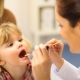
Polypas in the child's nose
Violation of nasal breathing is the most common problem in pediatric practice. Quite often, polyps in the nose lead to this unfavorable condition in a child. This article describes what parents should know about this pathology in a baby.
What it is?
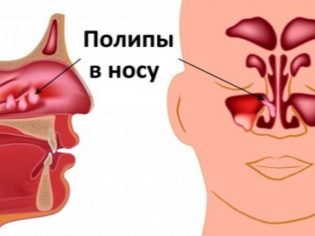
Normally, the internal surface of the nasal passages is lined with mucous membrane. Outside, it is covered with multiple ciliated epithelium. Normal mucosa is smooth. There are no projections and formations on it.
Pathological growth of tissue and leads to the appearance of specific formations, which are called polyps.
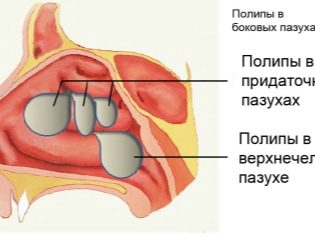
These elements can grow in the nasal passages, and in the paranasal sinuses. The sizes of polypoid formations are very different.
The shape of tumors can also vary significantly. It usually changes as the polyp grows. Most mature formations have a predominantly round shape. The growth rate of such polyps can be different and depends on a number of factors. Many doctors believe that the maturation of formations accelerates living in adverse environmental conditions.
Contaminated air a large industrial city has a pronounced damaging effect on the epithelium of the nasal passages, leading to increased growth of polypous tissue. Decreased local immunity also has a significant catalyzing effect on the growth of polyps in the nasal cavity. Children at an early age, with an imperfect immune system, are susceptible to polyposis much more than adults.
The proliferation of polypous tissue can be not only in the nasal passages. Such a tendency to neoplasms can lead to the fact that the body begins a massive growth of various polyposis formations. They can appear in the esophagus, uterus, genitals.
The growth and proliferation of polyps significantly depend on the effects of certain hormones. Many doctors note that during pubertal development in a teenage girl, the formation of polypous tissue may increase.
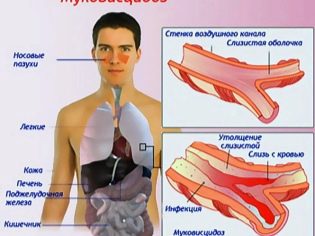
These tumors can develop at almost any age. Pediatricians and pediatric otolaryngologists note that polyps in the nose are more common in 10-year-old children. In some cases, the massive proliferation of polypous tissue indicates the manifestation of a very dangerous disease in a child - cystic fibrosis. This disease is quite rare, but is accompanied by the appearance of numerous adverse symptoms.
Many fathers and mothers mistakenly believe that polyps are malignant tumors. It's not like that at all. Nasal polyps have an extremely favorable course and almost never turn into malignant forms.
The treatment carried out in time is a guarantee of successful recovery of the baby and preservation of excellent nasal breathing indicators.
In some cases, there is a familial predisposition to the appearance of various polyps in the nasal passages. In this situation, the collection of anamnesis plays an essential role in the formulation of a correct diagnosis. The presence of polyps in childhood in any of the parents has a significant impact.
To date, doctors have not come to a common opinion about what the reason contributes to the development of multiple polyps in the nasal passages in a child. There are several versions that include:
- Bronchial asthma. The presence of a baby of this disease is the cause of respiratory failure.Oxygen starvation of the respiratory tract tissues leads to the proliferation of the epithelial lining, which ultimately contributes to the growth of multiple polyps.
- Allergic pathology. The entry of allergens into the children's organism, which has an individual predisposition, contributes to the disruption of the functioning of the upper respiratory tract. Especially dangerous in this case is contact with the provoking allergenic component during respiration. Allergy to the flowering of various meadow grasses and trees is a fairly common cause of the development in the child in the future of various polyps in the nasal passages.
