Causes and effects of premature aging of the placenta
Premature aging of the placenta is a threatening condition. Any pregnant woman can face it. Why the “children's place” begins to lose its functions ahead of time and what to do with these, we will tell in this article.
How to ripen "baby seat"?
The “baby seat,” or placenta, is a temporary organ that a woman and child need only during pregnancy. It has a spongy structure, one side fits snugly to the wall of the uterus, from which it draws supplies of maternal blood, and the other, through the umbilical cord, connects to the fetus. The placenta performs protective functions, preventing the mixing of the blood of the mother and baby. She also acts as an intermediary in gas exchange and nutrition: through the placenta through the vein in the structure of the umbilical cord, the baby receives fresh blood with oxygen and vitamins, and the two arteries inside the umbilical cord return the placenta back to the baby: urea, carbon dioxide, creatinine. The placenta produces hormones that are important for pregnancy and subsequent breastfeeding.
A week after ovulation, the fertilized egg enters the uterine cavity and its main task is to implant. This helps chorial shell, which "grows" in the maternal endometrium. At the site of attachment, chorion is formed, which is gradually transformed into the placenta. The formation of a “childish place” is completed by the 14th – 16th week of pregnancy. The final form of the young placenta takes on the 20th week. Until mid-pregnancy, the “baby seat” grows and expands. After that - only slightly adds in thickness.
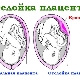
The closer to childbirth, the less functional the placenta is: it develops its resources, begins to age. At first, its membranes become wavy, then blotches of calcium salts appear in the placenta, then these blotches become more extensive - the placenta from the spongy becomes more dense, begins to become thinner. All these processes fit into four degrees of maturity.
If degrees replace each other on time, there is no danger. If the placenta "fades away" too quickly, they say about its premature aging.
Rates and deviations
The young and full of strength placenta has a zero degree of maturity. This means that the resources of the “children's place” are not exhausted - the baby receives everything necessary for its development. Normally, a zero degree of maturity is recorded before the 30th week of pregnancy.
The first degree of maturity of the placenta speaks of the changes that have begun: the growth of the mesh of vessels and tissues has ceased, the membrane becomes wavy. But its functions "childish place" performs properly - the baby is comfortable, and just enough. The first degree is normal for a period of 30-34 weeks of gestation.
The second degree of maturity describes active regressive processes in the “children's place”: fragmentary thinning of the placenta may appear, its structure becomes more dense, saline calcium deposits appear. If the 2 degree is established in the appropriate time frame, you can not worry - the placenta copes with its tasks without damage to the baby. The second degree will not be considered pathological if the gestational age is already 35–38 weeks.
Third degree - mature or old placenta. The structure, which previously looked like a fairly flat cake, becomes lobed: lobes are determined, the membrane is uneven, salt deposits are clearly distinguishable. Usually, grade 3 is fixed immediately before birth: in the last couple of weeks, and sometimes in just a few days before delivery.
If the doctor establishes an intermediate degree, for example, 0–1 or 1–2, it means that ultrasound showed signs of a transition from one stage of development of a “children's place” to another, but the transition itself is not yet complete. With transitional degrees, there are usually the most incomprehensible moments and misunderstandings. To make it easier to understand what is normal and what is not, you should know that a grade of 0–1 for a period of 27–28 weeks of pregnancy is not a pathology, but a variant of the norm.
After 30 weeks, the doctor can diagnose both the first and the transient (0–1) degrees. But a 1-2 degree at week 32 is a clear pathology, since there is still about a month before moving to the second degree. The onset of 3 degrees of maturity up to 38 weeks is also an alarming and dangerous situation in which, most likely, a decision on early delivery will be made.
The greater the time gap between normal and real state of the placenta, the more dangerous the consequences can be.
What is dangerous?
Since nature has important functions to protect the placenta, nutrition, oxygen supply, and hormonal support for the pregnant woman’s body, any changes in the structure of the placenta ahead of time can lead to serious complications. When aging is on time, it is physiological: the loss of some functions of the placenta, their decline is compensated by the organisms of the mother and fetus. It does not harm the child, since normally, the extinction of the function proceeds quite smoothly.
If early maturation is observed, then the baby receives not enough oxygen, the placenta copes worse with the removal of its metabolic products, it lacks nutrients. In addition, the placenta worse copes with protective functions. The most common consequence of premature maturation for a child is hypoxia.
