Training fights: symptoms and sensations during “false” contractions during pregnancy
Pregnancy is an amazing time when a woman becomes more sensitive to her feelings. Feelings can be very diverse, but today we will talk about those that cause the most questions - training (false) fights. From this material you will know how and why such a phenomenon occurs, how to distinguish such fights from true ones, how to behave during training fights.
A bit of theory - what is it?
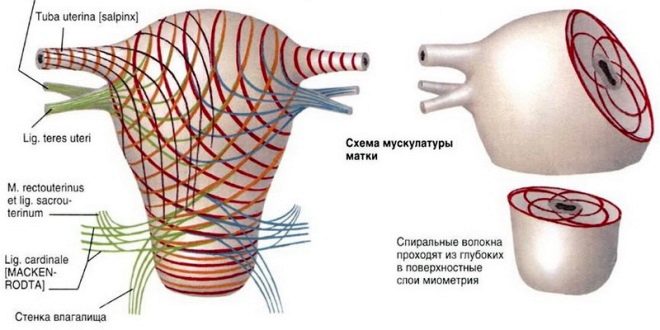
Contractions in a general sense are involuntary contractions of the smooth muscles of the uterus. In childbirth without labor, it would be impossible for a child to be born. Muscle contractions seem to push the fetus out of the womb when the time comes.
Training bouts are not related to labor they never lead to dilation of the cervix and the beginning of labor. They are called training because for a long time it was believed that it was precisely such short-term bouts of tension of the uterine muscles during pregnancy that the body of the expectant mother was preparing for a real workload during childbirth.
The question of why false (they are training) fights still appear is still open and very controversial. If we adopt the theory of training activity, it becomes not entirely clear how women give birth, who have not had a single training fight for the entire term of their baby. Believe me, there are a lot of such women, and they give birth without features, just like women, who during the whole pregnancy felt false contractions.
It turns out that training uterine muscles and does not matter so much for subsequent genera.
Medicine is known for another theory of the occurrence of training fights (synonym - Braxton-Hicks contractions). It is believed that these sensations are "phantom", not real and they are associated with increased excitability of the uterus itself, because with the onset of pregnancy and the growth of this reproductive organ, the nerve endings begin to perceive certain neurosignals differently. As a result, the brain is "deceived" and leads to the readiness of the musculature of the uterus (there is a feeling of tone). If this is not childbirth, then rather quickly the brain “adds two plus two" and cancels the "order" of high alert. Thus, according to this theory, contractions are "tricks" of the nervous system of a pregnant woman.
Often women are asked who Braxton and Hicks are, who compiled the first description of strange contractions that do not lead to childbirth. In fact, this is one person - the English Dr. John Braxton-Hicks, who in the XIX century observed pregnant women and described a mysterious phenomenon. Since that time, his colleagues and followers have not advanced a single step towards establishing the truth - the nature of the occurrence of false contractions remains a great mystery.
Speaking of training bouts, a woman should clearly distinguish several of their types. Those that appear long before childbirth, called false, training. And those that start a couple of weeks before giving birth are preliminary bouts. They are also known as precursors.They, like the early false ones, do not lead to the opening of the neck and the beginning of the expulsion of the fetus from the womb, but they occur more often. It is precisely the preliminary contractions that can rightly be referred to as training ones, since it is just before the birth that the muscles and ligaments begin to relax under the influence of a special hormone - relaxin. It is his action that becomes the beginning of the preparatory period of all organs involved in childbirth.
Do I need to be afraid of training bouts? The answer to this question lies in the definition of the phenomenon. They do not lead to the opening of the cervix, do not stimulate and do not bring the day of birth closer, they do not affect the condition of the fetus. Therefore, it is not necessary to worry, the main thing is to know how to behave in case of false cramping activity, and also how to distinguish such contractions from real ones. About this and talk more.
When do they start?
