Why did the child become ill hear and what to do?
The sooner the child has hearing problems, the more favorable the prognosis for treatment and rehabilitation will be. Therefore, parents should carefully observe the ability to hear from a baby. The appearance of the first signs of auditory dysfunction should be a signal for quick and decisive parenting.
Signs of violations
Since hearing impairments are congenital and acquired, it is important to control the auditory function in a child at any age. Attentive parents will easily notice that the child has become hard of hearing. Specific anxiety symptoms depend on the age of the baby.
In infants hearing loss is the hardest to determine, as they are not yet speaking. But well-hearing babies from three months of age react to new, especially loud sounds - they are trying to detect the source of sounds with their eyes, by turning their heads. Unexpected sounds make the crumbs start, reflexively throw up the arms and legs.
If a child, according to the results of medical examinations in the maternity hospital and clinic, has successfully passed an audio test, this does not mean that the pathology will not manifest itself later.
Therefore, parents of karapuz of the first year of life should be alerted by such symptoms as the lack of an adequate response to sounds of different loudness (there is a reaction only to very sharp sounds and silent sounds are ignored, there is no reaction to any sounds).
In older children alarming signs of deterioration of the auditory function are manifested in the absence of a quick reaction to the reversed words, observations Of course, it all depends on the degree of hearing loss, but in general, children often begin to ask again, clarify. The child is tense, he peers into the lips of the interlocutor, so as not to miss what was said. The child may complain of a strange noise in the ears, not responding to words spoken at a normal loudness or a whisper.
Since the state of hearing is directly reflected in speech, children, who for some reason have become less sensitive to perceive sound information, begin to speak at a slower pace, and also often turn up the volume of the TV, if there is something very interesting for them. A child can pull at his ears, as well as sticking out auricles, delaying them, trying to catch sounds.
How to check?
If you suspect hearing problems in your child, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Despite the advice to test it by ear at home, to treat with folk remedies, there are common otopathologies, in which the answer to the question of whether hearing returns, depends on the time of assistance, and this time is limited to a few weeks or even days.
Do not try to look for the cause of hearing loss yourself. The best solution would be to contact an ENT doctor.
If you have an appointment with the appropriate doctor, then you need to go to the pediatrician for an emergency appointment. With complaints of sudden hearing loss, the otolaryngologist will take a note of "cito" (urgent) from a pediatrician doctor out of turn.
There are many diagnostic methods. First of all, the doctor will need to exclude inflammatory diseases of the organs of hearing, as well as ENT pathologies, in which hearing can theoretically decrease - otitis, adenoiditis, ear ear plugs, eardrum pathologies, foreign objects in the ear (sometimes children are pushed into the ears of various small details).
With the help of an otoscope, a child is examined directly at the treatment in the office.After that, in the absence of mechanical or other objective reasons, the child is assigned to reduce the auditory function. visiting audiologist's office - This specialist assesses the degree of hearing loss, conducts tone audiometry. This study shows not only the degree of loss, but also the nature of the loss. Children up to 3-4 years old spend playing tonal audiometry.
Children older than 4 years old conduct additional research on the perception of whisper and colloquial speech. - if the baby does not hear the words reversed in a whisper from 6 meters, asks or does not react to them, they determine the threshold of audibility (from what distance he still picks them up and distinguishes them). If the damage to the auditory nerve is suspected, a baby is sent to the children's neurologist for an appointment.
Among the studies prescribed not only audiometry, but also tympanometry (study of the mobility of the eardrum and the condition of the middle ear), x-rays of the temporal bones. Only then can we talk about the exact causes of hearing loss and possible predictions for the future.
The reasons
The reasons for the decrease in auditory function can be different - from mechanical obstacles in the form of a foreign body or sulfuric plug to congenital developmental abnormalities of the organs of hearing.
Congenital hearing loss and deafness children are often hereditary. At the same time, mom and dad are well hearing - not a barrier to the formation of a fetus with a hearing pathology, because the problem is transmitted from both grandparents, grandparents, and the dominant and recessive types. Various intrauterine factors may affect the hearing of the child. This is especially dangerous during the formation and setting of the hearing organs, analyzers and brain parts responsible for hearing skills. Hazards include ARVI and influenza, rubella, toxoplasmosis, and parotitis, experienced by the mother during the first and the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy, rhesus conflict, smoking, taking alcohol and drugs to the future mother.
