Cryptorchidism in children
Baby's reproductive health should be taken care of even when he is lying in the crib and blowing bubbles. Otherwise, then you can never become a grandmother. One of the most serious threats to the health of boys is cryptorchidism. In this article we will tell you what it is, how to recognize such a pathology in a child and how to treat it.
What it is
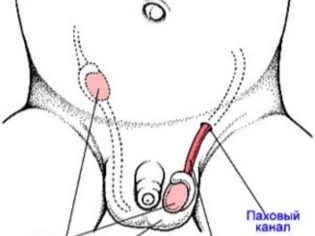
Cryptorchidism is the undescension of the testicles to the scrotum. In this case, the testicle may be located somewhere near the place where it should be normal, for example, in the peritoneum or inguinal zone, mainly in the area of the inguinal canal. Sometimes the gonads of boys generally “deviate from the course” and leave the inguinal canal, remaining subcutaneously in the thigh, pubis, and perineum.
Such a congenital pathology is found quite rarely in healthy and full-term babies - only in 3-4% of cases. However, in preterm infants, the frequency of cryptorchidism rises to 25-30%.
If the baby is not fully mature, and its birth weight is about 1 kilogram, then the doctors will find cryptorchidism with almost one hundred percent probability. In more than half of the facts, a “stray” testicle can be felt through the skin. However, sometimes this cannot be done, because there is a congenital developmental abnormality - the complete absence of one or two sexual glands in a child.
Causes and mechanism of occurrence
You should know that the male embryo always has temporary cryptorchidism. In other words, in boys, the testicles do not form in the scrotum.
They are laid and grow much higher - in the abdominal cavity in the kidney area. In the 18th week of pregnancy, the sex glands, which will later be assigned many of the most important functions for men, set off on their way to their natural habitat.
They begin to descend, moving smoothly and gradually down to the scrotum. From the pelvis to the scrotum, they usually descend at 28-30 weeks gestation. But this is not always the case. It is considered normal omission, which occurred at any time before birth, as well as in the first 6 weeks of independent life of the baby.
The testicle does not travel by itself, it is set in motion by a special cord consisting of connective tissue. It connects the gonad with the scrotum. At the right moment (by the middle of the second trimester of pregnancy), the burden is sharply reduced. The movement of the testicle contributes to increased intra-abdominal pressure, contraction of the intestine and the work of the appendages of the sexual gland. If one of these links fails, the testicle is not sent to the right place. Most often, it simply stops moving and remains in the abdominal cavity, but sometimes it migrates subcutaneously to any part of the groin area.
The main reasons for the emergence of cryptorchidism medicine sees in the weakness of the peritoneum, this explains why in newborn babies pathology occurs much more frequently.
However, there are other reasons that can lead to abnormalities:
- Genetic diseases. Cryptorchidism often accompanies Down syndrome, Noonan syndrome, and also occurs in children with mutations of certain genes responsible for the correct formation of sex. Chromosomal abnormalities may also be caused by the negative effects of toxic chemicals.
- Hormonal disbalance. If the body doesn’t have enough sex hormones that promote the testicle, or maternal estrogen has a stronger effect on it, then immunity or testosterone deficiency develops.Lack of this hormone slows down or does not start the process of prolapse of the gonads in the scrotum.
- Diseases of the mother. It is believed that cryptorchidism may develop due to the negative impact on the fetus, which occurs if the pregnant woman has had rubella, chickenpox, measles, toxoplasmosis. Sometimes the "culprit" of undescended testicles is considered diabetes.
- Hereditary physiological problems. Some anatomical features of the body structure can be transferred from the grandfather or father to the baby. So, shortening of the spermatic cord, a narrow inguinal canal through which the testicle is to pass, may well become a mechanical obstacle in the way of the sex gland.
- Medications. It has been scientifically proven that if a mother during a pregnancy took at the same time “Ibuprofen” with “Aspirin” or “Paracetamol”, then the risk of developing cryptorchidism is 16 times higher than that of the fetus of a woman who did not take such means.
