How many chromosomes does the sperm nucleus contain and what features does the chromosome set of sperm have?
The ability to transfer genetic information is very important for procreation. The features of the chromosomal set of the male reproductive cell further after conception cause the inheritance of certain signs. This article will tell you about how many chromosomes the sperm cell contains.
Features of the structure of the male reproductive cell
Genetic information that is inherited by the genus is encoded in separate genes located in the chromosomes.
The very first ideas of scientists about chromosomes that are inside human cells, appeared in the 70s of the XIX century. To date, the scientific world has not come to a common opinion about who among the researchers discovered the chromosomes. At various times this discovery was “appropriated” to I. D. Chistyakov, A. Schneider and many other scientists. However, the term “chromosome” itself was proposed for the first time by a German histologist G. Waldeyer in 1888. The literal translation means "painted body", since these elements are quite well stained with basic dyes when conducting research.
Most of the scientific experiments that clarified the definition of the structure of chromosomes were carried out mainly in the XX century. Modern researchers continue scientific experiments aimed at accurate decoding of genetic information that is contained in the chromosomes.
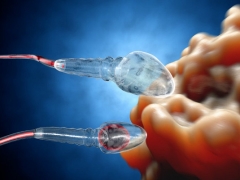
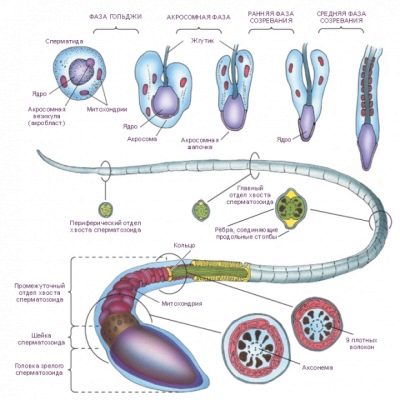
For a better and simple understanding of how the chromosome set of the male reproductive cell is formed, let us touch a little on biology. Each spermatozoon consists of a head, a middle part (body) and a tail. On average, the length of the male cell to the tail is 55 microns.
The sperm head has an ellipsoid shape. Almost all of its internal space fills a special anatomical formation, which is called the nucleus. In it are the chromosomes - the main structure of the cell, carrying genetic information.
Each of them contains a different number of genes. So, there are more and less gene-rich areas. Currently, scientists are conducting experiments aimed at studying this interesting feature.
The main component of each chromosome is DNA. The main genetic information inherited from parents by their children is kept in it. In each of these molecules is a specific sequence of genes that lead to the development of various traits.
The DNA chain is rather long. In order for the chromosomes to have a microscopic size, the DNA chains are strongly twisted. Recent genetic studies have determined that special proteins — histones, which are also in the nucleus of the germ cell — are also required for DNA molecule curling.
A more detailed study of the structure of chromosomes showed that, in addition to DNA molecules, they also consist of protein. This combination is called chromatin.
In the middle of each chromosome there is a centromere - this is a small area that divides it into two sections. Such a division determines the presence of each chromosome long and short shoulder. Thus, when examined in a microscope, it has a striated appearance. Each chromosome also has its own sequence number.
A common chromosome set of a living organism is called a karyotype. In humans, it is 46 chromosomes, and, for example, the fruit fly Drosophila is only 8.Features of the structure of the karyotype and determine the inheritance of a certain set of different features.
Interestingly, the formation of sex chromosomes occurs during the period of intrauterine development. In the fetus that is still in the womb, the sex cells are already forming, which he will need in the future.
Spermatozoa acquire their activity much later - during puberty (puberty). At this time, they become quite mobile and capable of fertilizing eggs.
Haploid set - what is it?
To begin with, one should understand what experts mean by "ploidy". In simpler words, this term means multiplicity. Under the ploidy of the chromosome set, scientists mean the total number of such sets in a particular cell.
Speaking about this concept, experts use the term "haploid" or "single." That is, the sperm nucleus contains 22 single chromosomes and 1 sex. Each chromosome is not paired.
The haploid set is a distinctive feature of the germ cells. It is not conceived by nature. During fertilization, part of the inherited genetic information is transmitted from the paternal chromosomes, and some from the maternal. Thus, the zygote obtained in the process of fusion of sex cells, has a full-fledged (diploid) set of chromosomes, in an amount of 46 pieces.
Another interesting feature of the haploid set of sperm is the presence of the sex chromosome in it. It can be of two types: X or Y. Each of them determines the future sex of the child.
Each sperm contains only one sex chromosome. It can be either X or Y. The egg cell has only one X chromosome. When merging the germ cells and combining the chromosome set, various combinations are possible.
- Xy. In this case, the Y - chromosome is inherited from the father, and X - from the mother. With such a combination of germ cells, a male body is formed, that is, a heir is soon born to a couple in love.
- Xx. In this case, the child "receives" the X chromosome from the father and the same from the mother. This combination ensures the formation of the female body, that is, the birth of a little girl later on.
Unfortunately, the process of inheriting genetic information is not always physiological. Quite rare, but there are certain pathologies. This occurs when only one X chromosome (monosomy) is present in the zygote formed after fertilization, or, conversely, an increase in their number (trisomy) occurs. In such cases, children develop quite severe pathologies, which further significantly impair their quality of life.
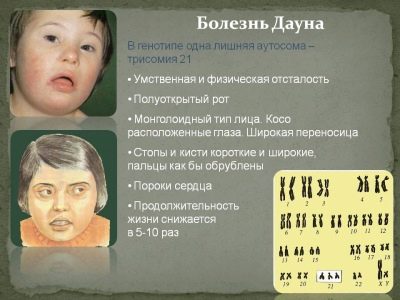
Down syndrome is one of the clinical examples of pathologies associated with impaired inheritance of the chromosome set. In this case, a certain “failure” occurs in 21 pairs of chromosomes, when the same third one is added to them.
A change in the chromosome set in this situation also contributes to a change in inherited traits. In this case, the baby has certain developmental defects, and the appearance changes.
Human genome
For the normal functioning of each somatic cell of our body, 23 pairs of chromosomes are needed, which were obtained by it after the fusion of the genetic material of the maternal and paternal cells. The whole set of such acquired genetic material, genetic scientists call the human genome.
The study of the genome has allowed specialists to determine that the human chromosome set includes a sequence of more than 30,000 different genes. Each of the genes is responsible for the development of a particular trait in a person.
A certain sequence of genes can thus determine the shape of the eyes or nose, hair color, finger length, and many other features.
About what is transmitted to the person with the genes, see the following video.