Graphs of height, weight and other important indicators of child development according to WHO
One of the most accurate ways to control the development and health of a child in the first years of life is to measure the physical parameters of a baby. The most significant indicators include the weight of the child, his height, as well as the circumference of the head and chest.
As a result of the work of the World Health Organization (WHO), various standards have been developed, which in most countries are taken by doctors as reference. One of them are the rules relating to the growth and development of children of different ages.
WHO is the organization that controls health issues in all parts of our planet. It was created by the UN to address the health problems of the population of the Earth.
Based on what data tables and graphs are built?
Until 1997, WHO standards simply fixed child growth parameters. At the same time, most tables were created on the basis of statistics on artificial-fed children. Now all the norms have been revised and they are based on indicators of breastfed babies. The norms show how children should grow and also help determine if an intervention is needed that can improve a child’s growth and healthy development.
The development of the norms currently in force was carried out in the interests of the health of children from different countries of the world. Comparison of the physical development of the child with these norms helps health workers in time to identify excessive or insufficient weight gain and other indicators.
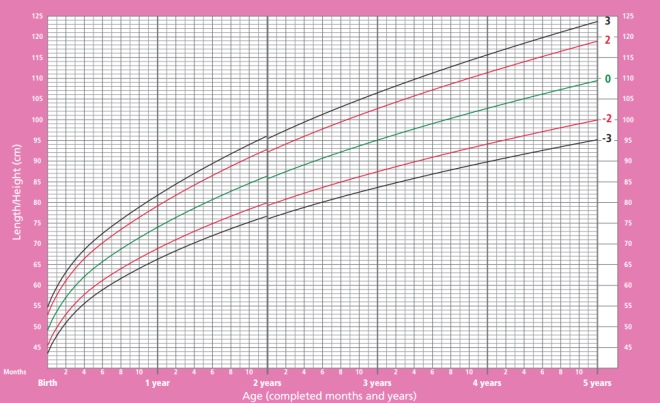
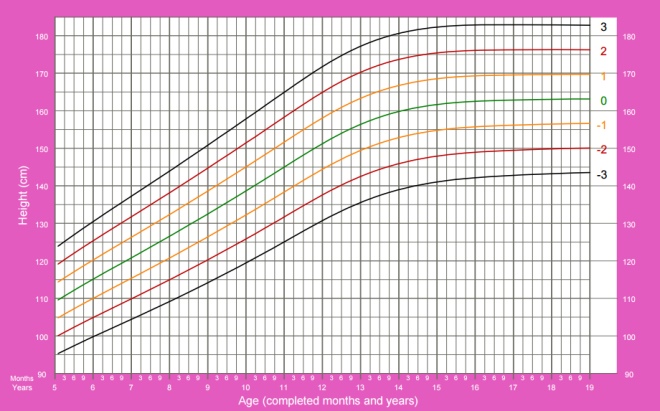
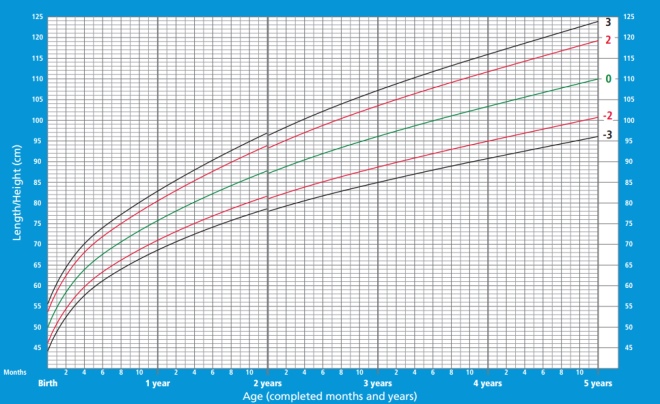
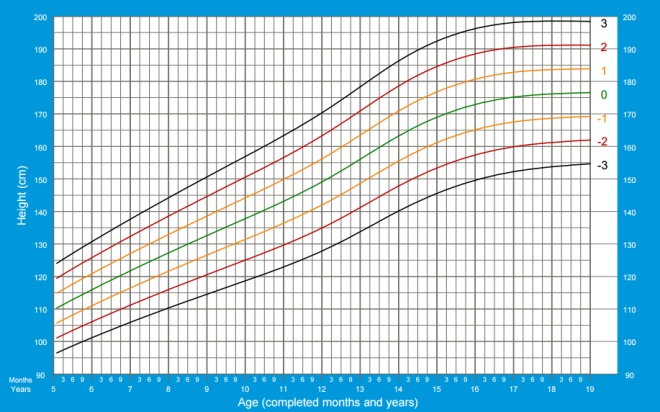
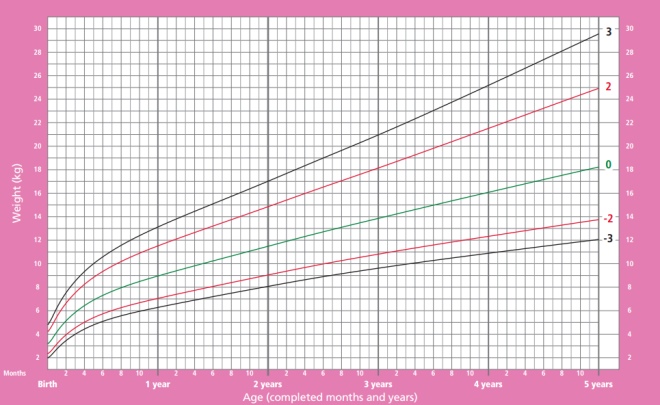
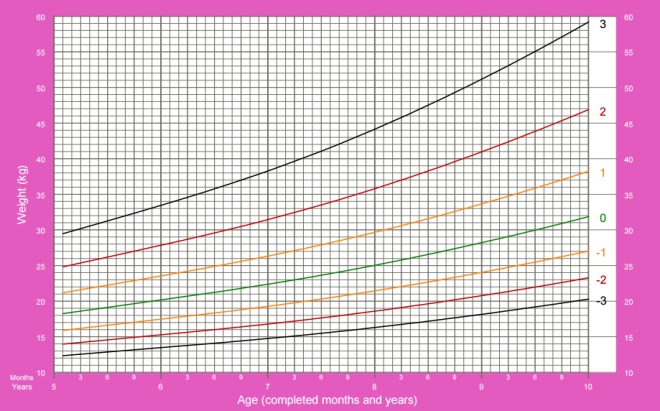
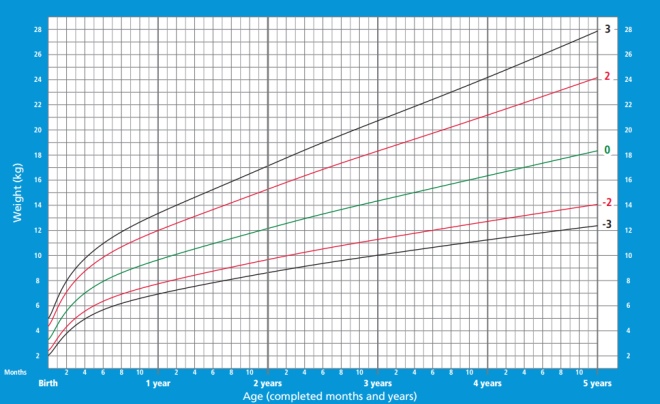
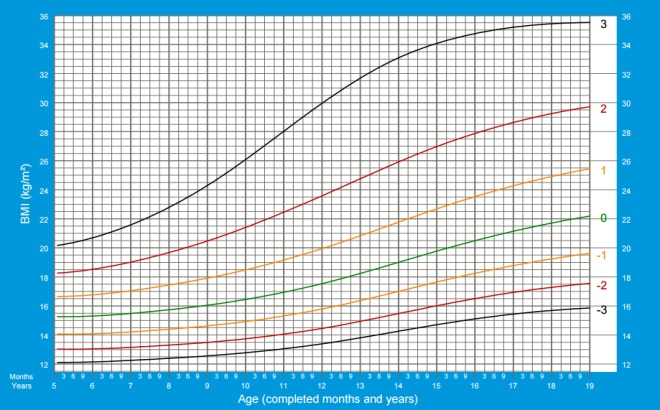
In the graphs below, horizontally (X axis), look for the child’s age, and vertically (Y axis), the indicator under consideration.
