What does the ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder, why does it make the child?
Diseases of the urinary system in children are very common, and they do not have an age requirement - both newborns and schoolchildren are equally affected. One of the most important diagnostic tools in pediatrics is considered an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder. How this examination is carried out, what it shows and how to prepare the child for the diagnosis, we will tell in this article.
About the study
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder refers to non-invasive methods for studying the state of the urinary system. The features of the anatomical structure and functioning of the links of this system, naturally, cannot be fully assessed only by ultrasound, although such diagnostics are considered to be fairly complete and accurate. But ultrasound is an integral part of the examination, along with urine and blood tests, if the child has symptoms characteristic of urinary pathologies.
The procedure is completely painless, the child will not experience any discomfort.
Regarding the dangers of ultrasound, medicine gives an official answer - the procedure is safe. Nevertheless, many parents are worried about the possible effects of ultrasound on the child’s body.
Indeed, not all the consequences have been adequately studied to date. Modern medicine has such a diagnostic tool only for the past 2.5 decades. For the same, to analyze the long-term effects, you need much more time. On the other hand, there is no data on the apparent or indirect negative impact of ultrasonic waves on the children's organism. Therefore, the procedure is considered safe.
The essence of the method lies in the fact that ultrasonic waves from the sensor penetrate through the tissue and are reflected, sending a response signal to the monitor as image. A special computer program, which is in each ultrasound scanner, allows the doctor to quickly understand the size, amount of fluid, other features, without resorting to complex mathematical calculations.
Ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder in a simplified form is included in the study of the abdominal organs and is recommended by the Ministry of Health to all children as part of a medical check-up at 1 or 3 months, and then after a year. At any other time, such a study can be performed separately, without evaluating other organs of the abdominal cavity (stomach, spleen, liver, etc.) according to indications.
Also, the specialists of the Ministry of Health added this type of ultrasound to the clinical examination program for children as young as one and a half years. This is due to the fact that in recent times the number of children who have kidney, ureter, bladder and adrenal gland diseases in an already advanced stage has been detected.
Indications
Sometimes mothers are surprised to receive a referral for such an ultrasound from a pediatric doctor in the absence of problems with urination in a child. Not always research is shown only to children with such pathologies. Quite often, it is recommended for children who were born premature to assess the functioning of the system and eliminate possible complications due to early birth. Also, the study is recommended for children whose parents suffer from diseases of the urinary system - quite often pathologies are inherited, but do not appear immediately.
In what other cases the child needs an ultrasound of the kidneys and bladder:
- when changing the color, the amount of urine, with the appearance of an unpleasant pungent odor;
- when crying while urinating in newborns or babies, or complaining of pain when bladder emptying in older children;
- with a small amount of urine or, conversely, with enhanced diuresis;
- impurities are distinguishable in the liquid with the naked eye - flakes, pus, blood;
- the child has anemia, pale skin, blue circles under the eyes;
- lower back pain in the side;
- closed blunt abdominal trauma that a child can get when falling belly.
Also, the undisputed basis for the appointment of such a diagnosis is a change in the composition of urine at the biochemical level.
If you and the child have no complaints, and the doctor found the urine tests to be bad, he must send the child to an ultrasound scan of the kidneys and bladder to see if there are grounds for anxiety and treatment, or there are no such reasons, and a laboratory error occurred.
Training
Whether preliminary preparation for research is necessary, usually the doctor who has given the direction informs. But even if the doctor forgot to tell the parents about it, the mother should remember how to two and two - training is needed. And she must be very thorough. It determines how accurate the results of the research will be. It is necessary to prepare the child for the examination procedure in advance; preparation begins 2-3 days before the date of the visit to the diagnostic room.
- From the diet of the child should be excluded foods that stimulate flatulence in the intestines. These are fermented milk products, carbonated drinks, bananas and grapes, as well as sweet pastries, bread and legumes, cabbage.
- At least three hours before the examination should not give the child to eat.
- An hour before the examination, the child should be given a drink of water. The bladder must be filled. This will help the doctor correctly estimate the amount of residual urine, understand the condition of the bladder and ureters. Children aged 1 to 3 years are given 100-150 ml of water or juice, children from 3 to 7 years old are offered a glass (250 ml) of liquid, schoolchildren from 7 to 12 years old - at least 400 ml, adolescents older - 600-800 ml .
An infant under the age of one year in the diet does not require any special restrictions. The only requirement is that the child should not be fed at the time of the diagnostic procedure. It is best to be examined before the next feeding. Before ultrasound, give the baby about 50 ml of liquid for half an hour, but no one guarantees that he will hold it. If the crumb wants to write, he will definitely not ask for your permission to do so at such a young age.
You need to take a clean diaper, second shoes and little mother's “tricks” to distract attention with you in the ultrasound room. If the child is small - it can be a dummy, a rattle, an object interesting to the child that he has long dreamed of reaching out, for example, your glasses. Distracting the baby will allow the doctor in a quiet mode to complete the examination.
If the child is at an age at which he can explain something, be sure to tell how the procedure goes, emphasizing that it does not hurt at all, it will not be scary. The child must be psychologically prepared.
