Additional chord in the heart of a child
The extra chord found in a child during planned examinations causes an experience for most parents. But it is better not to panic, but to find out more about whether an extra bad tail is dangerous and how its presence can threaten the health of the child.

What is it
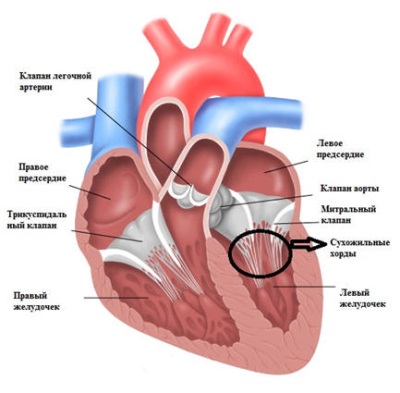
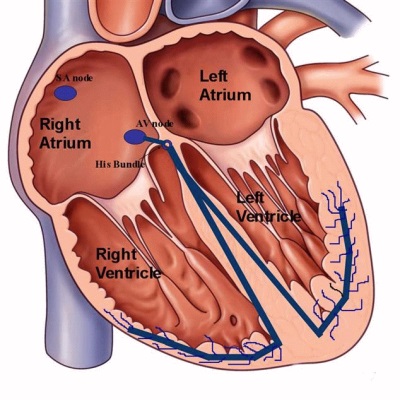
To better understand what constitutes an additional chord, you need to recall the anatomical structure of the heart and the features of its functioning. If this organ is working normally, then the blood moves in it from the atria to the ventricles. This movement is governed by special valves, the opening of which occurs due to the contraction of thin tendons in the ventricles, called chords. When they are relaxed, the flaps of the valves are closed, and as soon as the chords contract, the valves become tight, their flaps open and the blood passes into the ventricles.
Although some parents think that a child should normally have two chords in the heart, and the third chord in the child’s heart is additional, in fact, the chords in the ventricles are larger, but normally they all have the same structure and the same thickness. If atypical chords attached to the ventricular wall from one end are found among the tendons, they are referred to as additional chords. Such formations do not participate in the opening of valves, therefore they are also called false or anomalous.
What is the correct structure of the heart and how it should work, ideally, can be viewed in the following video.
The reasons
The appearance of an extra chord occurs during the laying of the heart during fetal development. The main reason for this deviation is called genetic predisposition. Most often, education is transmitted through the maternal line (in 90% of cases), but can also be transferred from the father. Other factors provoking the appearance of an extra chord are:
- Smoking or drinking in the first trimester.
- Bad environmental situation.
- Inadequate or unbalanced diet.
- Infection during pregnancy.
- Stress in a pregnant woman.
- Weak immunity of the future mother.
Kinds
An additional chord can be detected in any ventricle, but in 95% of cases it is the chord of the left ventricle of the heart in a child, which is abbreviated DHCLG. Only in 5% of babies with an extra chord is it located in the right ventricle.
Anomaly is single in 70% of detection, and in 30% of children, additional chords are represented by multiple formations. In its direction, the extra chord is transverse, diagonal or longitudinal. If we consider the localization inside the ventricle, then the chord is referred to as the basal, median or apical formations.
In addition, all the chords are divided into 2 types:
- Hemodynamically insignificant. Such formations refer to the variant of the norm, since they do not affect the blood flow. Most often, these are single strands in the left ventricle.
- Hemodynamically significant. Such chords affect the blood flow and can cause problems with the work of the heart.
Symptoms
If in the left ventricle of a child there are chords in a single quantity, it will often not have any manifestations. At the location of the anomaly in the right ventricle or in the presence of multiple chords, parents will notice the following symptoms:
- Fast fatiguability.
- Frequent pulse.
- Weakness.
- Reduced stamina.
- The appearance of dizziness.
- Complaints of tingling in the heart.
- Lability psycho-emotional state.
- Arrhythmias.

Note that a newborn with an extra chord often feels good and in most cases, clinical symptoms appear in school or adolescence when the child grows very quickly.
Diagnostics
In most cases, the additional chord, like the LLC, is detected with a planned ultrasound of the heart. This examination passes each baby in 1 month. If the pediatrician hears noises in the baby's heart, he can send the baby to the echocardiography before. To check the work of the heart with an extra chord, children are also assigned an ECG, and in order to identify hidden problems with rhythm, veloergometry and Holter monitoring are conducted during adolescence.
Effects
For most babies, the presence of additional chords, especially if it is LVHL, does not pose any danger and does not interfere in life. Sometimes these formations "dissolve" themselves - the heart grows in size and the chord shifts, becoming inaccessible for visualization with ultrasound.
Some chords that affect blood flow can cause problems with heart function, such as conduction disturbances and arrhythmias. In rare cases, a chord without treatment leads to ischemic stroke, endocarditis, thrombophlebitis, and other pathologies.
If the notochord in the heart is one of the symptoms of underdevelopment of the connective tissue, this pathology will also manifest itself as tall, lean physique, hypermobility of joints, bone deformities, problems in the digestive tract and kidneys.
Treatment
Drug therapy is prescribed to children with an extra chord only with clinical manifestations of the problem, for example, if the child complains of unpleasant sensations in the chest. Also, drug treatment must be prescribed for the detection of arrhythmias. In rare cases, when the false chord includes the pathways of the heart, it is excised or destroyed by cold.
Among the medications that are prescribed with an additional chord, there are vitamins of group B, potassium orotat, magnesium B6, panangin, magnerot, l-carnitine, actovegin, ubiquinone, piracetam and others. They normalize metabolic processes in the tissues of the heart, improve the conduction of impulses and nourish the heart muscle.
In addition, a child with an extra chord is advised to provide:
- Balanced diet.
- Daily exercise.
- Frequent walks.
- Hardening
- Minimum stress.
- The optimal mode of the day.
- Timely treatment of disease.
Such children are not prohibited from active games and moderate exercise, for example, swimming, gymnastics or jogging.
Opinion of Dr. Komarovsky
A popular pediatrician confirms that an extra chord in the heart, especially DHLH in a child’s heart, is in most cases not dangerous. In his practice, he not once saw children in whom the chord detected during the ultrasound scan was only a statement of fact, but it did not cause any inconvenience and problems to the child, but it did not appear outwardly.
Komarovsky emphasizes that the treatment of such children in most cases is not necessary and changing their lifestyle is not required. The only thing that a well-known doctor of parents warns is that grown children with an extra chord should not work as divers or jump with a parachute.
About what to do with pains in the heart, see the transfer of Dr. Komarovsky.