Against the background of oxygen deficiency, the baby’s brain and its nervous system suffer. Prolonged hypoxia can lead to the death of the child in utero. Often, it is intrauterine hypoxia that causes the fetus to lag behind in development, gross violations of the central nervous system.
Children who suffered from hypoxia in the womb are more painful, they may experience various neurological abnormalities, as well as dysfunctions of the musculoskeletal system. In addition, these children learn worse, disability is not excluded.
Lack of nutrients leads to a delay in intrauterine development of the baby. It is diagnosed during pregnancy. Height, weight, length of the limbs of the fetus behind the normal values characteristic of a specific period of pregnancy. Often the delay in physical development is accompanied by cerebral and metabolic disorders, which after birth is defined as mental and mental retardation. Against the background of fasting, various defects of the internal organs and the skeletal system of the baby can develop.
The delayed withdrawal of waste products of the fetus by an early ripened placenta creates a threat of intoxication and child death. A decrease in the barrier functions of the “children's place” can lead to the infection of the crumbs with dangerous viruses that can freely penetrate through the bloodstream to the baby. Intrauterine infection - a condition that is regarded as a threat to the life of the child.
What caused?
The placenta matures before its time for a variety of reasons.Most often, doctors are faced with the phenomenon of premature aging of the placenta in women who, while carrying a baby, continue to smoke or cannot deny themselves the pleasure of accepting alcoholic beverages. For women who indulge in the hope that “light” cigarettes are not dangerous, and red wine is useful, such a pathology after 30 weeks of gestation is quite common.
However, the absence of bad habits during pregnancy and before it does not guarantee that there will be no problems with the placenta. Maturing of the “children's place” ahead of time can be a consequence of a previous viral infectious disease, for example, SARS or flu in the early period, as well as infections that are sexually transmitted.
Pregnant women with Rh-negative blood, provided that they bear a baby with a positive Rh factor, can develop Rh-conflict, in which the placenta begins to suffer almost at the stage of formation. Its early maturation is often a consequence of those immune processes that take place during a conflict in the body of the future mother.
If a woman had diabetes before pregnancy, or she acquired gestational diabetes while carrying a baby, the likelihood that the placenta will quickly grow old is much higher.
With such ailments, hyperplasia of the placenta is usually observed (an increase in its thickness), which almost always leads to an early loss of its functions. Early aging of the “children's place” is also found in women who underwent several abortions: in this case, the thinned endometrium cannot ensure the normal development of the placenta. In this case, it is thinner initially, and is aging much faster.
Chronic diseases of the future mother, especially if they relate to the kidneys, liver, thyroid gland, heart and blood vessels, as well as blood clotting disorders increase the likelihood of premature maturation of the "children's place".
The speed of maturation of the placenta can be adversely affected by many medications, which is why expectant mothers are strongly advised not to take any medications, unless approved by her doctor. The destruction of placental tissues and blood vessels is also affected by the contact of the expectant mother with toxic substances, varnishes and paints, solvents, bleaches and other chemicals. Work on hazardous and hazardous production increases the likelihood of negative changes in the rate of maturation of the placenta.
Premature aging of the placenta is more common in women who live in large cities with unfavorable environmental conditions than women who live in a village or a small town where there are no large city-forming industrial enterprises. As well as pathology, according to the observations of doctors, is inherited - from mother to daughter.
Gestosis (late toxicosis) quite often leads to the aging of the “children's place” ahead of schedule. Dangerous from the point of view of the likelihood of the development of the pathological condition and the differences in blood pressure in the expectant mother, hypertension. If a pregnant woman even had a small placental abruption at any stage of pregnancy or there is a prevalence of a “baby seat”, the risk of early maturation is several times higher than that of women who do not have such problems during pregnancy.
During gestation of twins or triplets, the risk of early maturation is higher than during singleton pregnancy. And women with hormonal problems almost always have varying degrees of placental abnormalities, including the old placenta on inappropriate dates of gestation.
Symptoms and signs, diagnosis
There is no way to feel the degree of maturity of the placenta, as well as to determine its thickness and other parameters on its own. Accelerated maturation of the "children's place" proceeds completely without symptoms.That is why it is important to regularly visit the doctor, undergo all the required examinations, get tested and do an ultrasound scan. The sooner the anomaly is detected, the more favorable the doctors' forecasts for the upcoming treatment will be.
