What does the second stage of maturity of the placenta mean and what week is it normal for pregnancy?
As the fetus develops in the mother's womb, the structure of the placental tissue also changes. One of the important indicators of placenta as measured by doctors is its maturity. This article will tell you more about what the second stage of maturity of the placenta means and what week it is normal for pregnancy.
What does it mean?
Doctors allocate several degrees of maturity of the placenta, which correspond to certain periods of pregnancy. Determination of the degree of maturity of placental tissue must be carried out during a comprehensive examination of the future mother during different periods of pregnancy.
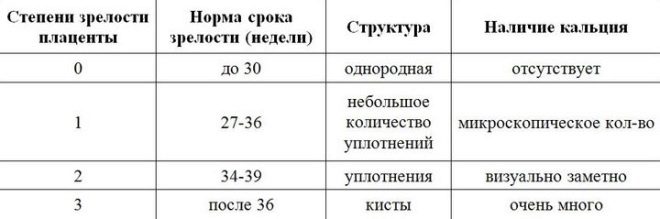
The general classification of the degree of maturity of the placenta provides 4 gradations - from zero to third. It is believed that the older the placenta, the less functions it is able to perform. This is understandable, since the female body gradually begins to prepare for childbirth, after which the placenta is not needed, by the end of pregnancy.
The placenta is needed by the child’s body only during its prenatal life. After birth, the baby can already exist independently. By the time of birth, he has already formed internal organs and systems, which means that the child can breathe and process independently all the nutrients he needs for nutrition and growth. During pregnancy, placental tissue was actively involved in providing these functions.
Each period of pregnancy must correspond to a certain maturity of the placenta. If this does not happen, then, as a rule, the course of physiological pregnancy is disturbed. A variety of causes and pathologies observed in the future mother’s body can lead to early “aging” of placental tissue. In such a situation, doctors conduct careful monitoring of the condition of the pregnant woman and her baby, as well as planning further pregnancy management.
If the second degree of maturity of the placenta in a woman was discovered much earlier than the allotted time, then in the future, the expectant mother is prescribed a number of recommendations. So, she should carefully monitor her overall condition and well-being of the child.
If the placental tissue ceases to fully perform its functions due to excessively early "aging", then in such a situation, the child in the womb will begin to experience some discomfort. This can lead to the fact that the baby's heart rate changes or its physical activity changes. In such a situation, a mandatory consultation with an obstetrician-gynecologist and a possible change of tactics for further management of pregnancy is required.
In some cases, with excessively early maturation of the placenta to 2-3 degrees of maturity, the expectant mother should be hospitalized in the hospital. There a woman can be up to the birth. This usually happens if the course of pregnancy is severely complicated and the threat of premature birth appears.
Norm
Placental tissue that has reached stage 2 of maturity is also called mature. Characteristic changes that occurred in the placenta are considered normal for a period of 34–39 weeks gestation.
It is important to note that these data are averaged. So, if a future mother, carrying a baby already 32-33 weeks of pregnancy, is detected 2 degree of maturity of the placenta, then she should not panic.In this situation, doctors also necessarily evaluate the way a particular pregnancy proceeds. If the fetus is developing well, and his mother has no adverse symptoms, then such a somewhat early maturation of the placenta does not threaten anything.
How to determine?
Determining the degree of maturity of the placenta is carried out by performing an ultrasound examination. Modern ultrasound machines can study placental tissue in pregnant women quite accurately. The indicators obtained as a result of the research are quite informative.
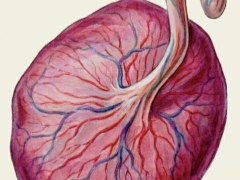
In order for the doctor to determine the 2-3 degree of maturity of the placenta, it should be noted several clinical signs. So, a specialist ultrasound necessarily evaluates the structure of placental tissue. In earlier pregnancy, the placenta has a smooth and even surface. There are no external signs of change on it. As the pregnancy progresses, the structure of the placental tissue also changes - it becomes more uneven and even rough.
The placenta, having a 2 degree of maturity, on the outer surface has grooves and grooves. Its thickness gradually begins to decrease. The indentations that appear in the placental tissue are quite deep and pass inside the placenta almost to the basement membrane. During the ultrasound examination of placental tissue, the specialist determines the presence of multiple linear bands of echoic zones.
As the placenta ripens, special compacted areas, calcinates, begin to appear in it. Placenta 2 degrees of maturity with calcifications is considered quite normal. The occurrence of dense areas in the placental tissue is associated with changes in the placenta in the final trimester of pregnancy.
The appearance of calcifications in the placental tissue at a period of 34-39 weeks of pregnancy is quite normal. Many future mothers begin to worry a lot about this when they learn about such an ultrasound "find." They are worried that the bloodstream of the child may be disturbed, but even in the presence of calcinates in this period, the placental tissue is able to perform its functions as provided by nature.
During a routine ultrasound examination, during which the doctor determines the basic clinical parameters of the placenta, Doppler sonography is also performed. It is usually performed during an ultrasound examination by the same specialist. The purpose of Doppler research is to determine the blood flow in the main blood vessels that provide blood supply to the fetus in the uterus.
In Doppler, the doctor can assess how well the uteroplacental blood flow functions. With premature aging of the placenta, it may deteriorate, which can also adversely affect the health of the fetus. Also, with the help of a dopplerographic study, physicians can determine the development of placental insufficiency - a dangerous condition that can lead to disruption of the intrauterine development of the fetus. This pathology can also develop when the placenta is too early to mature to grade 2–2 in early pregnancy.
Determining the degree of maturity of the placenta is a very important clinical sign.
In order to promptly identify various disorders and pathologically early maturation of the placenta up to 2 degrees of maturity, the expectant mother must always undergo ultrasound examinations prescribed by the doctor. This should be done by deadlines.
To assess the status of placental tissue is very important to conduct dynamic monitoring. This means that during the final period of pregnancy, women who had excessively early maturation of the placenta were diagnosed with several repeated ultrasound tests.This is necessary so that doctors can identify in time the dangerous complications that may arise in this condition. This will allow doctors to intervene in a timely manner and select the optimal tactics for further management of pregnancy, as well as to determine the correct method of obstetrics in a particular case.
In order for the placenta to reach stage 2 of maturity only by the prescribed period of pregnancy, The expectant mother should follow a number of recommendations and lead a healthy lifestyle. Scientists have found that active smoking can lead to excessively early maturation of the placenta. All bad habits of future mothers while carrying their babies should be excluded.
Balanced nutrition, complete sleep, elimination of stress, and regular walks in the fresh air will contribute to the normal functioning of placental tissue.
On what a placenta and what functions it performs, see below.