What does brain ultrasound show and why are children doing it?
Ultrasound scan of the brain is carried out to children from birth, the procedure is not dangerous for newborn babies. But why and how such a diagnosis is carried out, mothers are usually not told. In this article we will explain what the brain ultrasound shows and whether children need such a procedure.
About diagnostics
Ultrasound of the brain is a diagnostic method that is classified as fairly accurate, but it is not considered highly accurate. The method allows you to see gross abnormalities in the development of the cerebral cortex, the pathology of certain parts of the brain, which may indicate the presence of a child with severe congenital and acquired diseases.
For a child, this study is completely painless. About the dangers of ultrasound, official medicine does not know anything, and therefore it is necessary to agree to such an examination. The essence of the method is quite simple: ultrasound is reflected from the structures of the brain, and the reverse signal in the form of an image goes to the monitor. The doctor sees and analyzes it.
Electroencephalography as a method of studying the brain is performed for adults and children of school age, and neurosonography is carried out for newborns and children up to 1-1.5 years old.
How is it done?
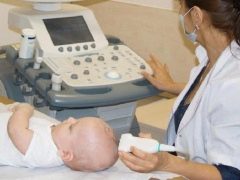
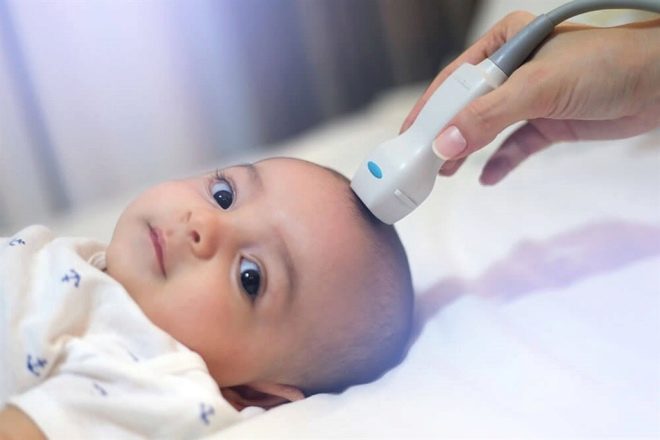
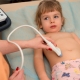
Children older than 1.5-2 years old ultrasound is performed through the temporal bones. For babies in the course of neurosonography, the study is applied through a loose spring. This is the answer to the question of how old people usually do NSG - until the spring is drawn out.
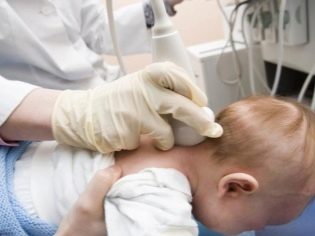
Ultrasound can be conventional, two-dimensional, and may, according to indications, be carried out with a Doppler. The second method will allow assessing the condition of the blood vessels and adjacent tissues. This ultrasound is carried out not only in the head, but also in the neck - so the idea of the blood supply to the brain and the vascular patency is more complete.
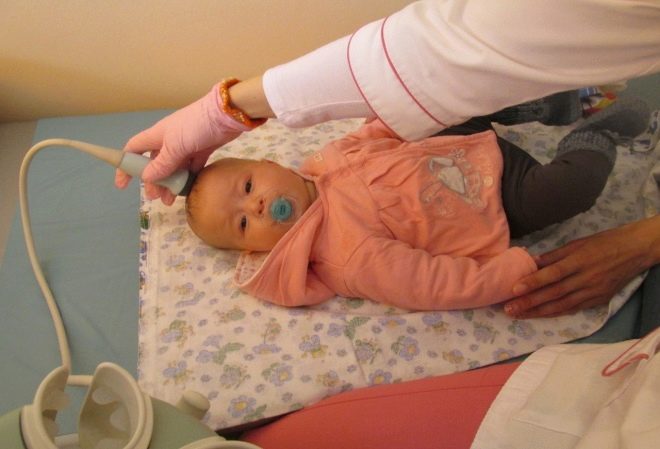
Ultrasound is performed with a traditional outdoor sensor or a Doppler sensor. The child is placed on the couch, after which the doctor examines the sensor through the scalp. The procedure takes about 5-10 minutes, after its completion parents are given an ultrasound protocol, which indicates the results.
