What is episiotomy and why is it sometimes used in childbirth?
Predicting what the process of childbirth for a specific woman in labor will be is impossible in principle. Despite all the achievements of medicine, the preliminary assessment of risk factors, some processes during childbirth are subject exclusively to the forces of nature. The doctor and the woman in labor has nothing left but to accept it. There are many ways to help the baby be born if the birth is difficult. One of them is episiotomy. In this article we will tell you what it is, how it is carried out and what consequences such an operation may have.
Special features
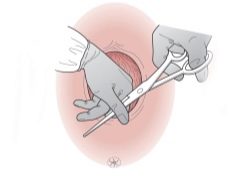
Episiotomy is one of the most common in obstetrics small operations. Its name comes from the Greek word "epision", which means "female external genitalia." The second part of the word means "dissection." In essence, this is the principle of this surgical intervention.
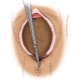
Episiotomy - perineal incision. At such a measure, obstetricians go when there is a big risk that a spontaneous rupture of the perineum will occur at the birth of a baby.
This measure is necessary and necessary. It helps to prevent serious consequences not only for women's health, but also for the health of the baby. A timely dissection of the perineum reduces the likelihood of a child having a severe cranial or traumatic brain injury during birth.
Dissection is performed during the second stage of labor, during attempts, the birth of the fetus. Anatomically, the female perineum is arranged in such a way that it is possible to surgically expand it if the passage of the baby’s head is very difficult. If an incision is made in time, then it will be possible to avoid a rupture, which is more difficult to heal, which can lead to unpleasant consequences - the prolapse of the pelvic organs, their prolapse, as well as heavy bleeding, which will be very difficult to handle.
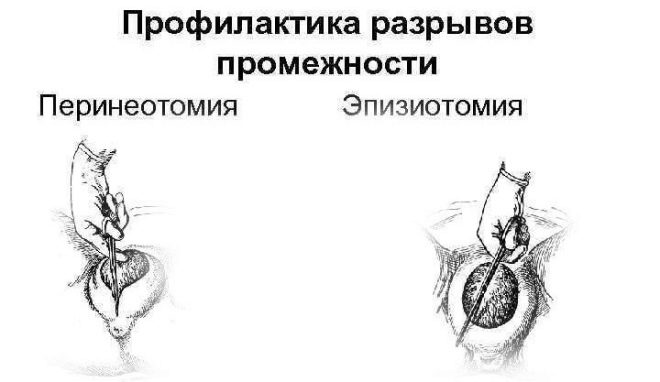
The medicine knows four types of episiotomy:
- mid-lateral (an incision is made with surgical scissors from the middle to the right or left side diagonally so that the end point of the incision is no closer than two and a half centimeters from the anus;
- perineotomy, which is also called median episiotomy (dissection runs perpendicular to the anus from top to bottom, not leading to the anus itself);
- lateral (incision at an angle of 45 degrees a couple of centimeters away from the center of the labia);
- J shaped (start to cut from the center of the labia of the labia with the transition to the lateral direction).
The location of the nerves, blood vessels, and some glands in the perineum, as well as the speed and characteristics of the healing of incisions after delivery, made wider the use of the first two types of perineal dissection.
Lateral episiotomy is considered undesirable because of the long and difficult healing of the sutures, J-shaped is also used very rarely, since, for all its complexity, it is not considered justifiable and can be easily replaced with median-lateral or median episiotomy.
Application history
In the history of different nations and countries there are references to the dissection of the perineum in women during difficult and prolonged labor.In ancient China, a hot piece of iron was used for this, in some tribes of Australia - thin and sharp shells and stones with pointed edges.
This tradition has reached modern medicine. In various countries for a long time dissection of the perineum was considered a normal practice and it was carried out not only with evidence, but also just so, just in case, to speed up the birth.
Since 1960, most European doctors have decided to abandon this approach, and only Poland, the United States, Australia and Bulgaria have decided to maintain their loyalty to the episiotomy. The proportion of fanaticism with which obstetricians cut perineal women there is different - in the USA, according to statistics, up to 36% of pregnant women undergo surgery, and in Australian clinics with dissection of the perineum up to 90% of all births occur.
