Why often fever after childbirth and what to do?
The birth of a child is a very pleasant event, but the woman's body in the process of childbirth undergoes severe overload, stress, and therefore the temperature rise after childbirth can be quite understandable. At the same time, it is precisely this symptom that can indicate that the puerperal woman has certain complications.
In this article we will try to understand the causes of fever after childbirth.
The reasons
Childbirth is always associated with pain and certain blood loss. In response, the woman's body activates the immune defense. A slight increase in temperature at the puerperal after the birth of the child into the world is the absolute norm. Physiological temperature, which should not cause anxiety and fear, should not be high and long.
Allowed is the temperature at 37.0-37.8 degrees for a day or two after childbirth.
Gradually, if there are no complications and the postpartum period proceeds normally, the immune defense adapts, the temperature drops to normal values. You only need to wait a bit - the early postpartum period lasts up to 42 hours.
A thermal defensive reaction can also manifest itself as a response to a complication. The risk of infection with natural childbirth is lower than with caesarean section, but it also exists. If bacteria or viruses have penetrated into the uterus, the increase in temperature will be the work of immunity, aimed at their destruction. In this case, the heat plays an important role, without it, the production of natural interferon will be slower, and therefore the body will be weaker against bacteria and viruses.
Complications of an infectious nature, inflammatory processes in the uterus in most cases are accompanied by high fever - up to 38.0-39.0 degrees.
The temperature may rise within 2-3 days after delivery. Simultaneously, there are abnormal discharge from the genitals, the woman feels pain in the uterus, in the lower abdomen.
To a greater degree of complications after childbirth, women who give birth at home are in suspicious clinics where some norms of sanitary requirements can be ignored. In the conditions of obstetric institution or perinatal center, the risk of infection is low - today, most of them use disposable instruments, antibiotics and antiseptics of the new generation.
At risk for the possible development of postpartum complications include:
- women with very low body mass;
- women in labor with HIV infection, the presence of tuberculosis, blood diseases;
- women who in the last trimester began to suffer from infectious lesions of the reproductive organs;
- women whose birth was hard and long, especially if the dry period (after the discharge of amniotic fluid) lasted more than 12 hours;
- Women in labor, faced with the need for any surgical procedures in the process of having a baby, even if it was just a perineal incision;
- women who, before the birth, led an inappropriate lifestyle - took alcohol, smoked, used narcotic substances.
The reasons for the increase in temperature can be not only infectious complications in the postpartum period, but also some other situations:
- cold or viral infection of the respiratory plan (it was cold in the delivery room, someone from the medical staff or the woman around her had an ARVI at the time of birth, but he did not know about it);
- problems with the balance of hormones (in the presence of the puerperal endocrine disorders).
The temperature may rise due to the exacerbation of a chronic disease, if the woman had it before pregnancy. Immunity weakens after childbirth, and therefore some "dormant" ills may well be felt again. With an increase in temperature in the postpartum period, pyelonephritis, nephritis, exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease, and cystitis can occur.
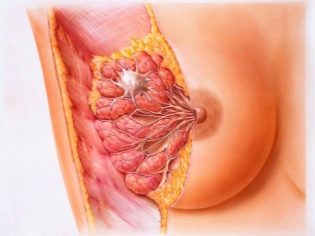
At 3-5 days after birth, the reason for the increase in temperature can be rapid processes occurring in the mammary glands and associated with the beginning of the active production of true breast milk after the transition.
Milk stasis in the glands, mastopathy is also accompanied by chest pain and high fever, which lasts until the problem is eliminated.
The reason for the increase in temperature may be incomplete discharge of the placenta. With a caesarean section, the doctor separates the "baby seat" manually, and before stitching the uterus, conducts a thorough revision. In a natural birth, it is almost impossible to see if the entire placenta has moved away. The remaining small fragments of it can lead to bleeding with a strong inflammatory process in the uterine cavity. Also, fever is accompanied by hypotonia of the uterus, in which the reproductive organ is poorly and too slowly reduced. In this case, there is an accumulation of lochia in the uterus - postpartum discharge.
If the temperature rose after discharge from the maternity hospital, a month after delivery, the reason should be sought in the woman’s lifestyle - she could get a viral infection, it is possible that the mother is not chronically allowed to sleep, she is tired. Even prolonged fatigue can be accompanied by fever and chills, and this is not unusual.
Features of measurement
After childbirth, it is no longer possible to measure body temperature with the traditional method - due to the proximity of the mammary glands, which begin the process of milk production, the reading of the thermometer in the armpit will be overestimated. They will not be true.
Therefore, it is recommended that a woman put a thermometer in the elbow bend, or use a thick towel, laying it between the filling breast and the axilla. Well, if the home first-aid kit has a contactless thermometer.
Woman's actions
Leave the fact of temperature increase after childbirth unnoticed, it is impossible to ignore it and underestimate. Given that violations of thermoregulation can be a sign of complications, be sure to talk about this with your doctor. Some women deliberately keep silent about the overestimated readings of thermometers on the bypass in the hospital. This is done so that the statement is not postponed to a later date.