The timing of the appearance of false contractions is another complex and controversial issue. Officially, in medical sources it is indicated that a woman can theoretically begin to experience Braxton-Hicks contractions after 20 weeks of gestation. In practice, these periods may well be different from the theory - for some, they start for up to 20 weeks, for some - only by week 30, and for some, only precursors occur, which begin a couple of weeks before the kid " will gather "in our world. There are women who generally do not feel any training stresses of the muscles of the uterus, and this, too, is completely normal.
Experienced obstetricians and gynecologists have long paid attention to a certain pattern in the appearance of Braxton-Hicks contractions on the number of previous births. So, in primipara women such sensations can appear much earlier. And multiparous usually such fights appear directly closer to the expected date of birth. This can be explained by the difference in the state of the smooth muscles of the woman who has given birth and who has never given birth. For those who have already given birth, smooth muscles are more elastic and stretched, the growth of the uterus and the intensive filling with its blood flow more “gently”, as usual.
The opinion that the early appearance of training fights increases the likelihood of premature birth does not correspond to reality. However, such sensations only look threatening at first glance, if you look at the phenomenon more closely, you can understand that the presence or absence of training activity of the uterine muscles does not affect the date of birth. Often, those who began to feel false contractions at week 20, prolong the pregnancy and give birth only after 42 weeks, and those who have not had such contractions go to the maternity hospital much earlier.
Symptoms and sensations
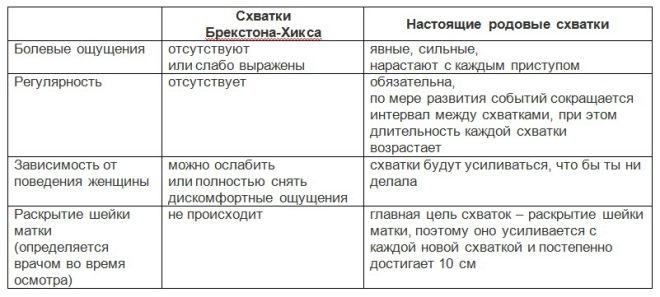
Many official medical sources authoritatively declare that the contractions are false or training - completely painless. In practice, and women's feedback is clear evidence, a lot depends on the individual degree of sensitivity. One pregnant, indeed, may not feel anything disturbing, but the other will be rather unpleasant.
Manifestation of tension muscles of the uterus. Many pregnant women describe that the "belly is stone", becomes more rigid. A pulling sensation may occur at the very bottom of the abdomen (due to the tension of the ligamentous apparatus that holds the uterus). A pulling sensation may appear in the lumbar region (for the same reason). Often women claim that sensations are very similar to how menstruation is felt.
There may be tension in the uterus for a few seconds or a few minutes. After that, it disappears and does not appear or appears, but not at certain cyclical intervals. Exactly that the training fights are irregular, and allows us to understand what is actually happening. Regular contractions are a sign of the onset of labor. Spontaneous episodes of toning - this is a false contractions.
Even if the fight repeats itself within an hour several more times, it will not become more tangible. Pain sensations intensify only with real, generic contractions, and with false ones, they always weaken, decrease.
The appearance of such a voltage can occur spontaneously at any time, even where it is completely inappropriate - at work, in transport, during an important meeting.
There are also circumstances that indirectly or directly increase the frequency of such false episodes.
- Active intimate life. With sexual arousal, with orgasm, there are small cuts in the smooth muscles of the uterus, so after intercourse for an hour or two, the appearance of Braxton-Hicks contractions is possible. This is not a reason to abandon intimate relationships, if the woman has no other contraindications.
- Most physical activity of the future mother. Slopes, weight lifting, walking upstairs, a rare rest, constant standing on your feet - all this can trigger the appearance of a false cramping activity of the muscles.
- Child's activity. Too active kids, who often and painfully "kick" the expectant mother from the inside, can also indirectly cause increased nervous excitability of the uterus.
- Stress. At the time of strong emotional experiences, a woman often feels the tension of the uterus, but most often false contractions "visit" expectant mothers after stress as soon as the woman relaxes a little.
