Open arterial duct (OAD) of the heart in children
The structure and work of the heart in the fetus differ from the functioning of this organ in children after birth and in adults. First of all, the fact that in the heart of the baby who is in the mother's womb there are additional holes and ducts. One of them is the arterial duct, which after birth normally should close, but this does not happen in some babies.
What is the open arterial duct in children
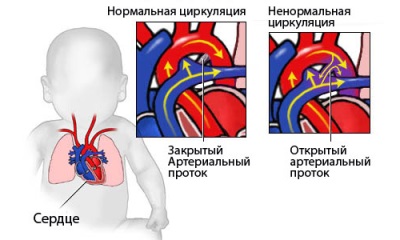
Arterial or Botallovym duct is a vessel present in the heart of the fetus. The diameter of such a vessel can be from 2 to 10 mm, and length - from 4 to 12 mm. Its function is the binding of the pulmonary artery with the aorta. This is required for the transfer of blood to bypass the lungs, since they do not function during fetal development.
The duct is closed when the child is born, transforming into a cordage impassable for blood, consisting of connective tissue. In some cases, the closure of the duct does not occur and this pathology is called the open arterial duct or abbreviated PAP. It is diagnosed in one of 2000 babies, and this happens in almost half of premature babies. According to statistics, girls such a defect occurs twice as often.
An example of what looks like a PDA on ultrasound, you can see in the next video.
When should I close?
In most babies, the closing of the duct between the pulmonary artery and the aorta occurs in the first 2 days of life. If the baby is premature, the rate of closure of the duct is considered up to eight weeks. OAP is diagnosed for children who have the Botallov duct left open after reaching 3 months of age.
Why does not all newborns close?
A pathology such as a PDA is often diagnosed with prematurity, but the exact reasons why the duct remains unclosed are not yet identified. The provoking factors include:
- Heredity.
- Low mass of the newborn (less than 2500 g).
- The presence of other heart defects.
- Hypoxia during prenatal development and during childbirth.
- Down syndrome and other chromosomal abnormalities.
- The presence of the mother of diabetes.
- Rubella in a woman during gestation.
- Radiation effects on the pregnant.
- The use of future mother alcohol or substances with a narcotic effect.
- Medication, negatively affecting the fetus.
Hemodynamics with PDA
If the duct does not overgrow, then due to the higher pressure in the aorta, blood from this large vessel enters the pulmonary artery by joining the pulmonary artery, joining the volume of blood from the right ventricle. As a result, blood enters the blood vessels of the lungs more, which causes an increase in the load on the pulmonary circulation, as well as on the right heart.
Phases
In the development of the clinical manifestations of PDA, there are three phases:
- Primary adaptation. This stage is observed in children of the first years of life and is characterized by a pronounced clinic, depending on the size of the open duct.
- Relative compensation. At this stage, the pressure in the pulmonary vessels decreases, and in the cavity of the right ventricle - increases. The result will be a functional overload of the right side of the heart. This phase is observed at the age of 3-20 years.
- Sclerosing of pulmonary vessels. At this stage, pulmonary hypertension develops.
Signs of
In babies of the first year of life OAP manifests itself:
- Palpitations.
- Shortness of breath.
- Minor weight gain.
- Pale skin.
- Sweating.
- Increased fatigue.
The severity of the defect is affected by the diameter of the duct. If it is small, the disease can proceed without any symptoms. When the size of the vessel is more than 9 mm in full-term babies and more than 1.5 mm in premature babies, the symptoms are more pronounced. They are joined by:
- Cough.
- Hoarseness.
- Frequent bronchitis and pneumonia.
- Lag in development.
- Weight loss
If the pathology was not revealed before the year, then the older children have the following signs of PDA:
- Breathing problems with little exertion (increased frequency, feeling of lack of air).
- Frequent infections of the respiratory system.
- Cyanosis of the skin of the feet.
- Not enough weight for your age.
- The rapid emergence of fatigue when moving games.
Danger
When the Botallov canal is unclosed, blood from the aorta enters the lung vessels and overloads them. This threatens the gradual development of pulmonary hypertension, cardiac wear and a decrease in life expectancy.
In addition to the negative impact on the lungs, the presence of the PDA increases the risk of such complications as:
- Aortic rupture is a deadly condition.