Modern scientists have proposed another hypothesis of the emergence of cryptorchidism. They tried to explain the lack of testosterone and the insensitivity to it by the attack of maternal immunity on the germ cells of the male fetus. According to this version, the defensive cells begin to take the male sex glands for a foreign microorganism, and try to suppress their vital activity in every possible way. However, this version has not yet received convincing scientific evidence.
Types of pathology
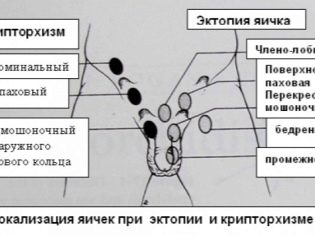
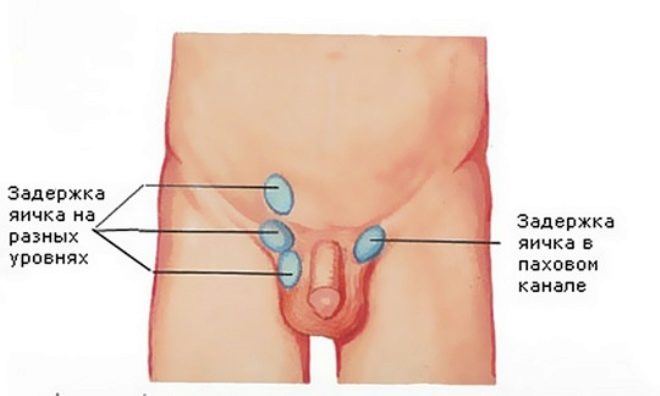
Cryptorchidism is of two kinds - true and false.. In the first case, the testicle remains in the abdominal cavity, inguinal canal, or is stationed at the groin ring. This is a very common form of the disease, it is characterized by the possibility of manual omission of the reproductive gland into the scrotum, but in practice this is not always the case.
False cryptorchidism also occurs very often. But with this ailment, the sex gland can be manually returned to its proper place. The condition is associated with increased muscle tone, which is responsible for lifting the testicle. This state of medicine is also called "migratory cryptorchidism."
Often in children, the testicle may leave the scrotum and return back up to 8 years. This usually occurs when the muscle tone increases, if, for example, the baby is cold or very frightened.
Ectopia is another type of cryptorchidism, in which the gonad is located under the skin of the thigh, at the base of the penis, at any point of the inguinal zone. Although the testicle is palpable, it is not possible to return it to the scrotum manually. This form of pathology is considered the most severe, it is rightly called one of the most indisputable causes of male infertility.
Cryptorchidism can be bilateral and one-sided. And on the side of undescription - right-sided, left-sided and full.
Signs of
A child with cryptorchidism doesn’t have pain and discomfort. In any case, until the boy reaches adolescence.
During puberty, the blood supply to the reproductive gland becomes more intense, which leads to squeezing of the testicle and causes unpleasant pulling pains during the tension of the peritoneum.
Typically, such sensations come during coughing, during bowel movements, physical exertion, especially if the area of the press is actively involved in them, as well as during sexual arousal.
Changes in the scrotum are noticeable almost from birth. The older the child becomes, the more pronounced the visual changes in the scrotal sac. The scrotum looks asymmetrical, underdeveloped.
Diagnostics
The pediatric surgeon will be able to establish the fact that the testicle is not descended. Having found out the whole family history, he will make a conclusion about the type and nature of undescension, and, accordingly, about the possibility of treatment. Manual examination of the scrotum sac, the canal in the groin is not sufficiently reliable and informative. The baby's testicle is small, it is easy to miss in the inguinal canal, and in the abdominal cavity it is impossible to grope it in principle.
Therefore, the most informative and accurate way to diagnose ultrasound is considered.
The diagnostician finds the testicle, measures it and assesses its condition (it is alive or atrophied), is there any pathological changes in it, and is there a way that the reproductive gland could be lowered into the scrotum. In addition to the general blood and urine tests that are required to consult a doctor, you will need to donate blood for hormones in order to determine the testosterone content and see if the testicles are functioning.
Treatment
False cryptorchidism, in which the sexual gland "walks" from the scrotum into the scrotum, does not need special treatment. It usually passes after 7-8 years, when the inguinal ring shrinks. But this form of pathology requires constant monitoring by the surgeon. Visit this specialist will have more often.
