Application of vacuum during childbirth
At all times, the midwives and midwives were puzzled by the question of how to help the child to be born into the world, if the birth goes hard, hard and long. At first, the child was “squeezed out” by hand from the womb, then over the course of many decades, the application of obstetric forceps to the underlying part was applied. Then, in order to reduce the birth trauma of the mother and especially the fetus, they began to apply the so-called vacuum during childbirth.
About the method of vacuum extraction and will be discussed in this article.
About the method
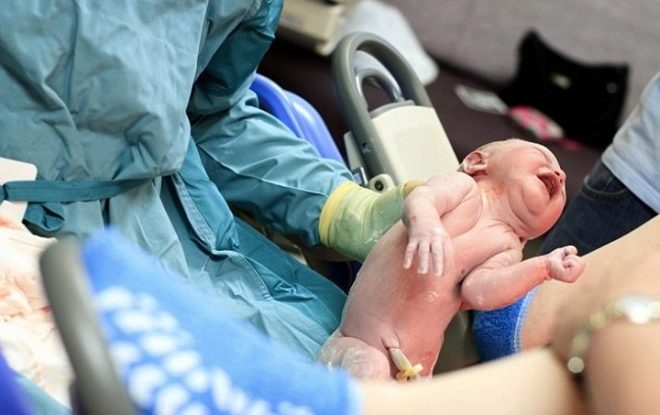
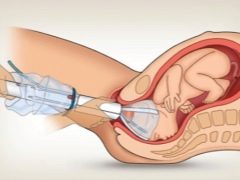
Since childbirth should be as safe as possible for a woman in labor and a baby, the issues of lesser trauma from using these or other methods of obstetric care today are considered one of the most important in obstetric practice. Vacuum extraction is a procedure for extracting a baby through physiological natural birth canal by imposing a special device on its head - a vacuum extractor. By creating a zone of reduced pressure, the fetus comes out faster and is born.
Extractors are used different - with a metal bowl on the head (Malstrem extractor), with a plastic bowl, which is safer for the fetus, and devices with soft bowls. Any of the listed devices consists of a bowl and a flexible hose connecting the bowl to the extractor-pump.
The frequency of application of vacuum in childbirth today is small - no more than 3-5% of all births.
And this is due to the fact that the diagnosis has become more perfect and that problems may arise with the birth of the baby's head, doctors often know in advance. In addition, the indications for cesarean section are expanded and sometimes it is much safer for the child to perform surgical deliveries.
In comparison with the forceps, which the head was captured earlier, the incidence of injuries of the skull and spine in babies during vacuum extraction was reduced. But until the end of the safe procedure is not considered, and therefore is mainly used only as an emergency.
Indications for use
All issues related to the use of vacuum extraction during labor are indicated by the letter of recommendation of the Ministry of Health of Russia No. 15-4 / 10 / 2-748 dated 07.19.12.
The document refers to the following states as direct indications for the application of vacuum:
- hypoxia of the fetus and other signs of extreme distress of the child in childbirth, negative symptoms are increasing;
- condition of acute hypoxia of the baby at the moment when his head is already at the exit from the small pelvis;
- the labor period of labor lasts too long (2 hours for the first time giving birth and one hour for giving birth again);
- pre-planned shortening of the second stage of labor, if attempts are not recommended for a woman to refuse a cesarean section;
- assistance in removing the head from the incision at caesarean section.
The procedure is carried out only by doctors who have similar experience of obstetric aid. A woman must give her written consent to such a manipulation.
The prerequisites for vacuum extraction are the opening of the membranes, the discharge of amniotic fluid and the head must be inserted into the pelvis. In natural childbirth, the cervix should be as wide as possible, and the bladder should be empty.
The Ministry of Health completely permits the delivery of labor using a vacuum without anesthesia, but quite often epidural anesthesia is allowed.
When not applied?
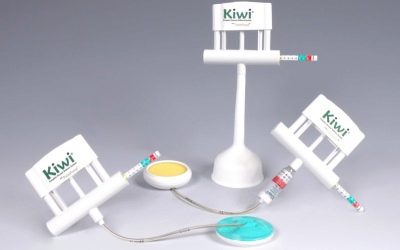
Vacuum deliveries (“kiwi” - according to the name of the extraction obstetric aid system) can be dangerous, and therefore the list of contraindications to manipulation is also indicated by the document of the Ministry of Health of Russia.
