Signs of incompatibility of partners for conception and table of compatibility for blood group and Rh factor
The planning stage of a future pregnancy is very important. For the birth of a healthy child should be considered quite a lot of different nuances. This article will tell about the signs of compatibility of partners for conception by blood group and Rh factor.
Special features
About blood types currently known quite a lot. But about how they can affect the process of conceiving a baby is much less.
To conceive a healthy baby, it is necessary that the blood type of his mom and dad are compatible. In this case, the risk of possible problems during pregnancy will be much lower.
In order to understand why partners become incompatible, you should refer to the basic knowledge of blood groups. The group has been defined since birth. Determine whether a person belongs to a particular blood group, specific protein molecules - agglutinins and agglutinogens. At the same time, agglutinins are in the liquid component of the blood - plasma.
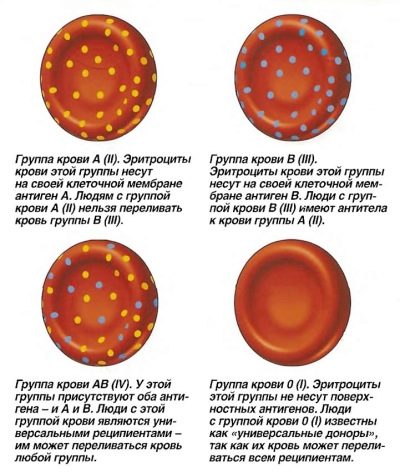
Currently, there are 2 types of agglutinins - a and b. The agglutinogens are found directly in the red blood cells — red blood cells that carry nutrients and oxygen to all tissues and organs. They are also known 2 species. Agglutinogens are usually denoted by capital letters A and B.
Different combinations of agglutinogens and agglutinins and determine the blood group in humans. Doctors distinguish 4 blood groups:
- 1 group. Also called O. They determine its agglutinins a and b, but there are no agglutinogens in plasma.
- 2 group. The second name is group A. It is determined by the presence of agglutinin b and agglutinogen A.
- 3 group. Also called B-group. It is determined by the presence of agglutinin a and agglutinogen B.
- 4 group. The second name used is AB. Determined by the presence of agglutinogens A and B in erythrocytes in the absence of plasma agglutinins.
For a long time, the importance of such an important indicator as the Rh factor in medicine remained a mystery. For the first time, the presence of special proteins in the blood — antigens that determine the Rh factor (Rh) was shown at the beginning of the 20th century by two doctors, Philip Levin and Rufus Stetson. They proved the presence of certain protein molecules in the blood by the example of the appearance of hemolytic jaundice in a newborn after transfusion to an incompatible blood group.
Nowadays, scientists know exactly how the Rh factor is determined. On the surface of red blood cells there are substances - D-antigens. If they are present, then this Rh factor is called positive. In the absence of D-antigens on the surface of red blood cells, negative rhesus is mentioned.
The presence of a certain Rh factor is a constant indicator, which is determined from birth and does not change throughout life. So, if both parents have a negative Rh factor, then the baby will have the same. If the future father and mother have different Rh factors, then the baby can have it either positive or negative.
Impact on fertilization
Blood type does not directly affect the process of conceiving a child.Also, it does not affect the possibility of conceiving a boy or girl.
If a conflict in the ABO system between the mother and the fetus arises in the future, this usually manifests itself in the appearance of a small jaundice in the baby after birth. In this case, the skin of the child acquires a jaundiced color. This condition usually passes after a few days, but requires constant monitoring of the child. Also, the conflict over the agglutinogen system can lead to the appearance of certain discomfort symptoms in a woman during pregnancy. The likelihood of developing toxicosis in the first half of pregnancy with morning nausea increases significantly.
For a long time, it was believed that different blood types of partners are the guarantee that a child will be born healthier and stronger. However, modern scientific research has refuted this claim. The risk of developing dangerous pathologies during childbirth also exists with different blood types of future parents.
Rhesus factor in the direct planning of pregnancy plays a fairly important role, but it does not significantly affect the conception of the baby. In this situation, doctors fear more development of a potential Rh-conflict that may occur during pregnancy.