- The green line on the graphs can be called the golden mean, this indicator is typical of most children and is considered optimal.
- Black lines - the boundaries of the normal set of the indicator, but approaching it should not be disturbed.
- If the weight goes beyond the black lines, you should consult with experts.
The graphs increase when you click on the image.
Norms and measurements
Growth
Measurement of the body length of an infant is carried out with a tape. The kid is placed on the table or bed so that his head rests on the side. Straightening the legs of the crumbs, mark the line under the heels and measure the distance from the side to this line. The growth of an older child is determined using a height meter.
Height of girls from birth to 5 years:
Height of girls from 5 to 19 years:
The growth of boys from birth to birth to 5 years:
Height boys from 5 to 19 years:
Weight
Weighing newborns and children up to one year is carried out on special children's scales. For authenticity, the child should be stripped, and the weight of the diaper, which lies on the scales, is taken away from the resulting indicator.
Girls' weight from birth to 5 years:
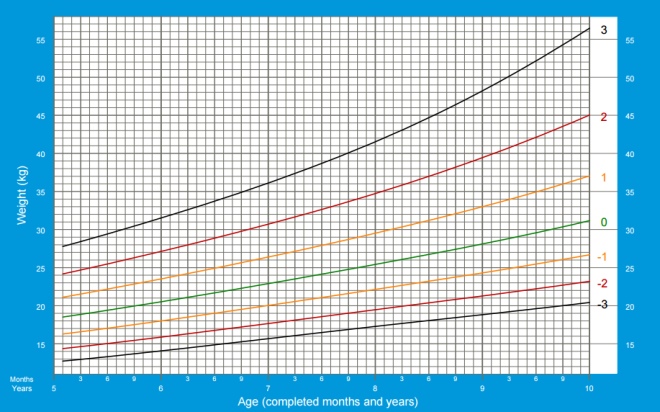
Weight of girls from 5 to 10 years:
Boys weight from birth to 5 years:
Boys weight from 5 to 10 years:
Head circumference
To measure using a measuring tape with a length of 150 cm, on which there are divisions in millimeters. In front of the tape (its zero division) is applied on the most convex part of the forehead above the eyebrows.After that, it should be wrapped around the head, starting from the right temporal region. Further behind it should touch the back of the head, move to the left temporal region and return to the forehead area.