Do not apply vacuum if:
- childbirth began early, before 36 weeks of gestation;
- if the estimated mass of the fetus is less than 2.5 kilograms;
- the skin of the baby’s head is damaged in the place where the extractor bowl is to be applied;
- there is reason to believe that the child has an osteogenesis disorder;
- a child may have genetic pathologies of blood clotting (according to genetic forecasts);
- the head of the fetus is too high, and acute hypoxia has already begun - it is better to make a cesarean section;
- the woman has a clinically narrow pelvis, there is a clear discrepancy between the size of the baby’s head and the size of the pelvis;
- the child is in a facial or pelvic presentation;
- severe preeclampsia;
- preceding unsuccessful attempts to impose obstetric forceps.
The extractor is not used if the child has already died, if the cervix has not fully opened.
How is it done?
A woman is asked to take a half-sitting position on the generic table. She should bend the legs at the knees, support her legs against the stops, spread her hips. The disposable bowl of the extractor is checked for tightness, absence of defects and rejection. The doctor specifies the position of the fetal head. Then a decision is made about the need for episiotomy - dissection of the perineum for its expansion so that the extractor bowl can pass into the genital tract.
Dissection is not considered mandatory at all, but it is attempted to be carried out in all cases, if the extractor is to be introduced quickly, that is, in emergency cases.
The doctor inserts a cup into the vagina with the side to which she is to be attached to the head of the baby. Then it is installed on the head so that the arrow-shaped seam divides it exactly in half.
At the same time, the task of the doctor is not to allow the edge of the bowl to be closer than three centimeters from the large spring. Discharge is created in the Kiwi system. One hand of the doctor is at the exit of the pelvis and helps to "push", the other controls the translational movement.
All tractions performed by a doctor using a vacuum must be completely natural, consistent with the biomechanism of labor. It is believed that the procedure was successful if the head began to move forward after the first or second traction, if the movement of the baby was progressive and even, if he made all the necessary turns and extension of the head, as if he were born independently, without help.
It is believed that the manipulation is successful, if the number of tractions was from 2 to 6, the bowl did not slide off the head of the fetus more than two times, the procedure was completed in 15-20 minutes.
Complications and possible consequences
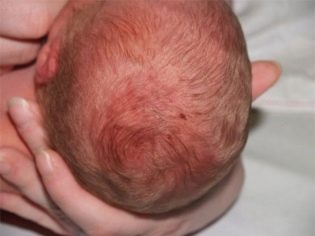
The birth of a child with the use of a vacuum can be dangerous for him and for the woman in labor if the doctor makes mistakes during the tractions, as well as during the imposition of the bowl. Most often, the baby remains a solid hematoma and abrasions on the soft tissues of the head. It can be not only a banal bruise, but also a cephalohematoma, as well as a subaponeurotic hematoma.
When cephalohematoma accumulation of blood is observed between the cranial bone and the periosteum detached from it.
If it is small, up to 3 centimeters, then it can dissolve on its own in the first weeks of a child’s life. In severe cefalohematoma, if it is more than eight centimeters, its opening and pumping of blood from the cavity is indicated. Forecasts are usually quite favorable, such a hematoma does not affect the development of the child, the functions of his body as a whole.
Subgillatory hematoma is less common, but it can be more dangerous. With her, blood accumulates between the aponeurosis and the periosteum. Predictions are less favorable.
The consequences for the child may be different. This and dystocia shoulders, and injuries of the cervical spine. A woman may have hematomas of the birth canal, tissue breaks, cervical injuries, and injury to the urethra.
The causes of complications are most often medical errors, the very “human factor” - inaccurate or initially incorrect establishment of the bowl on the baby’s head, improper removal of the fetus, violation of natural tractions, too strong traction, rocking movements during removal of the child.
Patient Reviews
Most women who have gone through the application of a vacuum in childbirth claim that there were no serious consequences for the child. But the presence of hematomas, including cephalhematoma, occurs in almost every baby. Most of them dissolve themselves over time and do not need treatment. Severe intracranial hemorrhage is reported infrequently.
The procedure itself, according to the women, is not too painful, for many it was applied against the background of the previously made epidural anesthesia. The use of a vacuum in childbirth usually does not affect the length of stay in the maternity hospital, and mother and baby are discharged in the absence of complications at the same time, that is, for 3 or 5 days.
For details on the indications and consequences of using a vacuum during childbirth, see the following video.