Extrasystole in children
When children have any heart rhythm disturbances, it is always a cause for concern and anxiety for their parents. The most common problem with the rhythm of heartbeats in children is its increased rate, called tachycardia, or the slowdown that doctors call bradycardia. However, there is another violation of the rhythm of heartbeats in children. It is called extrasystole.
What is it
Extrasystole is a type of arrhythmia in which the normal sinus rhythm of the heartbeat is disturbed by the appearance of the extrasystoles - premature heartbeats dislodged from the normal sinus rhythm.
At the same time a number of single extrasystoles is the norm.
The main danger of extrasystolic contractions is the risk of transition to other forms of arrhythmia and the negative effect on the pumping function of the heart. In severe cases, extrasystole can lead to cardiac arrest.
The reasons
The appearance of extrasystoles can lead to any heart disease, as well as diseases of other organs. The most frequent causes of such a heart rhythm disturbance are:
- Heart disease, which can be either congenital or acquired.
- Hypoxia at birth, causing damage to the central nervous system.
- Disease of the thyroid gland.
- Exercise stress.
- Take some medication.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Emotional overload.
- Intoxication.
- Myocarditis.
- Respiratory infections.
- Autoimmune diseases.
- Rheumatism.
- Dysthophic changes in the myocardium.
- Trauma of the heart.
Kinds
Depending on the cause of extrasystoles, these types of disorders are distinguished:
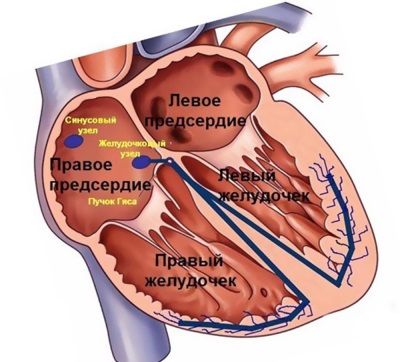
- Atrial extrasystole. In this form, contractions are stimulated by the site in one of the atria or in the septum between them.
- Nodal premature beats. It is also called atrioventricular by the name of the node that sets the rhythm.
- Ventricular extrasystole. The hearth stimulating contractions is located in one of the ventricles or in the septum between them.
You can learn more about ventricular premature beats in the following video, which will identify the main causes of the disease, and methods of treatment and prevention
With a lesion in the atria, the interatrial septum or in the atrioventricular node, such beats also called the "supraventricular" or "supraventricular".
Based on the types of extrasystoles diagnosed:
- Monomorphic extrasystole. It is provoked by a single source, and extrasystolic ECG complexes will be the same.
- Polymorphic extrasystole. Such an arrhythmia is also provoked by one source, but the form of the complexes on the ECG will be different.
- Polytopic extrasystole. Heart contractions occur in several foci, and ECG complexes differ in shape.
- Group extrasystoles. They represent 3 or more extrasystolic cuts in a row.
Symptoms
In some children, there are no obvious symptoms of extrasystoles, and the disorder is detected during a routine examination. If there are clinical manifestations of extrasystole, then often they are represented by a feeling of heart sinking and interruptions in his work.
The child may mark a short pause in the work of the heart, after which there is a strong blow. There are also complaints of short-term acute chest pain. Small children with extrasystole may be agitated and restless. Symptoms in infants are also characterized by disturbances in sleep and appetite.
Diagnostics
Most often, premature beats are detected:
- When conducting an ECG. This survey will most accurately determine not only the presence of extrasystoles, but also the place of their occurrence.
- When listening to the heart of a child. The doctor hears either one loud tone during an extrasystolic contraction, or two tones that follow each other, but with different intensity (the first is strong and the second is weak).
- When counting the pulse. Extrasystoles will manifest loss of pulse beats.
To clarify the cause of arrhythmia and determine the tactics of treatment, the child will additionally conduct:
- Echocardiography with doppler.
- Holter monitoring.
- Examination by a neurologist.
- General blood analysis.
- Determination of blood electrolytes.
- Evaluation of thyroid hormone levels.
- Consultation endocrinologist.
Treatment
If the child has extrasystoles, his treatment is selected only after clarifying the cause of such arrhythmia. If a baby has a single ventricular extrasystole, such a rhythm disorder does not require treatment. The extrasystole, caused by myocardial damage, is treated by a cardiologist, and in case of problems with nervous regulation, the neurologist prescribes therapy.
When extrasystoles are prescribed to the child, drugs that improve the nutrition of the myocardium and nerve tissues, sedatives, magnesium preparations, and potassium. In some cases, for example, if supraventricular premature beats are diagnosed in children, antiarrhythmic drugs are used.
Prevention
To prevent the occurrence of extrasystoles, it is important to avoid violations of the day regimen, strong psycho-emotional and physical overloads, and bad habits. Effective prevention of premature beats is called:
- Balanced diet.
- Daily walks.
- Favorable psychological climate.
- Sufficient sleep duration.
- Timely treatment of any pathologies.
- Moderate exercise.
- Strengthening of protective forces.