How do sperm and egg, how they differ?
Men and women are arranged by nature in different ways, and the differences between them exist at the cellular level. Male and female sex cells have a number of interesting features in their structure. This article will talk about how sperm and eggs are arranged, as well as how they differ.
Sperm structure
For the first time the scientific description of the anatomy of the male germ cell was made by the Dutch researcher Anthony van Leeuwenhoek. He did this in 1677, while not only described the main elements of the male reproductive cell, but also made sketches. Until that time, scientists had no idea how fertilization takes place, but after the discovery of Leeuwenhoek, it became obvious that the male germ cells — the spermatozoa — were involved in the conception process.
Interestingly, for quite a long period of time, the sperm cells were called "seed animals." The usual name for us sperm received only in the XIX century.
Each cell in the human body has a number of important characteristics and must perform certain functions. The main role of the spermatozoon is to reach the fallopian tube of the woman, carry out fertilization and provide its genetic material.
Each cell has its own set of chromosomes, it is in them and is a special genetic code. Each chromosome carries information about what signs a person will have in the future. So, genes that are in a certain sequence in the chromosomes, determine one or another hair color or eye shape.
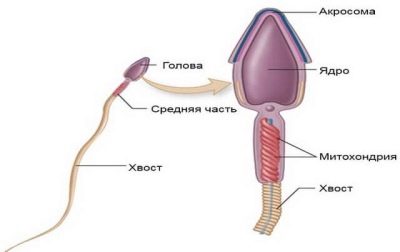
The size of the male reproductive cell is somewhat smaller than that of the female. Modern scientists have even established the length of the sperm - it is about 55 microns.
In appearance, the sperm is very similar to the tadpole. It has a head, a body (middle part) and a tail. Each of these departments has its own length. The sizes of the main parts of the sperm are presented in the table below.
Anatomical region | Length (µm) |
Head | 5 |
Body | 4,5 |
Tail | 45 |
In the process of sperm development, a number of very important transformations take place - it must fully mature and become suitable for conceiving. During the period of maturation, the spermatozoon significantly decreases in size. The nucleus is compacted and its cytoplasm decreases, while all the necessary intracellular organelles remain.
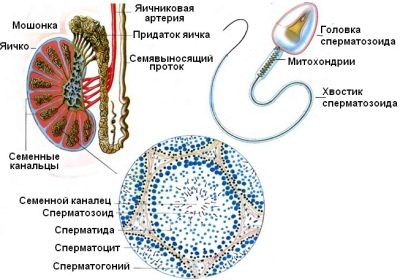
The middle part of a sperm cell is separated from its head by a certain narrowing, which is called the neck. Behind the middle part there is a moving tail, due to which spermatozoa are characterized by their ability to move. In inactive and sedentary male germ cells, the ability to conceive is significantly reduced. In order for the sperm to enter the fallopian tube, where it can meet with the egg, it needs to be quite mobile. The tail helps him in this - with the help of him the spermatozoon makes movements around its own axis.
Scientists have calculated and the average speed of movement of motile sperm. So, it is approximately from 0.1 mm per second to 30 cm per hour. It is believed that after intercourse, active spermatozoa are able to reach the fallopian tube in almost 1-2 hours.
In order to be active, prostate juice is necessary for sperm. It is produced by the male's secretory organ - the prostate.
Spermatozoa, activated by prostatic juice, during ejaculation, can carry out their movement for further fertilization.
You will learn more about sperm from the following video.
Egg structure
The number of female follicles is determined in the period of prenatal development. A little girl who is still developing in the womb begins to form eggs. By the time of birth, their number is about 1-1.5 million.
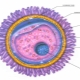
Female and male sex cells have certain similarities. Thus, ova, like spermatozoa, are necessary for the implementation of fertilization. Inside the female reproductive cell, there is a nucleus - in it, as in the sperm head, there is also a certain set of chromosomes that encodes important genetic information.
Outside the egg is surrounded by the outer shell. Make up its special proteins. The special structure of the outer shell of the egg contributes to the fact that only one sperm cell can penetrate into it at the time of fertilization.
The outer shell of the egg is also called the radiant crown, as it is covered on the outside with a large number of microscopic fibers. They are necessary in order to provide a small cell protection.
An important property of the female germ cell is its maturation. In each menstrual cycle in the body of a woman matures one egg. In the process of maturation, the female sexual cell goes through several successive phases.
Female eggs develop within a few days of the menstrual cycle. During ovulation, a mature egg leaves the follicle and enters the fallopian tube. If a meeting with sperm does not occur, it dies. In this case, pregnancy does not occur.
Ovules mature in the female body only during the reproduction period - this is the time when a woman can become a mother in a natural way. Reproductive time comes with the arrival of the first menstrual period and ends with the final onset of menopause.
Throughout life, the number of eggs given by nature from birth does change. This is influenced by many environmental factors. Among the most frequent causes of a decrease in the number of eggs in the female body are stress effects, concomitant gynecological diseases, and bad habits.
In the case of persistent violations of the process of maturation of eggs in the ovaries, a woman may face the problem of infertility.
You will learn more about eggs from the following video.
Differences between germ cells
Male and female cells have a number of differences. Comparative characteristics include several criteria.
First of all, male and female sex cells differ in size. The ovum is somewhat larger than the spermatozoon because it has a different structure. So, inside it is more cytoplasm. The size of the female reproductive cell is approximately 130 microns, that is, approximately twice as large as the male.
Also, sex cells in men and women differ in a set of chromosomes. The main genetic information is in the nucleus - the main organ of a small germ cell. This is where the chromosomes are located.
Scientists distinguish only two types of sex chromosomes - X and Y. The presence of the Y chromosome in the genotype determines the birth of a boy, but the paired X chromosomes are “responsible” for the future birth of a little girl.
The Y chromosome is found only in the sperm.Thus, the birth of an heir is possible only if at the time of conception fertilization took place under the influence of a spermatozoon that contains the Y chromosome. Her baby can only “get” from her father, as she simply does not exist in the female body.
Comparison between the eggs and sperm can be carried out on the ability to survive. By this term, specialists mean the ability of a cell to remain in external conditions without losing its basic properties and viability. It is believed that sperm are more viable than eggs. So, on average, they can persist in the female genital tract after intercourse for 3-4 days, while an unfertilized egg cell dies relatively quickly - 12-24 hours after it leaves the follicle.