- Cystic fibrosis. Genetic pathology, which is accompanied by the appearance of multiple adverse symptoms, including the growth of mucous membranes. This disease is associated with excessive formation of thick secretion - mucus. Its accumulation leads to a violation of nasal breathing, which ultimately can lead to the pathological proliferation of epithelial tissue of the nasal passages.
- Frequent inflammation in the sinuses. Chronic or prolonged sinusitis or sinusitis is a common cause of abnormal tissue growth. Improperly chosen treatment also contributes to the appearance of various polypous formations in the nasal passages of the baby.
As they grow, such elements go through a series of successive stages. The initial is characterized by the growth of polyps only in the upper part of the nasal septum. In the second stage, a moderate increase in connective tissue occurs, which is already manifested by a significant overlap of the lumen of the nasal passages and deterioration of respiration. The third stage is characterized by massive proliferation of polyps over the entire area of the nasal passages.
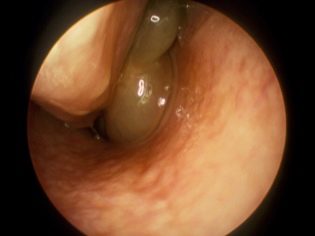
Polypous growths can be not only of different sizes and shapes, they differ in color. They may be gray, yellow brown or red. This feature is very individual and manifests itself in each child in its own way. In most cases, the growing formations in the nasal cavity have a shape that resembles in appearance a flowing drop.
The proliferation of polypous tissue can be not only within the nasal passages, in some cases, it moves to the paranasal sinuses.
Symptoms
Polyps in the nose can manifest in children in different ways. The severity of clinical manifestations depends on a variety of initial factors, as well as the stage of growth of these formations in a baby. Children at an earlier age tend to have more significant nasal breathing problems than adolescents.
Massive formations in the nasal cavity are accompanied by the development of the following symptoms:
- Severe congestion. This symptom can develop in a baby at any time of the day. The growth of formations contributes to the growth of congestion. The use of standard vasoconstrictor drops to eliminate this symptom usually does not bring significant effect.
- Rising cold. Usually accompanied by the release of a small amount of mucous discharge. When attaching a secondary bacterial infection, discharge from the nasal cavity becomes yellow or greenish, thick in consistency.
- Disturbance of smell. In severe situations, anosmia may even occur - a condition in which the perception of odors is impossible. In many cases, impaired sense of smell can cause a loss of appetite in a sick child.
- Itching around the eyes. This symptom is quite rare, but brings the child discomfort.
- Sensation of pressure in the projection of the paranasal sinuses. The child begins to feel a strong distention, which also leads to a violation of nasal breathing.
- Increase in shortness of breath. This symptom appears, as a rule, at the third stage of development of polyps. Severe dyspnea occurs mainly in babies with concomitant respiratory diseases.
Some experts note that babies with polyps in the nasal passages, more susceptible to the development of allergic reactions to various allergens, penetrating the body in an airborne manner. Such babies are also very susceptible to different smells and the effects of chemicals that irritate the epithelial cells of the nose.
Children's otolaryngologists have long established that in babies with polyps, the risk of developing chronic diseases of the paranasal sinuses increases several times. In this case, the course of the disease is usually chronic. In some cases, babies suffering from nasal polyposis have a high propensity to develop drug allergies.
The initial manifestations of this pathological condition are in many ways similar to the symptoms of a cold. The marked difference, as a rule, is that with the polyposis of the nasal passages the body temperature does not rise, there are no symptoms of intoxication. The appearance of severe nasal congestion in the event of the appearance of polyps is largely due to changes in the anatomical architecture of the elements of the nasal cavity. Expanding, polypous formations severely squeezing the blood vessels, which leads to the appearance of severe congestion.
Disturbance of smell in polyposis can either be transient or persist for quite a long time. With a protracted course of the disease, this symptom may become persistent. In some cases, even a surgical intervention cannot be restored to the sick child’s normal perception of various smells.
Too large polyps can even cause speech disorders in the baby.
The strong proliferation of polypous tissue contributes to the compression of the openings of the auditory tubes. Such an anatomical disorder leads to the fact that the baby's voice is changing and becoming more deaf and rude. In some babies this helps reduce hearing.