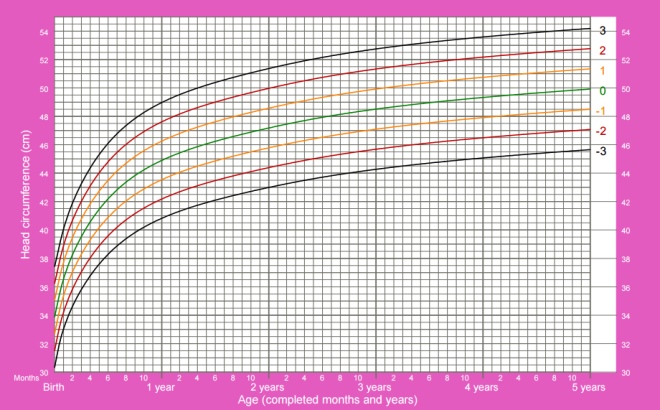
Head circumference of girls from birth to 5 years:
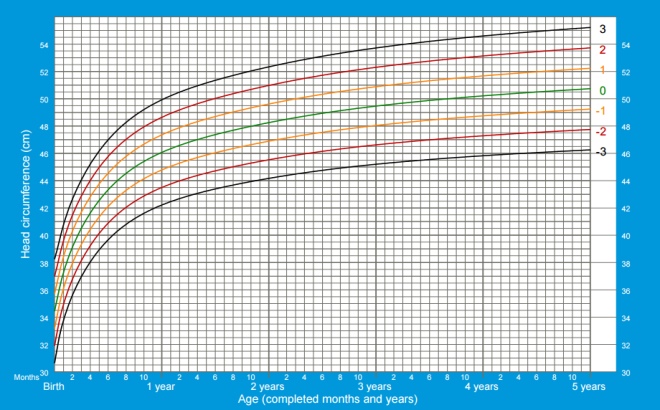
Head circumference boys from birth to 5 years:
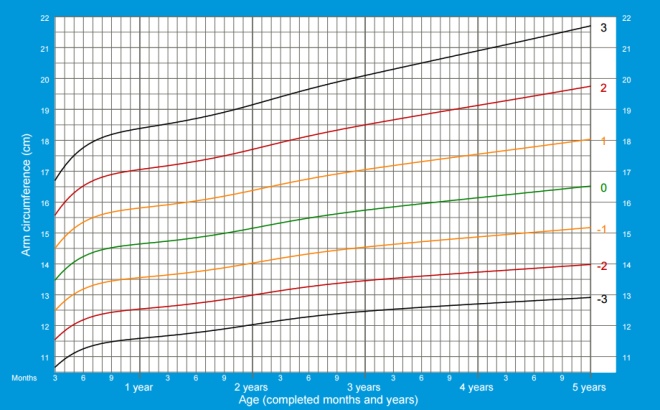
Shoulder circumference
This parameter is determined using a rubberized measuring tape, the length of which is 1.5 meters. On such a tape for measuring accuracy there are millimeter divisions. The shoulder is measured in two states - relaxed and as tense as possible. First, determine the circumference of the shoulder on the right hand down, imposing a tape on the thickest part of the biceps muscle. Then the arm should be bent in the elbow and the muscles as tight as possible, and then repeat the measurement. The difference between the obtained data will tell the degree of muscle development.
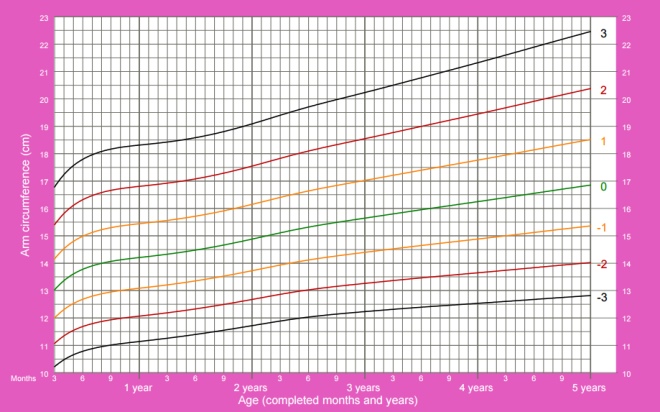
The circumference of the shoulder in girls from 3 months to 5 years:
The circumference of the shoulder in boys from 3 months to 5 years:
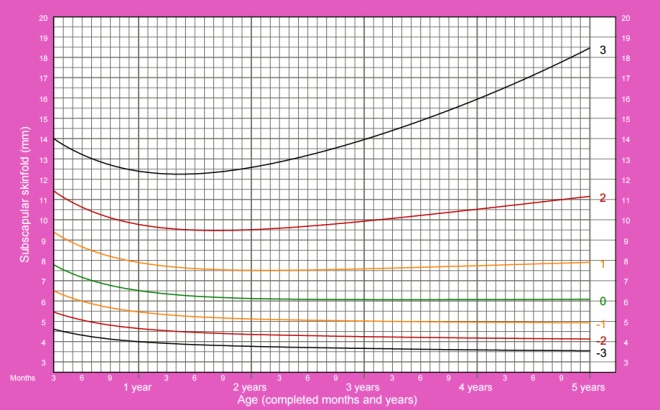
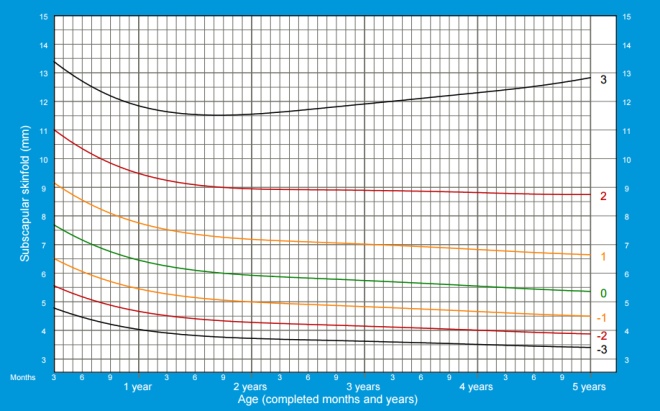
The thickness of the skin fold under the scapula
Measurement of this parameter is used to determine the percentage of body fat. Since a special device caliper is used for measuring, the determination of the thickness of the fold is also called caliperometry. Pinch the skin slightly below any scapula so that the resulting fold passes at 45 ° to the vertical line. In this case, the fold should be directed down from the spine to the side of the body.