Such actions are unacceptable, because the complication, if it arose, will still make itself felt. And then the woman after discharge will have to temporarily part with the baby and go to the hospital for help.
Almost all complications after childbirth require medical intervention and treatment. That is why in the first 42 hours after giving birth, women take the temperature in the obstetric institution three times a day, monitor its well-being and condition, and help with attaching the baby to the breast.
What should I tell my doctor? First of all, the temperature has risen. The specialist will be sure to carefully observe how long the increase will be. A brief, isolated case of fever after delivery is completely tolerated for immunological, natural reasons. Prolonged fever, even if the temperature is low enough - about 37.0 degrees, can be a dangerous symptom. That is why without a woman in labor she cannot understand this.
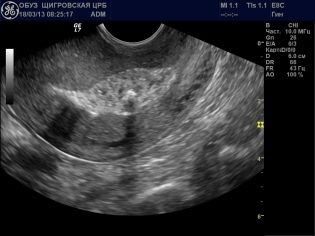
If the temperature rose in the early period before discharge, the woman will definitely take a blood test, an ultrasound scan will be performed to determine the cause of the heat.Ultrasound allows you to set the size of the uterus, the presence inside it of foreign inclusions (fragments of the afterbirth, for example).
What to do with the heat will depend on what causes this increase. If it is an inflammatory process, the woman will be prescribed treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs. Hypotonia of the uterus needs the use of reducing drugs that will intensify contractions. If there is stagnation of lochia or placental fragments in the uterus, obstetric cleaning is recommended. It is performed under intravenous anesthesia.
If during the stay in the maternity hospital the body did not present any surprises, and at home, after discharge, there was fever, chills, headache, you should pay attention to the associated symptoms. If a sore throat hurts, the woman most likely has a cold, if there is pain or pain during urination, there is a possibility of cystitis. Abdominal abdominal pain is considered the most dangerous pain.
When abdominal pain occurs in combination with temperature, and when abnormal discharge from the genital organs appears, you need to go to the hospital as soon as possible. Do not forget that acute inflammatory diseases of internal organs in the most advanced form can lead to the development of systemic sepsis.
In the medical examination and need the mammary glands against the background of increasing temperature. If, on the 5th day after the birth, the fever has risen and the chest is in pain, you need to see a doctor as soon as possible, because running mastitis may threaten the life of a woman. A woman may need surgery.
Immediately after birth, the temperature rises mainly for physiological reasons. After the end of the first rehabilitation period (42 hours), any temperature increase cannot be considered as physiological.
Is it possible to medication?
In most cases, as already mentioned, complications will require medication. But not all of them are combined with breastfeeding. If a woman needs, on the recommendation of a doctor, to stop breastfeeding for a while because of the heavy antibiotics that she needs, because of the necessary surgical intervention, then you shouldn’t leave to express your breasts, otherwise the milk will disappear completely or lactostasis will develop.
Modern effective antibiotics rarely require a course of treatment lasting more than 7 days. Most often they are prescribed for 5 days. That is why a woman will be able to return to breastfeeding after treatment.
If there is no need for antibiotics, a woman can be recommended anti-inflammatory, hormonal preparations, antipyretic drugs. Not all of them are allowed while breastfeeding. In each case, the doctor will proceed from the principle of least harm to the child and the maximum benefit for his mother.
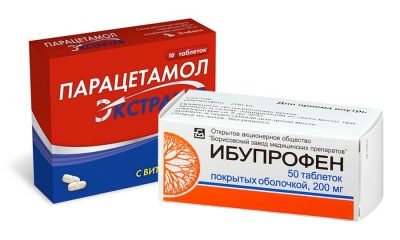
It is allowed to take Paracetamol and Ibuprofen from the temperature during lactation, although there has been heated debate in the professional environment regarding the latter drug recently. An international group of scientists said about the long-term adverse effects of the active substance - ibuprofen, on the human body. While these data have not received official confirmation.
Aspirin and analgin when penetrating into breast milk can pose a serious danger to the life and health of the baby. And because they are not recommended for breastfeeding.
Antipyretic powders with fruit flavors, which are now widely presented on the shelves of pharmacies, are also not recommended, because they contain a large number of dyes that are not shown to the nursing mother and her daze.
Folk methods
Given that most of the drugs are banned, many mothers try to follow the popular advice and recipes of traditional medicine. In the case of acne after childbirth, this is quite acceptable, but in the case of high or high temperature self-treatment is unacceptable.
Even if a woman has had a banal acute respiratory viral infection, rubbing vinegar and tea with honey will not be useful, after all, a pair of vinegar, and bee products can be a danger to infants.
But a woman can apply an abundant warm drink at a temperature - decoction of chamomile, tea with mint and melissa, apple juice will help reduce fever and strengthen immunity.
You can learn more about the temperature in nursing moms from the following video.