Special preparation for the diagnosis is not required. For infants and older children, it is important not to give antispasmodics and pain pills for a couple of days. Children older than one year are not given tea on the eve of the study, since it may affect the state of the vessels.
Indications
According to the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia, neurosonography is performed for all children at the age of 1 month or at 3 months. Ultrasound of the brain is included in the list of studies during the first in the life of the child's medical examination. This does not mean that the baby can not conduct such a study before - according to the testimony it is carried out in the maternity hospital, and in any children's hospital.
Sometimes ultrasounds of the brain are also included in medical examinations for children older than a year, it depends on the orders of the regional Ministry of Health. But at the request of parents, such a procedure can be performed at any age and in any region of the country.
Most often, premature babies need such a study - an assessment of the degree of development of the brain is usually required after the birth of such a baby, and then it is recommended to systematically monitor the development of the child.Neurosonography is also recommended for children who came to life through a cesarean section.
When does a child need to make such an ultrasound? There are many indications:
- inadequate behavior of the baby (lethargy, lack of normal appetite, frequent irrational crying, tremor of the limbs, strabismus);
- regular bouts of headaches;
- impaired hearing and vision in a child;
- memory impairment, low learning abilities, serious delay in speech, mental and psycho-emotional development;
- low blood pressure in a child, as well as episodes of syncope;
- history of convulsions;
- incoordination of movements, cases of falls and loss of balance, which were not caused by a mechanical obstacle - unreasonable;
- history of neck and cranial injuries, including birth injuries.
Ultrasound of the brain is considered mandatory for children who are to undergo surgery on the heart and blood vessels. Also, the method is included in the plan of examination of the child after injury, for example, after falling and hitting his head - in most cases, ultrasound will accurately show concussion, brain contusion, the presence of hematomas.
Ultrasound scanning is used in cases of suspected meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis, which are often the complications of acute infectious diseases in childhood. Also, a diagnostic examination is indicated if the doctor suspects a tumor process.
The following factors can also become the basis for the appointment of an off-schedule neurosonography:
- the baby's weight at birth, regardless of gestational age, was less than 2.7 kg - in low-weight babies, even if they eat well and “catch up” with their peers, some abnormalities of the brain are often detected, although most of them are functional, not requiring therapy;
- the child has some external developmental abnormalities (six-burst, shortening of the limbs, asymmetry of the face);
- the child did not scream at the time allowed for obstetrics;
- labor was heavy, protracted or swift, accompanied by premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
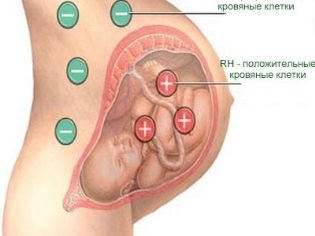
- The pregnancy proceeded against the background of a pronounced Rh-conflict between the mother and the fetus.
Do not be afraid of referral to NSG, sometimes doctors reinsure or want to make sure that the treatment that was previously prescribed to the child helped him. This happens quite often at the end of a course of treatment by a neurologist.
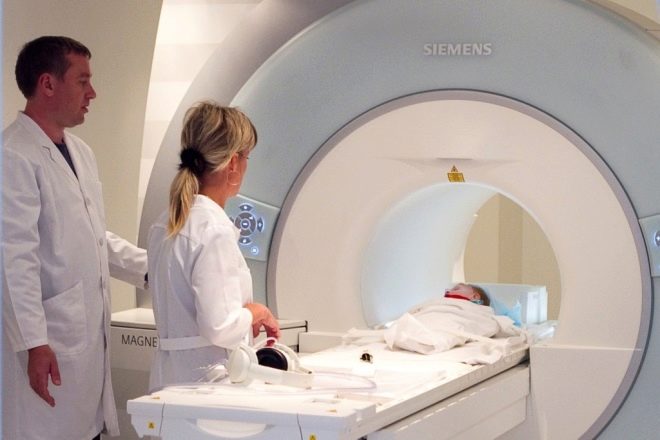
The final diagnosis of the child by ultrasound can not be established. This method is the first that only allows you to identify an existing problem. In more detail the essence of the problem is established with the help of MRI, computed tomography. MRI, by the way, is done for babies under general anesthesia, since there is no way to force the child to lie still for as long as the results of magnetic resonance examination are recorded.
