Heart rate: normal in children
Evaluating the work of the heart in a child, physicians first determine the frequency of his contractions (HR), because the change in this indicator immediately prompts the pediatrician if the baby's heart is in order. The parents should be aware of the peculiarities of measuring the frequency of heart contractions in children and the norms of this magnitude, since the heart is one of the most important organs in the children's body and its normal operation ensures the health of the toddler in general.
What is it?
The abbreviation "HR" means the number of heartbeats per minute. Many people call this indicator a pulse, but this is not quite true, since the heart rate indicates the number of heartbeats, and the pulse is determined by the expansion of the artery during a heartbeat. They coincide in a healthy child, but for some problems of the cardiovascular system, for example, in atrial fibrillation, the pulse may not be detected. This condition is called “pulse deficit”, measuring heart rate with it using a phonendoscope.
Every mother should know that the heart rate indicators in children are significantly different from the norms for an adult. In addition, the heart rate is different in age - in newborns, the frequency of contractions of the heart will be the highest, and as the child grows, the rate will decrease until it reaches the “adult” norms in adolescence.
Measurement rules
Most often, the heart rate in children is measured by a doctor, but this is fully within the power of the parents at home. The measurement will help to identify abnormalities and in time to contact the pediatrician for a more detailed examination of the crumbs.
To determine the frequency of contractions of a child's heart correctly, it is important:
- Measure heart rate at rest. Do not try to count the number of cuts in a baby after experiencing, active play, crying or physical exertion. Such effects, as a rule, will increase the heart rate and the measurement result will be incorrect.
- Do not force the child to measure heart rate. If the baby is against such a manipulation, his protest will also affect the results, so the determination of the frequency of contractions is better to be postponed until the baby becomes more compliant and calm.
- Measure heart rate in one position. It is best to do this when the child is lying, because going to a sitting position raises the heart rate by 10%, and to a standing position by 20%.
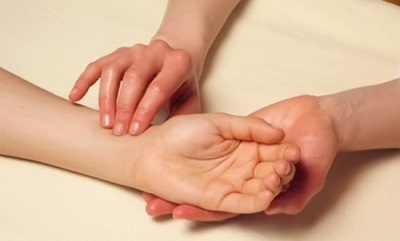
- Do the measurement right. Turn on the stopwatch, feel for a large vessel on the child's wrist or neck, then count the blows in 15 seconds and multiply the result by 4. So you will get a record in a minute. You can also count the blows in 30 seconds and multiply by 2, but this approach is permissible only in the absence of arrhythmia. If the baby's heart beats unevenly, the heart rate is counted for a full minute.
Norm indicators
As noted above, at different ages, the heart rate of children will be different.
The average for each age, as well as the limits of the norms of heart rate in children are presented in the table:
|
Age |
Rate per minute |
|
Newborn |
From 110 to 170 blows (average 140) |
|
From 1 month to 1 year |
From 102 to 162 blows (an average of 132) |
|
1-2 years |
From 94 to 154 shots (124 on average) |
|
2-4 years |
From 90 to 140 blows (an average of 115) |
|
4-6 years |
From 86 to 126 blows (average 106) |
|
6-8 years |
From 78 to 126 blows (average 98) |
|
8-10 years |
From 68 to 108 blows (an average of 88) |
|
10-12 years |
From 60 to 100 blows (average 80) |
|
12-15 years |
55 to 95 blows (average 75) |
|
Older than 15 years |
From 60 to 80 strokes (average 75) |
Causes of deviations
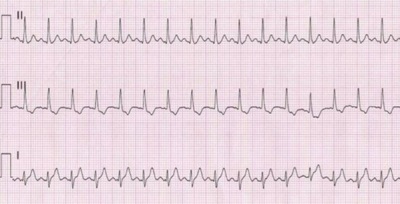
The results of measuring heart rate are affected by various factors, among which the most significant are emotions, body position, food intake, physical activity, medication, hot weather.If the child’s heart rate exceeds normal levels, doctors call this phenomenon tachycardia.
It may occur when:
- Infectious diseases.
- Anemia
- Problems with the endocrine system.
- Emotional overstrain.
- Lung diseases.
- Disorders of the heart.
- Exercise.
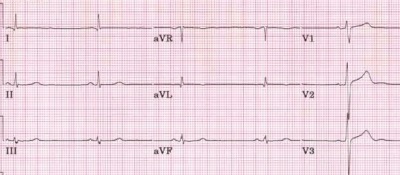
With a lower heart rate than a child of that age should have, bradycardia is indicated.
It can provoke:
- Sports.
- Hypothyroidism.
- Myocarditis.
- Poisoning.
- Some medications and other factors.
What to do when abnormal
When determining whether the heart rate of your child is normal, keep in mind that the table gives only an average figure. If the results you received deviate plus or minus 20% from the age norms, there is no need to worry. If the baby’s heart rate is much higher or too low than it should be, watch the baby, perhaps this is due to active games, strong emotions, physical exertion or hot weather.
If such factors did not affect the child, and you determined high heart rate or bradycardia at rest, you should immediately contact the child with the pediatrician. The doctor will double-check the indicator and, in case of violations, will refer the baby to the pediatric cardiologist.
On the violation of the norm of the rhythm of the heart in a child, see the program "Live Healthy".