doctors try to eliminate the risk of preterm birth. In the hospital it is much easier to monitor the general condition of the future mother and baby.
During therapy, the following principles must be followed:
- mandatory bed rest;
- the appointment of drugs that normalize the tone of the uterus;
- prevention and treatment of anemia and possible placental insufficiency.
If the bleeding is too heavy and does not stop, there is severe anemia, then a cesarean section may be performed. Life-saving operation can be performed in the critical state of the mother or fetus.
At full previa placenta cesarean section is performed. Natural childbirth at the same time can be very dangerous. At the onset of labor, the uterus begins to contract strongly, which can lead to rapid placental abruption. In such a situation, the severity of uterine bleeding can be very strong. In order to avoid massive blood loss and for the safe appearance of the baby, doctors and resort to performing surgical obstetrics.
A caesarean section can be performed in a planned manner and in the following cases:
- if the baby is in the wrong position;
- in the presence of extended scars on the uterus;
- with multiple pregnancies;
- with pronounced polyhydramnios;
- with a narrow pelvis in a pregnant woman;
- if the expectant mother is over 30 years old.
In some cases, with incomplete presentation, doctors may not resort to the surgical method of delivery. In this case, they, as a rule, wait for the onset of labor, and with its onset they open the fetal bladder. An autopsy in such a situation is necessary in order for the head of the fetus to start moving correctly along the birth canal.
If during natural childbirth, severe bleeding occurs or acute fetal hypoxia develops, then the tactics usually change and a cesarean section is performed. Monitoring the condition of the woman and the fetus is very important. For this, doctors monitor several clinical signs immediately. They evaluate uterine contractile activity, cervical dilatation, pulse and blood pressure in the mother and fetus, as well as many other indicators.
In medical practice, cesarean section is increasingly performed. According to statistics, obstetrician-gynecologists prefer this method of obstetric care in almost 70-80% of all cases of pregnancies occurring with placenta prevailing.
The postpartum period with placenta previa can be complicated by the development of a number of pathologies. The harder the pregnancy was and the more often bleeding developed, the higher the likelihood of the woman recovering heavily after pregnancy. She may develop gynecological diseases, as well as dream of uterine tone. Also in the postpartum period, there may be heavy uterine bleeding.
Track the health and general condition of the mother, who was carrying the baby with placenta previa, after pregnancy should be very carefully. If a woman feels very weak, she is constantly dizzy and continues bleeding for several months after giving birth, she should immediately consult her gynecologist. In such a situation, it is necessary to exclude all possible postoperative complications, as well as the development of a severe anemic condition.
Prevention
Prevent placenta previa 100% impossible. By following certain recommendations, a woman can only reduce the likelihood of developing this pathology during pregnancy. The more responsible the future mother will relate to her health, the greater the chances of the birth of a healthy baby.
In order to reduce the risk of placenta previa, a woman should be required to regularly visit a gynecologist. All chronic diseases of the female reproductive organs are best treated in advance, even before the onset of pregnancy. It is very important to conduct therapy for infectious and inflammatory pathologies. They are quite often the root cause of the development of placental tissue presentation.
Of course, it is very important to minimize the consequences of surgical interventions performed for various reasons. If a woman decides to have an abortion, then it should be performed only in a medical institution. It is very important that any surgical intervention be carried out by an experienced and competent specialist.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is also quite an important preventive measure. Proper nutrition, lack of strong stress and good sleep contribute to the good functioning of the female body.
In the next video you will learn more about the location of the placenta.