- Crowded bladder. If the future mother does not have the opportunity to go to the toilet (she is in a public place where there is no toilet, she is traveling in transport), then the bladder filled with urine is strongly compressed by the uterus. But there is also a counter pressure on the uterus. This effect causes a short-term tension of the musculature of the reproductive organ.
There is also an individual pattern of the appearance of contractions and certain actions of a pregnant woman. For example, some false tensions of the uterus begin to manifest themselves after a woman gets out of bed in the morning and stretches, and in others only after women get up from a sitting position. At the third - after visiting a shower. Therefore, you need to carefully observe in what situation the Brexton-Hicks fights most often develop in you, in order to reduce such situations to a minimum or to be psychologically prepared for them.
During the years of observation of pregnant women, doctors noticed that training bouts most often occur in the mornings and evenings. After a hearty meal, the likelihood of uterine stress is higher than after a moderate dinner or breakfast. On average, the period of false hypertonus lasts from 15 minutes to 2-3 hours, but there are single contractions, as well as longer periods - all very individually, two identical symptoms are not found.
Differences from true
The question of how to distinguish training episodes of cramping activity from real labor contractions is asked very often, especially primiparous. A woman who has no experience of childbirth, is afraid to confuse, do not identify in time, do not recognize the real contractions and do not have time in time at the hospital. The question becomes especially relevant as the expected date of birth is approaching - at 38-39 weeks, as well as a little earlier and a little later. Believe me, it will not be so difficult to distinguish one from the other. When the real contractions come, they will not at all look like false ones. Here are the main differences.
- Pain sensations. If childbirth begins, each subsequent contraction is felt more painful than the previous one. This never happens with precursor or early training episodes of tone. The neck of true contractions is revealed, which is why the pain will get stronger.
- The duration of the fight. If it is a matter of training and preparing for childbirth, then each subsequent fight will not increase in time. You can not worry.If painful pains, and each next lasts a long time, not less than the previous one, it is a question of generic activity. You need to arm yourself with a stopwatch or a special counter program on a smartphone and just measure the duration of two or three consecutive episodes of uterine stress.
- Frequency. Preparatory contractions are not regular. They can be repeated at arbitrary time intervals, whereas the real ones will be very rhythmic (they will occur at regular intervals). At first - at long intervals, then the fight will be strong, long, and the episodes will be frequent. If periods of tension in the uterus become frequent and occur at regular intervals of time, it's time to go to the maternity hospital.
- Measures to reduce sensations. If a woman with a false fight just changes the position of the body, takes a shower, drinks a pill, then she will feel a noticeable relief. True pains cannot be anesthetized; they also will not react to the shower and change of body position. It is impossible to stop the generic activity.
In order to accurately distinguish the type of contractions, it is necessary to analyze other related signs. If cyclic tension of the uterine muscles occurred after the discharge of the mucus plug, after the discharge of water, or the discharge and discharge of amniotic fluid occurred after the appearance of contractions, then you can’t hesitate - childbirth began, so it will be better for everyone if the woman is under the supervision of a qualified medical staff.
Among obstetricians such a joke goes: "If you are not sure that you are giving birth, it means that you have not yet given birth." Think about it and calm down. When the time comes, the question of the differences in the types of uterine contractions will not stand.
Are Brexton Hicks contractions dangerous?
This question from time to time visits all women in an “interesting position” who feel such sensations. Future mummies who have threats of premature birth, pregnancy pathology are especially worried. Let us calm everyone down at the same time - Braxton-Hicks contractions pose no danger to either the mother or the fetus.
There is one theory (it is difficult to say how scientific it is, but doctors often say this to their worried patients), which says that the training scramble increases the blood supply to the reproductive organ, and as a result, after the muscles relax, the child gets more nutrients and oxygen, but because false labor can be written in the category of useful and productive.
If there is still a lot of time left before the birth, and training fights are often visited, for example, they are present all night, then you should still visit a doctor to find out the causes of hypertonicity of the uterus. Even if such contractions disappeared the next morning, consult your obstetrician-gynecologist. So everyone will be calmer.
