Why does a baby have “goose” skin?
“Hair on end” and “goosebumps” are not only artistic embellished comparisons of the degree of fear or horror. This is quite a literal description of such a phenomenon as "goose" skin in a child. What it says, what are the causes and how to treat it - you will learn about all this by reading this article.
What it is?
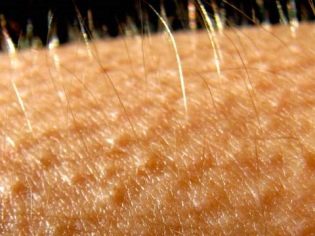
Feathers of geese grow from small tubercles on the skin, their structure is very reminiscent of human hair follicles. If the goose is plucked, then small protrusions appear in place of the feathers. The skin acquires a characteristic texture. Goose skin is called the condition of the child’s epidermis, in which the skin is covered with small pimples in the hair follicle.
Indeed, the external similarity is. But if a goose is a feature of the structure of the skin, then in humans it is a manifestation of the pilomotor reflex. It works like this: under the influence of external and internal factors (it may be cold or stress, a strong emotional experience) peripheral nerves that are responsible for perception are stimulated. They excite the nerve endings that suit the hairs on the skin. Smooth muscles are reduced, and hair "stand on end."
Nature has given such a reflex not only to man. For most animals, this skill is a way to demonstrate one’s own strength in threatening circumstances. Cats and dogs "raise" the wool when they need to frighten the enemy, because the pilomotor reflex gives them the opportunity to appear more. Porcupines went even further - they are not only bristling, but can also shoot needles towards the enemy.
"Goosebumps" on the skin of a person can be short-term, and may persist for a long time. Naturally, parents want to know why a child has “goose” skin — to fix it somehow.
The reasons
The natural physiological reasons for the appearance of pimples on the arms, legs, and body can be associated not only with cold or strong fear. Something pleasant (for example, waiting for a gift, anticipation of an interesting trip, listening to your favorite music) may well cause your child to have such an interesting effect on the skin. The peculiarity of this manifestation of the pilomotor reflex is that the “goosebumps” pass quickly and do not require any intervention and assistance.
If the “goose” skin of a child appears regardless of the emotions and the ambient temperature, then it is quite possible that we are talking about such a disease as hyperkeratosis. With it, the stratum corneum expands strongly, hardens - and eventually clogs the hair follicles. Most often "goose" skin appears on the forearms, elbows, back of the thighs, on the bottom, on the legs (especially on the knees).
Quite often goosebumps appear in newborns and infants, because their skin is thinner and tender. Not very often the bumps pop up on the face, cheeks, back and abdomen. However, this is also possible. Never hyperkeratosis appears on the palms, in the scalp and in the heels.
In some children, the bumps are pale pink, in others - more red. Most often, the rash blush, if the baby has not eaten something, he is allergic. In the normal state, "goose" skin does not bother the child, but itch may appear under the influence of allergens.
The affected skin areas with hyperkeratosis are very rough and rough to the touch, they look unattractive. This is all the harm from the disease. However, the desire of adults to rid the child of such a skin phenomenon is quite understandable and justified.
You need to understand that the disease indicates a completely specific violations in the body that caused the growth of the stratum corneum. By eliminating these factors, you can permanently save the baby from ugly rough skin.
Similar to the goosebumps of a child most often becomes due to:
- deficiency of calcium and zinc in the body, due to the lack of vitamins A, C, E;
- excessive dryness of the skin (due to insufficient humidity of the air, drying aggressive means to care for the body);
- insufficient hygiene procedures when the follicles are clogged purely mechanically;
- hormonal disruptions in the body
- allergic reaction.
In search of the true cause, you should definitely look at the skin of close relatives, quite often the child simply “inherits” the “goose” skin from someone of them.
Treatment
Treatment should begin with finding the cause of the changes in the epidermis. To do this, be sure to visit a dermatologist and pediatrician. The first specialist will assess the extent of the lesion, the second will prescribe laboratory tests. If the pediatrician deems it necessary, he will send the child to an allergist.
To establish a deficiency of calcium, zinc or vitamins can be according to the results of a blood test. This must be done so that the doctor knows exactly what substances are not enough to select the most effective vitamin complex or calcium supplements. Attempts to deal with this situation on their own with their parents rarely end in success, since the complex of vitamins and minerals bought at random almost never helps.
A blood test for hormones will give an idea of whether everything is in order in a baby with an endocrine system. This reason is most often detected in adolescents during the hormonal adjustment of the body, associated with intense puberty.
An allergist will carry out diagnostic tests, which in most cases will allow you to accurately determine the type and origin of the allergen that caused the appearance of goose bumps. Most often it is household chemicals, household dust, body care products - soap, foam, shampoo.
Therapy itself will be to eliminate the cause. In case of allergic hyperkeratosis, antihistamines may be prescribed to the child, both in the form of ointments and tablets. It is very important to eliminate the contact of the child with the source of the allergic reaction.
If the allergen is not found, it is recommended to remove carpets and soft toys from the house, not to use household chemicals (especially based on chlorine), to prevent the child from gaining access to it. You need to bathe your baby without soap. Baby hypoallergenic soap can be used no more than once a week.
Hormonal changes in the skin of adolescents are not made to be treated with medicines, since hyperkeratosis goes away by itself - as puberty ends. However, the child necessarily needs more careful care of the skin, without the use of alcohol-containing solutions, aggressive cosmetics. It is best to teach adolescent children to bathe with baby soap, and use hypoallergenic baby shampoos for washing their hair.
Lack of vitamins offset their additional intake. Dry skin of the child is a field for large-scale parental actions. First you need to check how humid the air in the room where the child lives. The hygrometer will help with it.
If the air humidity is lower than 50%, then it must be raised precisely to such values - and even higher (60-70%). This will help another special device - a humidifier.
After bathing with dry skin, you can use emollients and moisturizers without perfumes and additives. Best used "Children's" cream or liquid paraffin. While bathing you should not use foams, it is enough to use the simplest baby soap (no more than once a week).
In all cases of hyperkeratosis, you can make the child a light home massage using a special massage glove, without massage oil. It should be based on stroking and not very strong rubbing of the affected skin. It helps to restore a good blood supply to the skin.
Tips
The following useful recommendations should be considered:
- A child with a "goose" skin should not sweat, wear it according to the weather.
- In the summer, be sure to use sunscreen.
- The skin should be in contact only with natural fabrics (without textile dyes). The best option is white cotton underwear. Bed linen must meet the same requirements.
- When bathing, be sure to use a hard sponge and washcloth - this gives not only a massage effect, but also well peels the coarsened layer, cleansing hair follicles.
Why does a goose bumps appear on the body? The answer can be found from the video.