Episiotomy by doctors all over the world is recognized as a rather effective way to avoid perineal tears, eliminate severe pain when receiving spontaneous breaks in different directions, prevent postpartum urinary incontinence, and sexual dysfunction. At the same time, it is the surgical incision of the perineum that can itself cause all these problems. The attitude to the operation today due to this fact is very, very ambiguous.
In 2010, WHO conducted a study and concluded that the absence of incisions, even if the delivery is slow, is more preferable, because a woman without seams on the perineum recovers faster, less risk of complications.
Direct recommendations to ban episiotomy has not yet sounded, but The World Health Organization recommends abandoning planned episiotomy, limited to only emergency cuts in situations where there is simply no other way out.
Who do you spend?
According to the clinical guidelines of the Ministry of Health of Russia, episiotomy is not recommended for routine use. This means that a doctor cannot, at her own discretion, cut a woman's crotch without testimony. Even if the woman had previously had tears in the perineum, her dissection should not be planned.
The indications for incision of the female perineum in labor today are significantly limited by the World Health Organization, the Ministry of Health of Russia fully supports the restrictions. This is stated in the clinical guidelines set out in a letter dated May 6, 2014 N 15-4 / 10 / 2-3185. These recommendations are fundamental for all physicians who take birth.
Surgical intervention is carried out in the case when you need to minimize the probability of spontaneous rupture during pathological childbirth.
Such indications include a large fetus, the diameter of the head of which does not correspond to the carrying capacity of the vagina, pelvic or other incorrect presentation of the fetus, if the woman categorically refused a caesarean section and insisted on independent physiological labor.
Also, an episiotomy is performed when necessary to apply the tools - to put obstetric forceps or a vacuum extractor, which is impossible if you do not expand the entrance to the vagina by artificial means.
Dissection is recommended if a woman has poorly healed scars on her genitals, resulting from severe ruptures in previous births, as well as after performing a surgical repair of the vagina or female circumcision (and this happens in obstetric practice). If the scars are thin and heterogeneous, the risk of rupture over them increases tenfold.
Not so long ago, the dissection was carried out according to such indications as a high crotch or rigidity. Today, the Ministry of Health recommends that such concepts not be considered indications for mandatory episiotomy.
Rigid perineum may need a cut only if the head is not born within an hour. And the concepts of "high risk of rupture" and "threat of rupture" in obstetrics does not exist at all.And because cutting the woman's crotch just because it seemed to the midwife that a rupture is likely is not worth it.
In practice, the list of indications is somewhat broader. Dissection of the perineum can hold women who are prohibited from long and hard to push, for example, with myopia. This is done to speed up labor with minimal effort. At the same time, there is a safer delivery option for the mother - cesarean section, one of the indications for which is myopia.
Dissection of the perineum is also carried out in the case of fetal oxygen starvation of the fetus, which is detected in the process of childbirth. In this case, the doctor needs to quickly make a decision - cut through the perineum or decide on an emergency cesarean section. It all depends on the condition of the baby.
Episiotomy is also used for dystocia of the shoulder of the child - when they are wider than the head. This does not solve the problem, but the obstetrician after the dissection gets more space for the necessary manipulations.