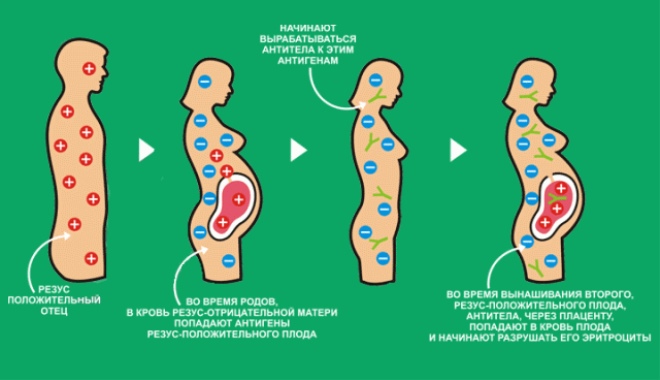
If partners have the same Rhesus group, then the risk of an immunological conflict is low. If there are different Rhesus groups, especially if in this case the woman has a negative Rh factor, the risk of an immunological conflict increases. In this situation, the baby can "inherit" the positive Rh factor from the father. The difference in Rh factors in the mother and the fetus, as was noted earlier, and provokes the development of negative consequences.
How to check pair compatibility?
Determining the blood type or Rh factor is currently simple. These indicators are quite easily and quickly checked in any diagnostic laboratories. It is possible to pass the analysis to future parents in a free, as well as in a private medical institution.
The test requires a small amount of venous blood. The result is ready pretty quickly. In order to assess the compatibility of the pair, it is necessary to determine the Rh factors and blood groups of both partners. Families that for a long time cannot conceive a baby and have problems with natural conception are especially carefully checked in this way.
Rh factor
Possible incompatibility of partners is necessarily evaluated according to different criteria. The most important of these is the Rh factor. For the convenience of assessing the compatibility of partners, use a special table below.
Rh - the factor of the future father | Rh - future mother | Risk of developing probable complications | The probability of Rh - the factor of the unborn child |
Positive (+) | Positive (+) | - | "-" / "+", the probability share is 30/70% |
Negative (-) | Positive (+) | - | "-" / "+", the probability share is 50/50% |
Positive (+) | Negative (-) | The probability is more than 50% | |
Negative (-) | Negative (-) | - | Negative (100%) |
The most common situation that causes confusion is the appearance of a “negative” child in a “positive” couple. Very often in this situation, the question arises about true fatherhood. Immediately dispel the myths and say that such a situation really takes place in practice. Inheritance of the Rh factor is subject to genetics. In this case, the baby may inherit the positive Rh of its parents, or maybe not.
The opposite is negative Rh factors for both parents. In this situation, the baby can be born only with the same rhesus.
By blood type
In order to determine the compatibility of blood groups of future parents, a special table is used. It can be used to determine the likelihood of a child’s blood group, as well as assess the risk of incompatibility. Such a table is presented below.
Future father’s blood type | Future mom's blood type | Probability compatibility | Signs that a child inherits |
1 (o) | 1 (o) | - | 1 (o) |
1 (o) | 2 (A) | - | 2 (A) / 1 (O), the probability share is 50/50% |
1 (o) | 3 (B) | - | 3 (B) / 1 (O), the probability share is 30/70% |
1 (o) | 4 (AB) | - | 2 (A) / 3 (B), the probability share is 50/50% |
2 (A) | 1 (o) | The development of complications of the pathology of pregnancy and the possible Rh-conflict (the probability ratio is 80%) | 1 (O) / 2 (A), the probability share is 60/40% |
2 (A) | 2 (A) | - | 1 (O) / 2 (A), the probability share is 30/70% |
2 (A) | 3 (B) | The development of Rhesus-conflict - about 70%, the risk of premature onset of labor - 50% | 1 (O) / 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB), can be inherited with equal probability |
2 (A) | 4 (AB) | - | 1 (O) / 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB), can be inherited with equal probability |
3 (B) | 1 (o) | 40% - the proportion of miscarriage and dangerous pathologies during pregnancy, 80% - the risk of a possible Rhesus conflict | 1 (O) / 3 (B), the probability share is 30/70% |
3 (B) | 2 (A) | 60% - the share of development of dangerous pathologies during pregnancy | 1 (O) / 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB), can be inherited with equal probability |
3 (B) | 3 (B) | - | 1 (O) / 3 (B), the probability share is 50/50% |
3 (B) | 4 (AB) | - | 1 (O) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB), with equal probability |
4 (AB) | 1 (o) | Almost 100% development of Rh-conflict, dangerous pathologies of the course of pregnancy, as well as the formation of fetal intrauterine defects | 2 (A) / 3 (B) with equal probability |
4 (AB) | 2 (A) | 40% - the proportion of the likelihood of developing dangerous pathologies during pregnancy and rhesus conflict | 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB) with equal probability |
4 (AB) | 3 (B) | 40% - the proportion of the likelihood of developing dangerous pathologies during pregnancy and rhesus conflict | 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB) with equal probability |
4 (AB) | 4 (AB) | - | 2 (A) / 3 (B) / 4 (AB) with equal probability |
It is important to note that these data are indicative. In practice, there are cases when, even with a conditionally favorable prognosis, an immunological conflict developed. This table only allows you to assess the potential compatibility of partners and assume the blood type of the future baby.