True cryptorchidism can be treated both medically and surgically. Drug treatment makes sense when the testicle has not reached its destination at all and is located next to the scrotum. Any conservative therapy helps the reproductive gland to advance to the scrotum by only 30-50%. Therefore, the probability of successful treatment in the region of 60-90% of doctors can be guaranteed only when the testicle has a short way to go.
If the gonad has stopped in the abdominal cavity, then it is considered inappropriate to spend time on taking medications, you need prompt treatment.
Best results are achieved if therapy begins at the age of 6 months and 1 year. However, it does not make any sense if the child has already joined the ranks of adolescents when testosterone levels naturally increase.
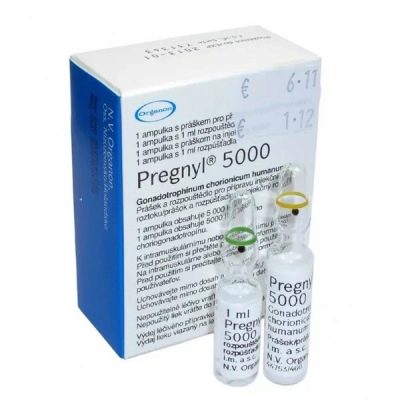
For treatment, use "Horiogonin" or "Pregnil" (hCG preparations), make injections in courses in the age dosage prescribed by the doctor. Statistics show that every fifth baby who was cured with the use of medication, cryptorchidism returns after some time. Reviews of parents who have decided on the drug treatment of the child, say that these statistics are higher, and the disease returns much more often than official sources say.
Surgery is considered a more reliable method of treatment. Children can do it from 9-10 months of age, however, surgeons often do not hurry and wait up to 2 years. After 7-8 years, it makes no sense to perform the operation, since the body begins the process of puberty.. The younger the child at the time of the operation, the greater the likelihood that the testicle, which is returned to the site, will function normally, produce sperm of adequate quality and provide the boy's body with male sex hormones.
If the disease was first discovered only after the child was 8-10 years old, the “lost” testicle should be removed. Even if it has not been atrophied, in any case it will not fulfill its functions, and the risk of the development of malignant tumors in it increases many times. The operation is done with the use of laparoscopy, it can significantly simplify and shorten the rehabilitation process. Unfortunately, the opportunity to save the reproductive gland and to establish its work exists only with some forms of true cryptorchidism. When ectopic testicle immediately be removed.
The fact is that the longer the gonad is in the abdominal cavity or under the skin (as in ectopia), the more it suffers and changes.
The first changes begin in the period of intrauterine development. Seminal function is impaired, the composition of tissues changes, because the temperature in the scrotum is lower than in the abdominal or subcutaneous region.
During the rehabilitation period, antibiotics and bandages are prescribed for the child, and after removal of the stitches, a special massage is given.
Implications and predictions
Parents often tend to underestimate cryptorchidism, and its consequences may be more than serious:
- infertility and impaired fertility (impotence, etc.);
- the rebirth of the testicle, located outside the cavity of the scrotum, into a malignant tumor;
- problems with the hormonal sphere - obesity, lack of secondary sexual characteristics, violation of the "breaking" of the voice, lack of body hair of the armpits, pubis, the formation of the body according to the female type (wide hips, narrow shoulders);
- testicular torsion, trauma and other acute conditions requiring urgent surgery.
The prognosis of doctors with true cryptorchidism depends on how early the disease was detected and the appropriate treatment was provided.
If the operation was carried out as soon as possible for a child under 2 years old, then the probability of preserving the childbearing function is quite high.
It is about 50-70%. Unfortunately, no one can guarantee one hundred percent probability.
Delaying treatment, trying to be treated with folk remedies, to carry the child to the healers, most often leads to the fact that the most favorable time for treatment is spent, and during surgery after 3-4 years, doctors already give much less chances of preserving reproductive function - only thirty%. As they grow older, they decrease. When ectopic chance of saving the gland is not.
The fact that parents should know when cryptorchidism in children, see the following video.