Technique of
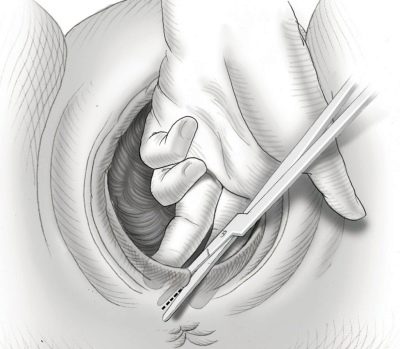
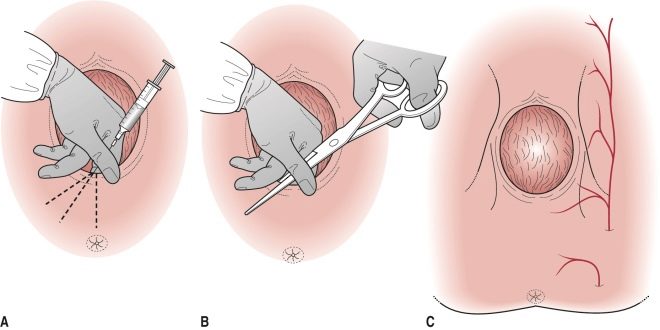
After the decision to conduct an episiotomy is taken, the perineum is treated with an antiseptic solution before dissection. A woman may have an epidural anesthesia if the catheter is already in the spinal canal, or local anesthesia with lidocaine. Often, dissection is performed without anesthesia. If the tissues of the perineum are strained, the woman will not feel acute pain when dissecting.
To perform the dissection is possible only in the case when the attempt is at the maximum stage of its development, and the head peeps out from the vagina by 3-4 centimeters. Outside attempts to dissect the perineum is impossible.
Surgical scissors are used for cutting. One branch of them is introduced in the direction of the intended incision, when the woman is calm and relaxed, outside the attempts. Then the obstetrician waits for the start of the contraction and at the peak of the attempts a quick movement makes an incision.
It is not possible to calculate the length of the incision to the millimeter, so the midwife makes it an arbitrary length. It is believed that an incision with a length of less than three centimeters is inefficient and dangerous - the perineum is not substantially widening, but a small incision may begin to spontaneously tear further.
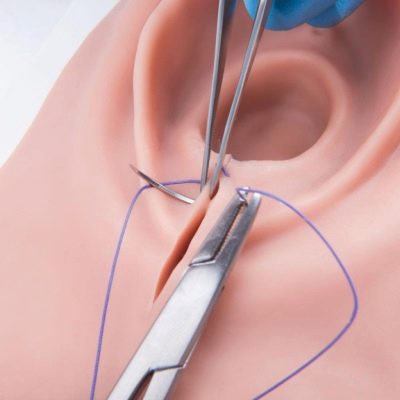
Epiziorrhaphy or perineorrhaphy is suturing the incision and restoring the integrity of the tissues. They are held after the baby is born, the afterbirth goes away and the cervix is examined by a doctor due to possible ruptures and injuries. If even the perineum was cut without anesthesia, it is common to infiltrate anesthesia before suturing — it is necessary to inject lidocaine or another analgesic directly into the tissue to be stitched.
The choice of material for suturing and the technique of seams affect the features of wound healing, regardless of how the perineum was cut. Suturing can be performed with silk surgical threads, which do not dissolve. They will need to be removed after healing.
This method (the technique of jester) involves the imposition of stitches resembling eights, passing through all layers of tissue. Such stitches are often inflamed and infected in the postpartum period.
Closure can be layered and gradual. First, restore the integrity of the posterior vaginal wall. Then sew the muscles. Submersible seams are made using self-absorbable material. Outside make a solid cosmetic seam. Upon completion, the perineum is again treated with an antiseptic solution.
Restoration and care tips
The place where the incision is made, in all respects, is not too convenient for him to be able to easily and simply carry out the necessary care in the postpartum period. After a cesarean section, the suture is isolated from the rest of the body area with a sterile dressing.Imposing such a crotch is not possible - a woman needs to go to the toilet, wash, you need to ensure the unobstructed discharge of postpartum discharge - lohii. All this does not imply dressings.
Lochia itself, which is released from the genital tract, is a desirable breeding ground for disease-causing bacteria. That is why there is a possibility of infection in the area of post-operative sutures and for the same reason Stitches require careful maintenance.
The perineum is often strained - when moving, walking, the urging of the urge during bowel movements, because the risk of seams divergence is quite high. If the puerperal does not comply with all recommendations of the doctor, complications can be very serious. The most common questions from women after an episiotomy require detailed and detailed answers.
How to sit?