The reason for the absence or reduction of the ability to hear from the crumbs can be birth injuries.
Congenital abnormalities of hearing are usually detected in the first 2-3 years of a baby’s life, although minor defects in the functioning of a child’s hearing system may be found much later.
Acquired hearing impairment - The most common phenomenon in childhood. Hearing can temporarily decrease, for example, during otitis or a cold, and in most cases such a decrease is reversible, the ability to hear normally returns 3-4 weeks after the illness on its own. But also flu, acute respiratory viral infections, purulent otitis, otitis of the inner ear may well be the cause of persistent hearing loss.
Irreversible or progressive hearing loss often develops after meningitis, scarlet fever, measles, infectious parotitis (mumps). Infections that are complicated by hearing impairment most often result in damage to the auditory nerve. And inflammatory diseases of the ears - to the defeat of the sound-conducting departments.
With chronic adenoidsif the doctor recommends their removal, and parents insist on treatment with folk remedies, persistent hearing loss on one or both ears often develops.
The cause of hearing loss can be a traumatic brain injury, and the use of streptomycin-based antibacterial drugs (neomycin, monomitsin, gentamicin). These antibiotics are ototoxic.
How to treat?
After the examination, the clinical picture will become clear. Depending on the cause, treatment is prescribed.
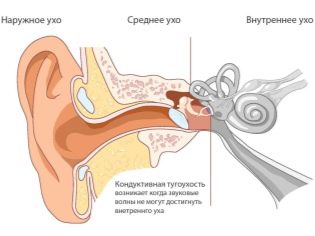
- With ear plug it is removed, the ear is washed by the doctor, hearing is restored to the full. Foreign objects found in the ear are removed, after which the hearing is also restored without any treatment.
- But for the most part, unfortunately, the problem of hearing loss is related with the development of hearing loss. It is conductive in which the conductive apparatus suffers. Most often it is associated with pathologies in the outer or middle ear.Often detected sensorineural (neurosensory) hearing loss associated with the defeat of the sound-receiving apparatus, which includes the auditory nerve, the inner ear. Sometimes mixed hearing loss is detected.
Violation can develop rapidly and be discovered by doctors in a few hours.
- Sharp Forms - hearing impairment for no more than 28 days.
- Subacute - up to 3 months.
- Chronic Pathology is a hearing loss for more than 3 months.
Sudden and acute forms are best treated, which is why parents are advised to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
The more time passes since the onset of hearing impairment, the less optimistic the doctors' forecasts will be - with chronic hearing loss, only hearing aids with hearing aids and cochlear implantation surgery, which is not always shown to everyone and does not always help, help restore hearing.
- For treatment acute and subacute conductive hearing loss usually prescribed medication, physiotherapy. A pneumomassage of the eardrums is performed, electrophoresis is performed, the auditory tube is flushed.
- With sensorineural hearing loss start urgent treatment with drugs that improve the blood circulation of the inner ear. The administration of Prednisolone in certain dosages helps well if the hearing loss is sudden or acute. In the chronic form of the disease, these measures, alas, are ineffective.
- With 2-3 degrees of hearing loss prescribed wearing hearing aids. If this turns out to be ineffective and the intelligibility of speech does not improve, the child constantly asks again in the devices, it is recommended that cochlear implantation.
None of the methods that help rehabilitate a child with a hearing loss in chronic hearing loss does not lead to full recovery. Lost rumor is not returned. Doctors consider a great success in stopping the fall in hearing perception at a stable level. Therefore parents should pay great attention to the prevention of such problems:
treat all ENT-diseases in time and correctly, do not self-cure for influenza, ARVI;
regularly monitor the behavior and reactions of the child to notice possible violations in time;
avoid finding the baby where there are loud and harsh sounds to prevent the development of acoustic trauma;
teach your child to take care of their ears - do not push toys and parts into them, do not clean them with sharp objects, monitor the hygiene of the hearing organs.