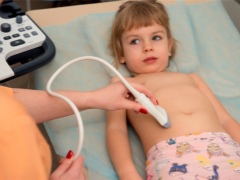
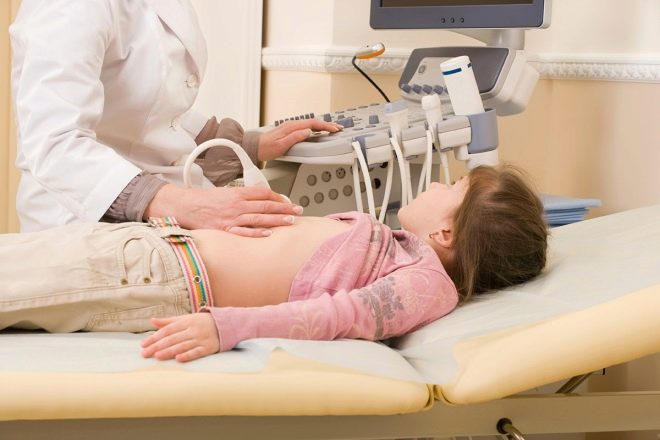
How is it done?
The examination is carried out on the couch in the prone position, only in some cases the doctor may ask to have the child sit down if, by virtue of his age, he already knows how to sit. If you suspect a kidney failure, they are asked to stand up. But you will have to lie during the survey in three positions - on the back, on the stomach and on the side. In such positions for the external sensor with which research is conducted, the review for the doctor will be the most complete.
To facilitate the sliding of the sensor and the best penetration of ultrasonic waves, a special colorless gel is used, which is odorless and does not cause allergies or local irritation. It is applied on the abdomen, lower back, on the sides. The gel does not leave marks on clothes, it is easy to wipe it at the end of the study with a disposable dry paper napkin.
These studies are recorded in the protocol, which is issued on the hands immediately after the diagnosis.
Norms
Decoding the conclusion is the business of professionals. Independent reasoning in this case is inappropriate. But if you really want to verify the data with the existing norms, especially if the doctor was laconic and did not tell his mother everything he knows, we give the norms in the table:
Age | Left kidney, mm | Right kidney, mm | The thickness of the parenchyma (mm) | Width of the pelvis (mm) |
0-28 days | 48-51.0 x 20.5-21.2 | 47.5-50.0 x 20.3-24.6 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
1-6 months | 52.3 -53.8 x 22.9-23.8 | 52.7-56.9 x 26.1-28.2 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
7-12 months | 61.8 x 24.6 | 60.6 x 29.7 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
1-4 years | 69.6-76.0 x 27.6-30.2 | 68.3-75.4 x 31.2-32.7 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
4-10 years | 82.5-86.8 x 31.9-34.6 | 80.5-85.4 х 34.5-36.3 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
10-14 years | 95.5-114.79 x 37.8-45.5 | 94.5-113.1x 37.9-41.0 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
Over 14 years old | 116.7 x 46.8 | 115.2 x 42.1 | 15-21 | No more than 10 |
Reasons for rejection
The increase in the parenchyma and the width of the pelvis is often the first sign of inflammation. The reason for it can be and salt, and metabolic disorders, and colds, and viral ailments. The size of the kidneys, their structure, the condition of the ureters and the bladder help to establish the presence of a wide variety of diseases and conditions - glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, urolithiasis.
Anomalies of the structure of organs can also be detected, as well as acquired and congenital tumors and neoplasms, cysts, impaired urine outflow due to the narrowing of certain parts of the kidney, ureter. The true causes of pathology, if any, will help establish a comprehensive study. Detection of urolithiasis, for example, cannot be considered reliable without confirmation from the laboratory - an elevated salt content (urates, oxalates, etc.) must be detected in the urine.
It should be noted that not all pathologies, especially in the early stages, make themselves felt by the appearance of characteristic symptoms. Occasionally, diseases of the urinary system organs are discovered quite accidentally when two or three urine tests in a row do not show the best results.
And therefore to refuse inspection if it is recommended by the doctor, it is not necessary. Kidney and bladder diseases respond well to therapy if the problem is detected on time and treatment is started as early as possible. Running forms are more difficult to treat.
Many parents note that the data obtained in one clinic may differ significantly from the data obtained in another. Much depends on the qualifications of the doctor, on the resolution and quality of the equipment on which the study was conducted. That is why sometimes several different doctors can set completely different diagnoses for the same child.
Many mothers who have the sad experience of numerous studies of the kidneys in children, urge not to trust the tables and norms, not to be guided by them, because much in size depends on how tall a child is, its weight, age and other, especially individual developmental features. Ultrasound of the kidneys in adults is more accurate than in children, because the size, especially in children under one year old, is small, the error is quite large. This, in the opinion of mothers, quite often becomes the reason for establishing erroneous diagnoses, which over time are not confirmed.
Today, mothers have a great choice - clinics and doctors for every taste and budget. Find a good specialist will help reviews of other parents who have problems with insufficient or overdiagnosis with ultrasound of the kidneys. Entire topics in parental forums are devoted to this issue.
How do ultrasound children do, see the next video.