Types of umbilical cord attachment to the placenta: norms and risk of deviations
The normal course and development of pregnancy cannot be imagined without two extremely important organs - the placenta and the umbilical cord. They are directly related to each other during fetal development. This article will tell you about the types of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta, as well as the rate and danger of deviations.
Norm
The umbilical cord, or, as it may be called, the umbilical cord is an elongated flagellum, inside of which blood vessels pass. They are necessary for the fetus to receive all the necessary nutrients for growth and development during its intrauterine life. Normal umbilical cord looks like a gray-blue cord that attaches to the placenta. Normally, it is formed at the earliest gestational age and continues to grow with the growing baby.
The umbilical cord can easily be visualized already in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. It is well defined during the ultrasound examination. Also, by means of ultrasound, the doctor can assess the condition of actively forming placental tissue. During the examination, the doctor must also evaluate how the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta.
Finally, the umbilical cord is formed only by 2 months from the moment of conception. As the umbilical cord grows, its length increases. At first, the umbilical cord is only a few centimeters long. Gradually, it increases and reaches, on average, 40-60 cm. The umbilical cord can be finally determined only after delivery. While the child is in the womb, the umbilical cord may collapse somewhat.
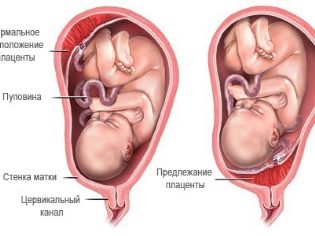
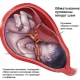
Normally, the umbilical cord is attached to the center of the placenta. Doctors call such an arrangement the central one. In this case, fetal development proceeds physiologically. The blood vessels that are located in the umbilical cord reach the placenta and provide sufficient blood flow.
With eccentric attachment of the umbilical cord, it is attached not to the central part of the placental tissue, but closer to its edge. Usually in this case, the umbilical cord does not reach to the edge of the placenta a couple of centimeters. The eccentric attachment of the umbilical cord is usually not accompanied by the development of any adverse functional impairment. However, the paracentral attachment of the umbilical cord to the placental tissue requires a sufficiently careful attitude of doctors to the development of pregnancy.
The easiest way to determine the type of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta is if the placental tissue is located along the front or side wall of the uterus.
If for some reason the placenta is located on the back wall, then in this case it becomes much more difficult to determine the type of attachment. In this case, it is better to conduct surveys on the devices of the expert level. This allows for more informative and accurate results.
However, the central attachment of the umbilical cord to the placental tissue is not always formed during pregnancy. Abnormal attachment options in this case can lead to the development of various functional disorders.
Pathologies
Doctors identify several abnormal options for attaching the umbilical cord to the placenta.Thus, the umbilical cord can be directly attached to the edge of the placenta. Experts call this attachment a regional one. This condition is characterized by the fact that the blood vessels located in the umbilical cord, are close enough to the edge of the placenta.
Lateral attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta is not always the cause leading to the development of dangerous complications during pregnancy. Obstetricians and gynecologists emphasize a condition in which the umbilical cord is located at a distance of less than 0.5 of the radius of the placenta from the edge. In this case, the risk of developing various complications is quite high.
Another clinical option for attaching the umbilical cord to the placenta is an enveloped one. Also this condition is called pleuisty. In such a case, the blood vessels that are located in the umbilical cord are attached to the amniochorial membrane.
Normally, the arterial vessels, which are located in the umbilical cord, are covered with varton jelly. This gelatinous substance protects the arteries and veins that are in the umbilical cord from various injuries. When the umbilical cord attaches to the placenta, the blood vessels are not covered with varton jelly throughout. This contributes to the fact that the risk of developing various traumatic injuries of arteries and veins is quite high.
According to statistics, the shell attachment of the umbilical cord occurs in pregnancy with one baby in approximately 1.2% of cases. If the expectant mother is waiting for twins, then in such a situation the risk of developing this pathology increases and is already almost 8.8%.
In obstetric practice, there are cases when the umbilical cord can change its attachment to the placenta. The reasons for this may be different. This may be due to inaccuracies in determining the initial place of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta (the notorious human factor), as well as due to migration of placental tissue during pregnancy. Note that the change in the place of attachment of the umbilical cord does not occur often.
Possible consequences
Abnormal attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta threatens with the development of a number of complications that may occur at different stages of pregnancy. In order to determine them in a timely manner, doctors resort to various diagnostic methods, the main of which is ultrasound examination. Ultrasound in this case is assigned several times. This is necessary so that doctors can assess the dynamics of the development of pathology and carry out the correction of the resulting violations in time.
Since blood vessels pass through the umbilical cord, to assess the intensity of blood flow, doctors resort to the appointment of another diagnostic method - doppler sonography. This examination allows you to assess whether there are any defects in the blood supply to the placenta and the body of the fetus. On how the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta, possible complications depend in many respects.
When the umbilical cord attaches to the placenta, the risk of various traumatic injuries is quite high. Also, with this type of attachment, the risk of developing dangerous bleeding, which can develop during childbirth, is quite high. Some researchers believe that with this type of attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta, the risk of the development of intrauterine growth of the fetus is quite high.
In some cases, the shell attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta is accompanied by the development of combined pathologies. Thus, in this state, anomalies and malformations of the internal organs of the fetus (including heart and vascular defects, defects in the structure of the musculoskeletal system, esophageal atresia), vascular pathologies, the appearance of accessory lobes in the placental tissue and other disorders may also develop.
Another possible complication that may develop when the umbilical cord is attached to the placenta is the development of fetal hypoxia.In this case, a sufficient amount of oxygen, which is necessary for tissue respiration, is not supplied to the child’s body. The resulting oxygen deficiency contributes to the fact that the functioning of the internal organs of the fetus is impaired. This situation is fraught with the development of dangerous pathologies that can occur even after the birth of a child.
With the shell attachment of the umbilical cord to the placenta, a caesarean section is often a method of delivery. In some cases, natural childbirth can be dangerous by developing dangerous birth injuries and injuries. In order to avoid them, doctors and prescribe a cesarean section.
Note that the choice of method of obstetrics is chosen individually, taking into account the various features of the specific pregnancy.
On the low placentation during pregnancy and the location of the placenta, see the following video.