From this table it also follows that the first blood type of the future father is perfectly “combined” with others. There is no risk of an immunological conflict. In this case, the probability of developing a healthy pregnancy increases significantly. It can also be assumed that the first paternal blood group is not absolutely decisive for the baby. The maternal data also influences the determination of a child’s blood type. In this case, the blood type of the baby may be different.
The third group of blood can be said to be the most "problematic." As can be seen from the table, it is rather badly combined with 1 and 2 groups. In this case, with the 3 and 4 group, the combination is already more favorable.
Pregnancy for representatives of the 4th blood group is better to plan for people who have similar groups. According to the table, the 4th blood group is rather poorly combined with others, except for “its”. The risk of developing Rh-conflict with a combination of 4 groups and the first is the most unfavorable. Unfortunately, a completely healthy pregnancy without any negative consequences is unlikely.
How does the discrepancy occur?
To determine the biological incompatibility of partners, unfortunately, in most cases it becomes possible only after conception and during pregnancy. Also, negative signs of Rh-conflict or incompatibility of the ABO system can be assessed in a baby after his birth.
For example, with a combination of 4 paternal blood groups and 1 blood group of the mother, there is a rather high risk of developing dangerous pathologies of fetal intrauterine development. They contribute to the fact that the baby can significantly lag behind in its physical development. The probability of the formation of malformations of internal organs is also quite high. Babies born with this combination of blood groups have a rather high risk of congenital diseases of the kidneys and heart.
Often during pregnancy, doctors talk about Rhesus conflicts. In this case, the Rh factors in the mother and fetus differ. Conflict occurs when a Rh-negative woman bears a Rh-positive baby. In such a situation, the female body perceives the child as an alien antigenic “object”. At the same time, the risk of developing dangerous pathologies during pregnancy and even miscarriage is quite high.
One of the most serious conditions, which is a consequence of such an immunological conflict on the Rh factor, is hemolytic jaundice of newborns. With this pathology, the erythrocytes with the accumulation of bilirubin in the tissues begin to decay in the children's organism. The large amount of bilirubin formed contributes to the fact that the child's skin color changes - it becomes yellow. The course of hemolytic jaundice is usually severe and is carried out in hospital conditions.
The development of Rhesus immunological conflict is a certain "lottery". In medical practice, it also happens that even in the case of the development of Rh-conflict during pregnancy, pathology does not occur. Such a situation is possible if the female body for some reason was already familiar with rhesus antigens, that is, sensitized to them. This is usually possible with previous blood transfusions, etc. Thus, a different Rh factor in the mother and fetus does not always lead to the development of dangerous pathologies.
Is it treatable?
Doctors note that the biological compatibility of partners is a rather complicated topic. To conceive a healthy baby, several factors must work. Even at the stage of direct fertilization, in some cases, certain problems may arise.
One of the most common of these is the immunological conflict that occurs in connection with antisperm antibodies. These specific proteins can have a detrimental effect on the male sex cells - the sperm. In some cases, these antibodies occur in the female body, significantly preventing the conception of the baby.