Signs of premature aging of the placenta in later periods, when the consequences of placental insufficiency are already apparent, are mainly felt as a change in the infant's physical activity. Increased activity speaks about the initial stage of hypoxia: movements of the baby become sharp, can cause severe pain to the pregnant woman. So the crumb tries to massage the placenta with the arms and legs, trying to get more oxygen.
Protracted hypoxia is manifested by reverse signs - the baby almost stops moving. He enters the mode of saving oxygen and nutrients, trying to expend as little energy as possible. The complete cessation of perturbations can be a sign of the death of the baby.
To establish the fact of hypoxia, intrauterine growth of the fetus, its intoxication and other adverse conditions can only be a doctor. That is why it is so important not to miss visits to the antenatal clinic.
When changing the behavior of the baby, the woman is prescribed a study of the placenta and the characteristics of uteroplacental blood flow on the USDG, ultrasound, and CTG. Cardiotocography, which can be performed from 28-29 weeks of pregnancy, can give a fairly accurate answer to the question of whether the baby has a change in condition.
The degree of maturity of the placenta is set on ultrasound, starting from the 20th week of pregnancy. In earlier terms, neither the thickness of the “children's place” nor its maturity characteristic have diagnostic value.
Treatment
Despite the fact that the consequences can be quite serious, a woman should not panic: premature aging of the placenta is always more favorable than its pathological immaturity. With early detection of pathology, doctors can help the baby and his mother. Treatment is usually carried out in the hospital.
The choice of tactics depends on the time period. If the premature maturation of the placenta is detected at 31-35 weeks of pregnancy, the doctors try to do everything possible to save it and extend it, because the baby is not yet ready to be born at this time. A woman in the hospital is monitored, provided with the necessary therapy, CTG is performed daily in order to find out whether the condition and well-being of the baby has changed. Once every few days, ultrasound is done to control the processes occurring in the placental structures.
If the gestation period is more than 36 weeks, then doctors are more likely to make a decision on early delivery: stimulation of labor or cesarean section. Although, if the degree of deviation from the norm is small, they can put on preservation and try even at least two weeks to support the baby inside the mother's womb with medication so that he can gain weight.
The standard treatment regimen contains antispasmodic drugs (“Papavern”, “No-shpa") To reduce the contractility of the smooth muscles of the uterus. To improve blood flow in the system "mother-placenta-fetus" used "Curantil", "Actovegin»Both in tablets and in the form of intravenous drip injections. Vitamin preparations are used to fill the baby's nutritional deficiency. If you suspect fetal hypoxia, a woman is recommended oxygen cocktails.
If infectious diseases became the cause of premature ripening of the “children's place”, in parallel with the standard scheme, the woman is given appropriate treatment with antiviral or antibacterial drugs. In case of late toxicosis, diuretic preparations are prescribed to reduce puffiness, and means for lowering blood pressure, if the expectant mother has hypertension.
If systematic observations of the baby indicate the slightest negative changes in his condition, the preserving therapy is canceled and an emergency delivery is carried out. This is necessary in order to save the child's life.
Tips for expectant mothers
Prevention of problems with the placenta during pregnancy does not exist, because there is no possibility to influence the maturation and aging processes of the “children's place”, and even expensive advertised medicines are powerless in this matter. The fact that the placenta may have problems, a woman should remember even at the planning stage of replenishment of the family.
It is necessary to stop smoking, alcohol, uncontrolled medication in advance - antibiotics, anticonvulsants, hormonal drugs, including contraceptives are especially dangerous.
If a woman is undergoing treatment with such agents or is protected with hormonal oral contraceptives, before conceiving a baby, you should consult with your doctor and pass the necessary tests to avoid problems in the future.
From the first weeks of pregnancy, it is important to monitor your diet, avoid contact with toxic substances, radioactive radiation, do not work at night, because lack of sleep leads to hormonal disturbances. If bloody discharge occurs at any time, you should consult a doctor to exclude placental abruption, and receive the necessary treatment if it occurred.
A woman should breathe fresh air, walk, if the weather allows, sleep with an open window. The more oxygen she receives herself, the more she can give it to her baby through placental blood flow. You should also avoid viral infections, carrying out proper and timely prevention of influenza and ARVI, especially during periods of massive morbidity.
During pregnancy, it is not necessary to change the sexual partner: any infection can cause lesions of the placenta.
About premature maturation of the placenta, see the following video.