On which day after ovulation does the embryo implant take place and how long does it last?
Women who are planning a pregnancy have probably heard about implantation, but not everyone knows exactly how and when this most important process occurs. In the meantime, it depends on the success of the implantation whether the pregnancy will develop further or end at the very early stage, when the woman does not even suspect that there is a new life inside her. In this article, we will talk about when implantation occurs and how long it takes.
How does this happen?
Implantation refers to the process of implanting a fertilized egg into the wall of the uterus, where the fetus will grow and develop throughout the gestation period. Before this happens, the very conception itself must occur.
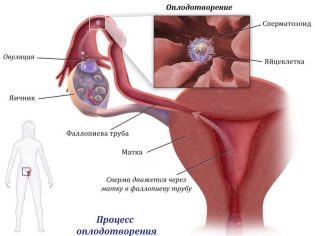
On the day of ovulation, a mature female reproductive cell ready for fertilization emerges from the follicle on the ovary into the ampullary part of the fallopian tube. Fertilization takes place there. Spermatozoa may already be at this point in the tube, if sexual intercourse was performed before ovulation, or reach the destination after ovulation during the day. That is how much time an egg lives and retains the ability to fertilize.
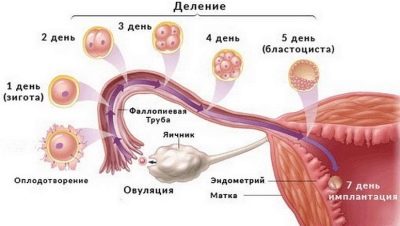
As soon as the male and female gametes meet, the process of turning an egg into a zygote begins - a special new cell containing an individual set of chromosomes borrowed from a sperm cell and an oocyte. Female and male chromosomes merge, form a new life. Zygote begins to split into new cells, the number of which increases constantly. At the same time, it begins to move in the direction of the uterus, because only there nature has provided optimal conditions for the development of the fetus.
At this stage, the embryo is inactive, the villi on the inside of the tube itself, as well as light spontaneous contractions of the walls of the fallopian tubes, help him to move forward through the tube. This journey takes 3 to 5 days. On day 5, the fertilized egg finally descends into the uterine cavity and begins to look for a “refuge”. Another day - two she can swim in the uterus, all the while crushing continues. Two layers are formed: the inner one, from which embryonic structures will be formed later, and the trophoblast, the outer layer, which will have to assume responsibility for implantation.
The egg cell becomes a more complex structure - the blastocyst. At this stage, it is very important for her to stick to the wall of the uterus. As soon as the fertilized egg is attached to the uterus, the implantation process begins. By simple mathematical addition it is easy to establish that from the moment of ovulation to the beginning of implantation usually 7–8 days pass. Sometimes implantation takes place only at 8–9 days, and this is also considered to be quite normal.
The implantation itself lasts about 40 hours. Adhesion, the primary attachment to the wall is called the stage of adhesion. After this, the second stage begins - invasion (immersion). Troboflast forms the special finest villi.These threadlike antennae begin to secrete enzymes that dissolve the endometrial cells of the uterus.
Gradually, the villi dive further and further into the uterine tissue. A recess is formed, in which the fertilized egg reliably sinks. The villi are connected to the blood vessels of the maternal organism, and the embryo that previously ate only that which was in the nutrient medium of the uterine cavity, begins to receive everything necessary from the mother’s blood.
At the same time, the production of a special hormone begins, the presence of which is practically excluded in the body of a non-pregnant healthy woman, human chorionic gonadotropin. It is hCG, when the concentration of the substance reaches a sufficient level in the body, will allow you to make a test or a blood test for pregnancy. Its level gradually increases, and already 4 days after implantation or 10 days after conception a blood test for hCG can answer the question whether a pregnancy has occurred. Test strips in the urine will detect HCG from the first day of the delay, that is, 14 days after conception.
If the implantation is successful, the pregnancy begins, the development of the embryo continues, hormones change, the woman becomes pregnant. If unforeseen circumstances arise at least at one of the stages of the attachment of the ovum, the pregnancy will not come: the ovum will die and come out with endometrial fragments during the next menstrual period.
Early and late attachment
If the gestational egg passes unhindered through the fallopian tubes, is crushed and developed at a normal rate, then the implantation may be early. Such in medicine is considered to be full immersion of the blastocyst in the endometrium up to 7 days after ovulation.
If the lumen of the fallopian tubes is narrowed, the advance along the fallopian tube is slowed down, the embryo cells do not divide rapidly enough, the endometrium is insufficiently thick, and the implantation process can be delayed. Late attachment is considered to be implantation that occurred after 9 days from the moment of ovulation.
The implantation time by and large does not affect the further development of pregnancy, but late and early insertion has its own nuances.
- Early implantation is prognostically worse than lateBecause the gestational egg can sink into the uterus too early, when the endometrium has not yet reached full readiness to accept it. In this case, implantation either does not occur, or occurs, but with certain defects, which later, on a more serious period of gestation, can result in placental insufficiency, detachment and abnormal development of the placenta, or everything will end in a miscarriage in the early period.
- Late implantation is more favorable due to endometrial maturity.but too late, the “arrival” of the ovum may again end in the absence of implantation, because the special structures of the endometrial cells, pinopodia, appear only during the “implant window” and disappear a couple of days before the next menstrual cycle. Without them, the stage of immersion will be much more difficult and may end in failure.
Some features of terms
If a woman becomes pregnant not in a natural way, but through IVF, the estimated implantation dates begin not from the moment of ovulation, because it does not occur in the IVF cycle, but from the day after the embryos are transplanted into the uterus.
In general, the implantation process itself after IVF lasts a little longer than 40 hours, and it begins later. The 5-day embryos are the fastest and the best implanted, a little worse are the embryos of three days. The first can begin to attach within a few hours after the transfer. The second sometimes takes about 3-4 days to just begin to delve into the endometrial layer. Implantation after cryotherapy is almost always late.
A blood test for hCG to determine whether the implantation took place and whether a pregnancy has occurred, is recommended to be carried out not earlier than 14 days after embryo transfer.
According to statistics, three-day embryos take root with a probability of 40%, five-day - with a 50% chance, and two-day, six-day and older successfully implanted no more than in 20-25% of cases.
Can you feel the attachment?
Officially, medicine claims that feel the implantation a woman cannot: there are no signs and symptoms that directly indicate microscopic cellular processes occurring in the uterus. But in practice, many women claim that they still had unusual feelings. Medicine does not deny such an opportunity, because after implantation, the hormonal background of a woman changes and theoretically she can feel something unusual if her level of individual sensitivity is rather high.
These symptoms include headache, dizziness and weakness, which occurred about a week after ovulation, feeling chills, fever up to 37.0–37.5 degrees, increased anxiety, depression, irritability, nausea. Some women in this period may feel disgust for sex, while others, on the contrary, feel heightened arousal.
Occasionally, discharge of a bloody nature appears, which are called implant bleeding. So the blood comes out of the small blood vessels damaged by immersion of the ovum. The volume of such bleeding does not exceed 2 ml, it quickly ends, sometimes proceeds in the form of "daub".
Some women note that they didn’t feel anything, and the first sign of pregnancy for them was a more reliable delay of the next menstruation from the point of view of diagnosing the “interesting position”.
Implantation cannot be seen either by ultrasound or by other modern diagnostic methods. No analysis will show whether this important process has begun and whether it will complete successfully. Only a week after implantation, you can do a pregnancy test or donate blood for hCG to get a result.
For information on how the conception and attachment of the embryo to the uterus occurs, see the following video.