How to behave during false fights?
If there are false contractions, the woman will have to accept them. Even if the stress of the uterus gives unpleasant sensations, then there are many ways to alleviate the condition and live with these training episodes to the most part, with relative comfort. What do we have to do?
- Change body position in space. If the training fight has begun, you need to try changing the position. If at that moment the woman was lying, it is better to stand up and walk, if you are sitting down - to lie down, and if you are standing down - to sit down or take a horizontal position. The “posture of the cat” helps well - the knee-elbow position with the backbone deflection. It is possible not to waste time in it and practice proper breathing, this is useful when the time comes to give birth.
- Do not mention it. If a false fight is fairly gentle and doesn’t bother you much, it’s best to ignore it - turn on your favorite movie, good music, open an unfinished book, or return to handicrafts set aside for later. This will help to distract.
- Walk. The advice is simple and effective.During a leisurely and sedate walk in a park or a public garden (away from the city roads), a pregnant woman and her baby get positive emotions and oxygen. Regular walks reduce the frequency and duration of false contractions several times.
- Water treatments. A warm shower helps to remove unpleasant symptoms. From the bath is better to refrain. It is a shower for 5-10 minutes that will help to completely relax and get rid of the tension of the walls of the uterus. If the woman has contractions often and is very concerned about her, it makes sense to buy a subscription to the pool, in a special group for expectant mothers - swimming will help reduce the frequency and duration of Braxton-Hicks episodes.
- Medicines Pills and other medicines should be resorted to only in extreme cases, if the sensations are very disturbing. Previously it will not be superfluous to consult a doctor. Most often, pregnant women are recommended for removal of increased uterine tone. candles with papaverine (rectally) orNo-shpa"(Orally).
- To eat or drink. It helps some. Even a glass of milk, water or a light vegetable salad can work wonders - the uterus quickly relaxes and the state returns to normal.
When do I need to see a doctor?
In all cases when the training tension of the uterus walls is prolonged, when they last more than 6-8 hours (all day, all night), a doctor should be visited. In some situations, it is better not to risk it and go immediately to the hospital, call an ambulance. These situations include the appearance of regular and prolonged contractions and unusual discharge at up to 36 weeks - the onset of preterm labor is not excluded.
Increasing pain, repetition of three episodes of uterine tension in 10 minutes - the basis for urgent hospitalization, it is best to come to the hospital.
Especially attentive need to be women who are about a month before giving birth. Training fights in this case may be abnormal. With normal preliminary cervical ripening occurs simultaneously, that is, the body is fully prepared for childbirth. In this case, the tension of the uterus rarely lasts more than 7 hours and may disappear and appear, but the very next day. Sleep pregnant good, full, appetite is not changed. This preliminary period is typical for approximately 65-70% of women.
The anomalous process is indicated by a clearly prolonged “training” - painful, irregular contractions, the baby's movements are also painful, the cervix does not mature, does not smooth out and does not shorten, the woman's body is clearly not ready for childbirth. This occurs in approximately 15% of pregnant women.
Abnormal preparatory contractions most often occur in women with overweight, with preeclampsia, in future mothers who have large children, in women with chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, and heart.
If earlier the expectant mother had many abortions, dystrophic changes of the uterus are not excluded, which will also lead to a pathological period of preparation and will require medical assistance.
The risk group includes women who give birth before the age of 18 or after 30 years (if the birth is first), whose pregnancy proceeds against the backdrop of high hydration or a small amount of amniotic fluid, in women with a narrow pelvis. If an abnormal preliminary period is suspected, you should also consult a doctor. A woman can be stimulated to give birth if the cervix does “mature” or stop contractile episodes with the use of sedatives and take time out for the preparation of the cervix with drugs.
If a child experiences hypoxia (and this often happens during abnormal "training"), a decision may be made to perform a cesarean section. In any case, the doctors will make a decision that is optimal for the particular pregnant woman.
How to distinguish the real fights from false, look in the following video.