Change the Rh factor or blood group, alas, it is impossible. However, knowing them, it is possible to clarify in advance the risk of developing dangerous complications of the development of pathologies during pregnancy.
Any “conflict” pregnancy is a reason for a more careful and attentive attitude on the part of doctors to the state of health of a pregnant woman, as well as to the intrauterine development of her baby.
While carrying a baby, a patient who is at high risk of developing an immune conflict pregnancy is carefully monitored by doctors. In order to promptly identify the development of her dangerous pathologies, a pregnant woman is carried out a whole range of diagnostic studies. These include:
- Ultrasound examination. With it, you can determine the main signs of fetal lag in intrauterine development. From a certain period of life of the fetus, an ultrasound specialist will necessarily evaluate the size of his liver, the clinical signs and size of the placenta, the amount of amniotic fluid. Comprehensive assessment allows you to identify pathology at the earliest stages.
- Doplerography. A more detailed method for assessing fetal development. It is used in obstetric practice in immunocompromised pregnancies in order to more accurately assess the potential risk of pathology.
- The study of cord blood for bilirubin. Amniotic fluid can also be used for this study. This diagnostic procedure is performed only in difficult and severe clinical cases, as it is invasive and may have a number of negative consequences.
What to do?
If the risk of developing an immunological conflict is high, then the doctors will offer the expectant mother some special manipulations that should help reduce the risk of developing dangerous pathologies in her future child. Such measures are considered more prophylactic, since they help to significantly reduce the potential likelihood of developing fetal abnormalities in the child and improve the course of pregnancy.
One of the preventive measures used is the "immunization" of a pregnant woman with immunoglobulins. This procedure is performed, as a rule, at the 27-28 week of pregnancy.Its goal is to temporarily “freeze” female immunity so that a stormy response to the entry of foreign fetal blood antigens into the female organism does not begin.
It is important to note that this procedure is carried out only on the strict prescription of a doctor. There are certain contraindications for its implementation, which are necessarily determined by the doctor in each specific case.
A significant disadvantage of this technique is the weakening of the pregnant woman’s own immunity. Such intervention can lead to the fact that the immune system of the expectant mother will simply not be able to withstand various infections. In such a situation, even a banal flu or cold can have quite unfavorable consequences.
In medical practice, there are also varieties of this procedure. Thus, the introduction into the female body of immunoglobulin can be carried out after childbirth. Usually, such injections are performed in the first 72 hours after the birth of the child. This procedure allows you to further "immunize" the female body. Subsequent pregnancies in this case, the risk of an immunological conflict is reduced.
There are quite invasive methods used in "conflict" pregnancy. Immediately, we note that they are performed in fairly difficult cases, when there is no other alternative. The essence of the invasive technique is to introduce certain biological components through the umbilical cord into the placenta to the fetus or even perform a blood transfusion. This procedure is carried out with the aim of restoring and normalizing the work of red blood cells in the children's organism, the erythrocytes.
Doctors strongly recommend that all women at risk of developing an immunocompromised pregnancy regularly visit their doctors while carrying babies. It is very important that medical care in such a course of pregnancy is provided in a timely manner and in full. In this case, it is possible to reduce the likelihood of the development of dangerous pathologies of intrauterine development in a baby, as well as to avoid the formation of serious diseases.
You can “circumvent” a situation in which the risk of an immunological conflict is high is possible with the help of in vitro fertilization (IVF). In this case, conception is carried out under the strict control of a fertility specialist. This doctor knows exactly which cells are taken for fertilization. Also in a special laboratory, you can determine all the basic properties of germ cells immediately before conception. In this case, the doctor at the planning stage of pregnancy can accurately calculate the Rh factor and even suggest the blood group of the unborn child.
Very often, if the risk of an immunological conflict is quite high, a Rh-negative embryo is selected for "landing" in the uterus. IVF has already helped quite a few couples, who have been identified biological incompatibility, conceive their long-awaited kids.
You will learn more information about the Rh factor and the Rh-conflict of the blood during pregnancy from the following video.