Decoding Neurosonography
If we talk about neurosonography for babies up to a year, then the parents receive a rather detailed conclusion, in which the doctor describes the features of the brain structures.
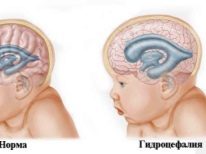
It is noted whether the divisions are symmetrical, the furrows and gyrus are visualized well, and the shape of the brain structures. The presence of fluid in the interhemispheric spaces may indicate hydrocephalus. Normal liquid should not be.
The ventricles of the brain should be symmetrical. Cysts, tumors, hematomas in the normal should be absent. Radiant beams in a healthy baby should be described as hyperechoic.
As for the abundance of numbers in custody, parents should not pay much attention to them, if in conclusion the doctor indicates that no pathologies have been found. But for those who are particularly interested, we give the averaged norms:
- anterior horns of the lateral ventricles of the brain - 2-4 mm;
- occipital horns of the lateral ventricles - 10-15 mm;
- the body of the lateral ventricles of the brain - a maximum of 4 mm;
- third ventricle - 3-5 mm;
- fourth ventricle - no more than 4 mm;
- interhemispheric fissure - 3-4 mm;
- large brain cistern - no more than 10 mm;
- subarachnoid space - 3 mm.
These results are considered the average norm for newborns and children up to 3 months. For older animals - the norms may be different, some of the parameters remain the same, some change to increase.
What can detect a baby?
Ultrasound rather accurately shows a variety of deviations from the norm. The following anomalies are found most often in infants:
- cyst choroid plexus;
- subependymal cysts;
- arachnoid cyst;
- hydrocephalus;
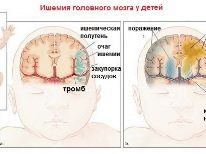
- ischemia;
- hematomas of brain tissue;
- hypertensive syndrome.
Not all pathologies require serious treatment. For example, a choroid plexus cyst is often detected, but it does not pose any danger and in 99.9% of cases it resolves itself. The presence of subependymal cysts usually indicates that the delivery was difficult. Such formations can also pass by themselves, and can turn into ischemia if they begin to increase in size. Requires observation and ultrasound in the dynamics.
Such a cyst as arachnoid, necessarily requires treatment. She herself will not pass. Treatment must also be prescribed for hydrocephalus. Hematomas of the brain tissue, which are often considered a variant of the norm for premature babies, cannot be normal for babies who were born on time.
Oxygen deficiency usually leads to ischemia, which the baby experienced during the period of intrauterine development.
There are many variants of the detected pathologies.
Only a qualified doctor will be able to accurately answer the mother's question about the causes, consequences and predictions, about the need for treatment. All that is required of parents - just trust the professionals.
Reviews
Many mothers believe that ultrasound of the brain can be harmful to a newborn or infant. They express their concerns on thematic forums on the Internet. You can endlessly argue opponents and supporters of ultrasound diagnostics and never come to a common opinion. To do or not to do such an ultrasound, it is up to parents to decide, neither doctors nor the Ministry of Health can force anyone to go for a diagnostic study by force. If your child was prescribed neurosonography, before refusing, re-read the section on pathologies that can be detected using this method, and also consider that it is not possible to detect them by other means.
Some mothers, on the contrary, would like to carry out such an examination, but the doctor does not consider this expedient and does not give directions. In this case, the output is offered by private medical centers and clinics, where the procedure can be done quickly, without a queue or referral. The average cost of research in Russia is from 1,500 to 3,500 rubles (depending on the region and the specific medical center).
In social networks and women’s forums, one can often find allegedly competent comments from “specialists” who claim that abandoning a routine study of a child’s brain through ultrasound will save a child’s health. The conclusions of these “specialists” who claim that because of the diagnostics some “bubbles” are formed in the child's brain, which then grow and cause significant damage to health, are not supported by anything, and from the point of view of educated and sensible people, they are absurd.
Many mothers, who normally belong to this type of research, insist that it is better to take a test certificate at the time when the baby is guaranteed to sleep.
In a dream, such an examination is quite possible, and children usually tolerate the procedure much better, they do not worry because of the touch of a stranger (doctor).
See why in the next video about why a baby should do an ultrasound of the brain.