- Endocarditis is a bacterial disease with valve damage.
- Heart attack - the death of the heart muscle.
If the diameter of the open duct is significant and there is no treatment, then the child begins to develop heart failure. It is manifested by shortness of breath, rapid breathing, high pulse, decrease in blood pressure. This condition requires immediate treatment in the hospital.
Diagnostics
To identify the child UAP use:
- Auscultation - the doctor listens to the baby's heartbeat through the chest, determining the noise.
- Ultrasound - this method detects an open duct, and if the study is supplemented by a doppler, then it is able to determine the volume and direction of the blood, which is discharged through the PDA.
- X-rays - this study will determine changes in the lungs, as well as cardiac boundaries.
- ECG - the results will reveal an increased load on the left ventricle.
- Sounding chambers of the heart and blood vessels - such an examination determines the presence of an open duct with the help of contrast, and also measures pressure.
- Computed tomography is the most accurate method that is often used before surgery.
Treatment
The doctor determines the treatment tactics taking into account the symptoms of the defect, the diameter of the duct, the age of the child, the presence of complications and other pathologies. OAP therapy can be medication and surgery.
Conservative treatment
To him resorted to unexpressed clinical manifestations of vice and the absence of complications. As a rule, treatment of babies in whom the AOA is identified immediately after delivery is first medicamental. Child can be assigned anti-inflammatory means, for example, ibuprofen or indomethacin. They are most effective in the first months after birth, because they block substances that prevent the canal from closing in a natural way.
Diuretics and cardiac glycosides are also prescribed for babies to reduce the load on the heart.
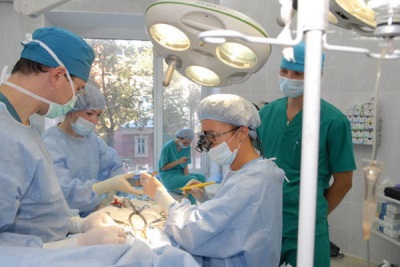
Operation
This treatment is the most reliable and is:
- Catheterization of the duct. This method of treatment is often used over the age of 12 months. It is a safe and sufficiently effective manipulation, the essence of which is the introduction of a catheter into the large artery of a child, which is fed to the OAP to install an occluder inside the duct (a device for blocking blood flow).
- Bandaging duct during open surgery. Such treatment is often carried out at the age of 2-5 years.Instead of dressing it is possible closure of the duct or clamping the vessel using a special clip.
All these terms sound a bit scary, but in order not to be afraid, you need to know what your child will do and how it will happen. In the next video you can see how the occluder is installed in the duct in practice.
Indications for surgical intervention in the OAD are such situations:
- Drug therapy was ineffective.
- The child has symptoms of stagnation of blood in the lungs, and the pressure in the pulmonary vessels has increased.
- The child often suffers from pneumonia or bronchitis, which is difficult to treat.
- The child developed heart failure.
The operation is not prescribed for severe kidney or liver diseases, as well as in a situation where blood is not thrown from the aorta, but into the aorta, which is a sign of a serious lesion of the pulmonary vessels, which is not corrected surgically.
Forecast
If the Botallov duct does not close in the first 3 months, then this happens on its own very rarely. A child born with a PDA is prescribed medication to stimulate the overgrowth of the duct, which is 1-3 courses of injections of anti-inflammatory drugs. In 70-80% of cases, these medications help to eliminate the problem. With their ineffectiveness, surgical treatment is recommended.
The operation helps to completely eliminate the defect itself, ease breathing and restore lung function. Mortality during surgical intervention in OAP is up to 3% (almost no fatal cases occur in full-term babies), and in 0.1% of operated children, the duct reopens after a few years.
Without treatment, few of the children born with large PDA live to be more than 40 years old. Most often, they have from the second or third year of life pulmonary hypertension is formed, which is irreversible. In addition, the risk of endocarditis and other complications increases. While surgical treatment provides a favorable outcome in 98% of cases.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of OAS in a child, it is important:
- For the period of pregnancy to give up alcohol and smoking.
- Do not take medicines not prescribed by a doctor during pregnancy.
- Take measures to protect against infectious diseases.
- If there are heart defects in the family, consult a geneticist before conception.