After birth, in which doctors were forced to dissect the perineum, you can not sit, because it is likely to lead to a divergence of the seams. How much a ban on such a position will be in effect depends on how large the wound is sutured in the crotch area. Usually, women are not recommended to sit down for 2-2.5 weeks. If the cuts were deep and extended, the puerperal could theoretically sit down not earlier than 3-4 weeks later.
You can not sit down, but you can sit down with the support on the hip from the side opposite to the incision. If the episiotomy is performed in the direction to the left, you need to sit down with the support on the right thigh.
Eating, drinking tea and feeding the baby at this time is recommended either standing or lying on its side. There are no restrictions on weight lifting for women after physiological childbirth with an episiotomy, but still it is necessary to limit the weight of the child and not to strain without need. It is necessary to walk and stand with caution, to prevent an abrupt change in the position of the body, in which the muscles of the perineum will strain.
How long does the healing take? Seam care
The duration of the healing of sutures depends directly on how carefully and correctly they will be processed. If there were no complications in the early postpartum stage, there was no inflammation, accretion of the wound edges occurs within 5-6 days. If the seams were applied with the use of threads that do not dissolve on their own, it is decided to remove them after a week. If pathologies and complications of the suture are identified, the healing time may increase indefinitely.
In order to contribute to faster healing, a woman should remember a few simple but important rules for the care of the stitches:
bedding in the hospital, and then the pads need to be changed regularly - it is best every 2-3 hours;
after the end of bowel movement or urination, each time you need to gently wash the genitals in the bidet with warm water and immediately change the gasket;
you need to wash yourself with your palm in the direction from the pubis to the anus, and not vice versa (this will help to prevent the entry of intestinal bacteria into the wound area);
You can wash yourself with a weak solution of potassium permanganate (this will dry the area of the wound surface);
wipe the crotch with seams rubbing or sharp movements can not, it is better to use sanitary napkins and put them in a neat pro-wipe movements;
In the hospital, the stitches are treated every day with green paint, the midwife does it, but at home the woman can ask for help with the treatment of her husband or some of the close female relatives.
If severe problems with the appearance of stitches are detected in the maternity hospital, edema appears, signs of inflammation can be recommended by physiotherapy methods, such as laser therapy, exposure to ultrasound. To relieve pain, painkillers may be recommended for women.
Sometimes circumstances develop in such a way that a good suture, which does not cause doubts in the doctors at the maternity hospital, after discharge, unexpectedly disperses or becomes inflamed. The reason in most cases lies in the loss of vigilance by the puerperal. - on discharge, some of the excess happiness simply forget how to get into a car, as a result, the seams are damaged.
The road home must pass for a happy mom in the back seat of a car in a reclining condition with support on the thigh from the healthy side. This should not be forgotten.
Take a bath in the first month is not worth it. It should be limited to showers and scourers. If there is no bidet, then you need to wash with running water from a jug or ladle. It is prohibited to wash in the basin with standing water.
The rate of healing of stitches depends on hemostasis. therefore In the diet must be present products that have a positive effect on blood density. It is not recommended to eat bakery products, flour, fat and fried. Constipation should not be allowed, therefore, in case of difficulty in emptying the bowels, it is worth using enemas, microclysters or laxatives permitted for nursing mothers.
To make the scar more even, women are recommended to use special products, such as gel, a month after the episiotomy.Contractubex". It moderately affects the production of collagen and prevents the appearance of ugly and rough colloidal scar.
Mode of physical activity and sports
Every young mother wants to get in good shape as soon as possible after giving birth - to lose weight, get rid of the tummy, which does not immediately come to its former form. Therefore, the question of whether episiotomy affects sports is quite relevant for women in childbirth.
In general, the mode of physical activity of women who have undergone such surgery is not much different from the mode for ordinary puerperal women who did not have a perineal incision.
Two weeks after giving birth, it is allowed to perform a general strengthening exercises, which will include simple and calm exercises, without stretching the legs and squats. After two months you can do fitness, swimming, yoga.
Get rid of the abdomen will help postpartum bandage, which will gently support the abdominal muscles.