The thickness of the skin fold under the scapula in girls from 3 months to 5 years:
The thickness of the skin fold under the scapula in boys from 3 months to 5 years:
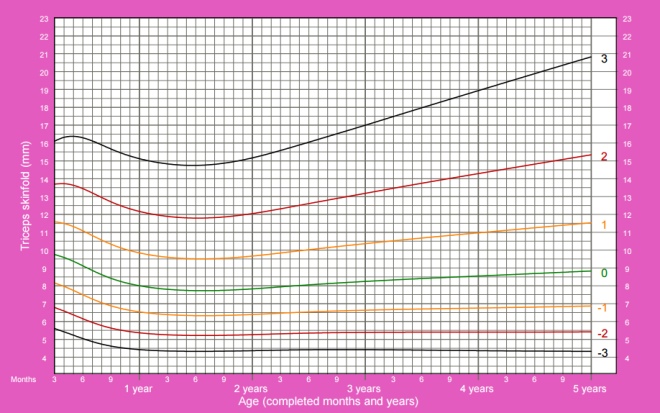
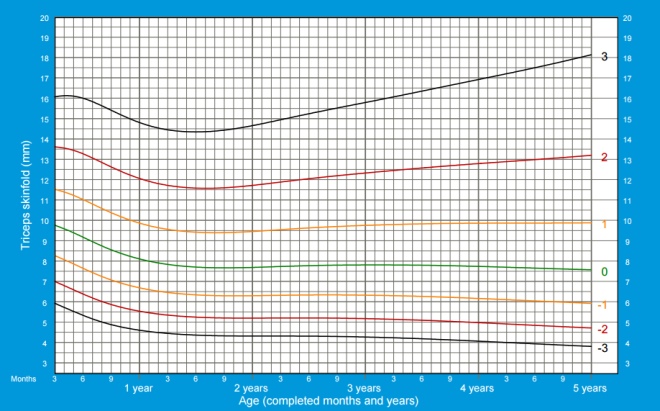
The thickness of the skin fold above the triceps
The thickness of the skin fold above the triceps characterizes the percentage of body fat.
To measure the child must give up. At the midpoint between the acromion process of the scapula and the elbow bone of the ulna, the skin is dragged off by holding the tissue between the thumb and index finger. The caliper is placed in the middle of the distance between the beginning and the end of the skin fold. The skin is not released, and after 2 seconds, the thickness of the fold is measured with an accuracy of half a millimeter. Measurements are usually carried out 3-4 times, and then calculate the average value (indicators should not differ by more than 1 mm.)
The thickness of the skin fold over the triceps in girls from 3 months to 5 years:
The thickness of the skin fold over the triceps in boys from 3 months to 5 years:
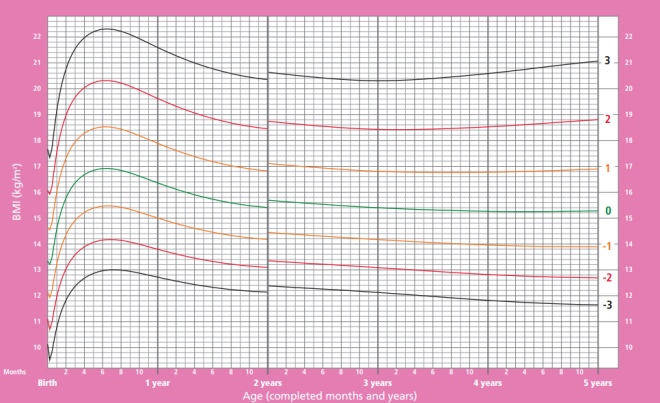
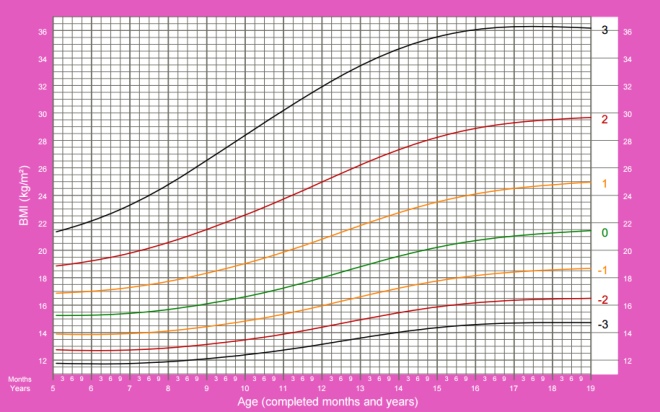
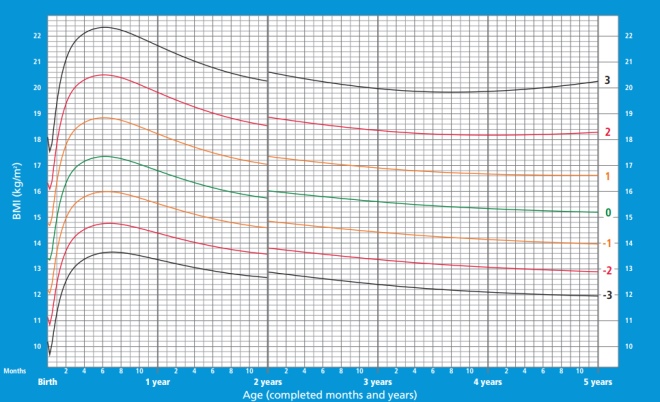
How is body mass index (BMI) calculated and what does it show?
The body mass index helps to assess whether a person’s weight corresponds to his height, which determines whether his weight is normal, excessive, or insufficient.
To determine this indicator, the weight in kilograms is divided by the height in meters, taken in a square.
BMI of girls from birth to 5 years:
BMI of girls from 5 to 19 years:
BMI of boys from birth to 5 years:
BMI of boys from 5 to 19 years:
Is there a relationship between the norms and the type of feeding of the child?
The WHO standards that are currently in force are designed to take breastfeeding into account, as this organization is now following a strategy to support breastfeeding and adequate complementary feeding. If earlier the standards did not take into account the peculiarities of the rapid growth of babies of the first 6 months who received exclusively breast milk, now the reference indicators have been changed taking into account the fact that in babies there is no excess weight