In small babies, large polyps can also be detected independently. Abundant proliferation of polypous tissue contributes to some changes in appearance. The sick baby usually opens the mouth, and the nasolabial folds are strongly smoothed. Obstructed nasal breathing leads to the fact that the child is actively breathing through the mouth. If the baby’s polyps appeared at a very early age, this also contributes to the change in the shape of the nose.
Violation of oxygen supply due to impaired nasal breathing leads to the fact that over time the baby appear symptoms of tissue hypoxia. This condition is manifested, as a rule, by an increase in headache. In the first stages of the disease, it is expressed slightly, and then gradually increases.
Diagnostics
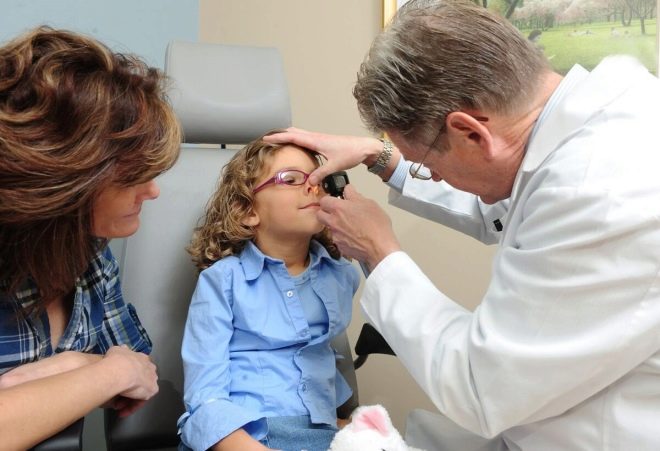
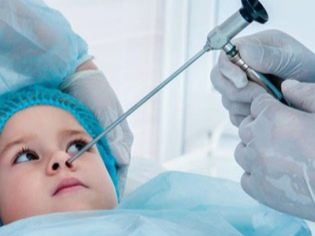
If parents suspect the symptoms of polyposis in their child, then they should contact the infant otolaryngologist with the baby. An extended clinical examination is required to determine the correct diagnosis. During this study, the doctor carefully examines the nasal cavity and other organs with a special tool. In difficult clinical situations, additional examinations may also be required.
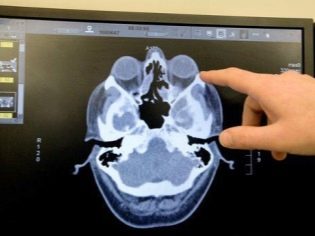
Polypous formations that grow in the area of entry into the nasal passages, the easiest to diagnose. If they are located more deeply, then in these cases additional instrumental examinations are required. One of such tests is computed or magnetic resonance imaging. This study provides fairly accurate results.
Conducting computer and magnetic resonance imaging allows for the necessary differential diagnosis. One of the basic diagnostic tests is radiography. This method can not be used for young children - because of the relatively high radiation exposure. Radiography also reveals polyps that grow in the area of the paranasal sinuses.
Treatment
Polyps can be treated with medication and surgery. To normalize nasal breathing, doctors use mainly antihistamines and hormones. They are appointed mainly by courses and lead to the achievement of a good therapeutic effect. Usually these tools are used in the form of a nasal spray. For such treatment, drugs based on budesonide, fluticasone, triamcinolone, etc. are used.
If the treatment with hormones has not led to a positive effect, then surgical therapy is carried out.
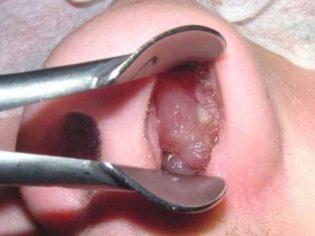
Polypectomy is a method for removing polyps and improving nasal breathing. To carry out the excision of formations, you can use a surgical instrument or a laser. Polyposis treatment can be performed using endoscopic therapy.
For information on how polyps appear in the nose and how to treat them, see the next video.