Possible complications and consequences
Do not forget that an episiotomy, for all its simplicity in execution, is still a surgical intervention, and therefore after it various complications are also not excluded.
Even in the generic process, the surgical incision may be aggravated by its subsequent spontaneous divergence, up to a finding of the fact that the perineal rupture is 3-4 degrees. In this case, not only ruptures of the skin, but also ruptures of muscle tissue, as well as injuries of the intestinal sphincter and intestinal wall can occur. In the most difficult situations, a vaginal-rectal fistula may occur.
The seal on the seam is considered quite alarming. We must seriously consider the situation when a bump appeared on it. This may be a manifestation of improper joining of the wound edges, complicated by the healing of individual layers with layer-by-layer healing.
A suture that heals for a long time, as a rule, has one or more complications. The following symptoms are considered dangerous:
suppuration in the area of suturing;
green, gray, brown or yellow discharge from the genital tract or from the postoperative suture area;
putrid or fishy smell;
increased pain;
asymmetrical arrangement of the genital lips in relation to each other;
swelling seam, redness, if they persist for a long time;
high fever, feeling of weakness, chills, dizziness;
any problems with urination - pain, difficulty urinating;
violation of the integrity of the seam.
The divergence of the seam is manifested by blood and blood discharge from the area of suturing. After removal of the remaining threads, if they were not self-absorbable, the unhealed wound areas heal independently, growing together by the method of secondary tension. Sometimes stitches are put on again if the first ones go apart, but only on condition that the healing did not take place on the most part of the wound.
If there is a suspicion of seam divergence, it is necessary to consult a gynecologist.
A wound can inflame due to contact with pathogenic or opportunistic bacteria that live in large numbers in the intestines and perineum. The idea of possible inflammation should be allowed, if for a long time the swelling and tenderness in the area of suturing do not disappear. The appearance of pus is a reliable sign of infection. Contact also need to see a doctor in the antenatal clinic. In this case, the wound in the perineum is washed, purulent contents are removed, and, if necessary, drainage is established. Treatment requires the use of antibacterial agents, which is not always combined with breastfeeding.
Asymmetric labia, lump on the rumen can be a manifestation of hematomas. If they are small, antibiotic treatment is also recommended, but if the hematomas are solid and deep, sometimes it is necessary to resort to surgical help to remove hematomas.
One of the most debated effects of episiotomy by women is dyspareunia. Under this term lies the pain that a woman may experience in the vagina during sexual relations. It is recommended that a woman refrain from sexual intercourse for up to one and a half months after delivery with a perineal incision. Then the relationship is not forbidden, but may not be too pleasant for the woman herself.
At least a woman and her partner cannot influence dyspareunia. Neither gels nor lubricants can significantly alleviate the discomfort. Correctly chosen poses will help to reduce them. After half a year, dyspareunia usually disappears.
Prevention
To avoid episiotomy during childbirth, a woman during pregnancy is recommended to perform exercises that increase the elasticity of the muscles of the perineum - Kegel exercises. A light external massage with any neutral oil can also help a woman - massages the genitals for 5 minutes a day. Blood supply improves, muscle elasticity increases.
In the process of childbirth, a woman should strictly follow the instructions of the obstetrician or doctor and push only when there is an appropriate command.
Slower passage of the baby through the birth canal reduces the risk of tears and the likely need for episiotomy. Proper breathing should be applied, it is taught in the courses of expectant mothers.
Reviews
According to women, it is quite difficult to work out the seam at home. It is especially difficult for women whose postpartum period has fallen on hot summer weather - the seam heals harder, requires constant "airing" and drying with green paint.
About a third of women complain of discomfort during sex. But they argue that the troubles are limited to a feeling of skin tension during frictions. Neither excitation nor orgasm has much effect on perineal dissection.
In the first weeks with seams in an intimate place, according to reviews, it is very scary to go to the toilet. Women are afraid of straining, resulting in constipation.
In general, women who underwent such an operation claim that the dissection is better than a gap, although recovery from an episiotomy requires restraint, patience, and strict adherence to all medical recommendations.
After watching the next video, you will learn more about episiotomy.