Breastfed babies are currently considered to be the WHO standard of normal child development in natural conditions. The organization recommends breastfeeding babies under 6 months only, and after half a year to ensure children receive safe and adequate nutritional supplements, while continuing to breastfeed until 2 years of age or longer.
You can watch a presentation on promoting one of the WHO breastfeeding initiatives in the next video.
Should standards be taken literally?
The weight and height of an infant are affected by various factors, among which the most important are the type and frequency of feeding, problems with the mother’s milk or allergic reactions to the mixture, prematurity, heredity, environmental factors and various diseases.
If the indicators are moderately different from the norm in any direction, it is not dangerous, but it can affect the health of the child, for example, the baby will recover longer than babies with normal weight. With strong deviations, both parents and physicians should direct their efforts to identifying their causes.
WHO notes that more than half of deaths at an early age are associated with a significant deviation of the child’s body weight from normal values. As for large deviations in growth rates, they threaten problems with the musculoskeletal system of the child.
Statistics show that approximately 3% of children with severe deviations from the norms do not get sick and are completely healthy. However, it is impossible to be sure that a child with indicators that do not fit in the norm belongs to these 3%, since the consequences often manifest themselves after a few years. Therefore, any abnormalities in body weight and height should attract the attention of the doctor.
How do norms help WHO deal with child nutritional disorders?
The statistics that WHO constantly collects show that every year several million children die from malnutrition, and at least 20 million children around the world are overweight. Also, these organizations confirm that malnutrition is the most common cause of death and health disorders of infants.
The norms developed by WHO allow to evaluate the nutrition of children and to control it, which is especially important in infancy and early age. Assessing the performance of a certain contingent of children and comparing them with the standards, determine trends and health risks. This applies to both malnutrition and excess.
In the next WHO video, you can learn 5 key principles of safe nutrition.