Ultrasound of the hip joints for newborns and infants
Ultrasound examination of the hip joints in newborns and infants is a fairly accurate method, which allows to establish certain developmental anomalies of the musculoskeletal system at a very early age.
The pathologies may be different, but one thing unites them all: the earlier it is possible to find them and begin treatment, the more favorable the predictions for the health of the baby. That shows such an ultrasound, who is assigned and what are the rules, we will tell in this article.
About diagnostics
Ultrasound of the TBS (hip joints) is included in the first screening, which is conducted for children at the age of 1 month. This study is conducted by children for free. At any age, such a diagnostic examination can be appointed by an orthopedic specialist, if he suspects certain visual abnormalities in the development of joints by visual examination of a child.
Such a study with the help of ultrasound allows to assess the condition of the joints, their position, size. Most often at an early age occurs subluxation of the hip joint and precursors. Less common full dislocation. All of these stages are easily diagnosed when conducting a painless, non-invasive examination procedure using ultrasound.
In hip dysplasia, the doctor will be able to accurately determine the severity of the pathology, which is necessary for the appointment of an exact treatment regimen. The danger of failure of a routine screening ultrasound of the hip joints lies in the fact that the existing pathology for a long time may go unnoticed. Late treatment or lack of it can lead to very serious consequences: lameness, movement disorders, disability.
The Russian Ministry of Health recommends a study for all infants. But especially in need of it:
- premature babies;
- children in the family who have relatives with joint pathologies;
- children who were in a breech presentation during pregnancy;
- babies who were hatched and given birth in large cities, in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- babies born to pregnancy accompanied by low water, severe toxicosis, vitamin deficiency and anemia.
As for the targeted direction to such an examination, it is most often given in the presence of such symptoms:
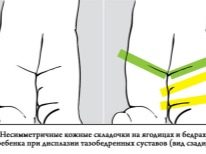
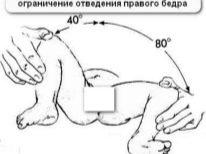
- skin folds on the legs of the newborn are not symmetrical;
- dilution of the hips of the baby is difficult, limited;
- joints when moving legs create a crunch or click;
- the baby’s legs are not just in good shape, the doctor qualifies him as hypertonus;
- the child was not born alone - he is one of twins or triplets;
- birth trauma and neurological disorders were found in the baby;
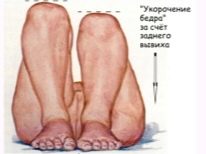
- limbs have different lengths.
How is it done?
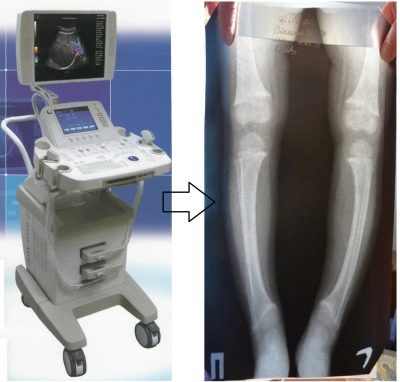
TBS ultrasound is a classic ultrasound based on the properties of ultrasonic waves to penetrate tissue, reflect from the surface of organs, joints, bones, and fluid cavities. The return signal goes to the monitor and forms an image that the doctor decrypts.
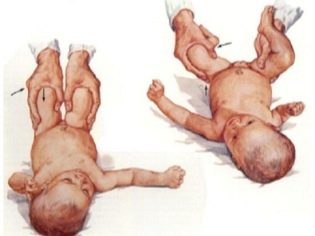
The procedure is performed on a standard couch. The child is laid on its side. The doctor will bend the legs in the hip joints while simultaneously applying the sensor to the pelvic region of the baby. Both joints are examined alternately.
The procedure takes no more than 10-15 minutes, it is painless and completely safe for the child. Parents can not worry: the harmful effects of ultrasound - no more than speculation, not confirmed by science and medical statistics.
Children at the age of 2-8 months are not considered to have a diagnostic procedure. It is during this period that the ossification of the femoral head is actively ossified, areas of darkening appear, and therefore the diagnosis loses a substantial percentage of accuracy.
Do I need training?
The only thing that parents should do before such an ultrasound is to feed the baby as best as possible. The more calm and quieter the baby is during the examination, the more accurate the results will be obtained by the doctor.
Experts recommend feeding the child half an hour before undergoing the diagnostic procedure.
Mom also needs to take with her a diaper with which she made the couch in the office, a pacifier and a rattle in order to divert the little one’s attention if he nevertheless decides to “show character”. The baby’s clothing should be easy to unfasten and take off.
Decryption
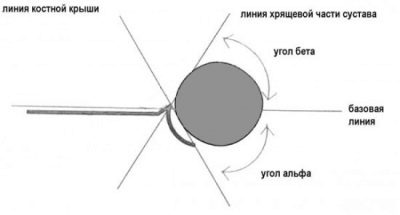
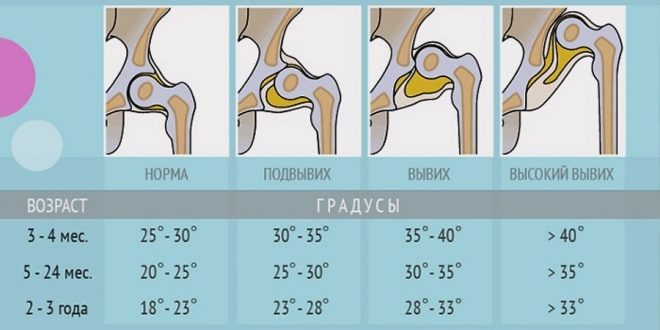
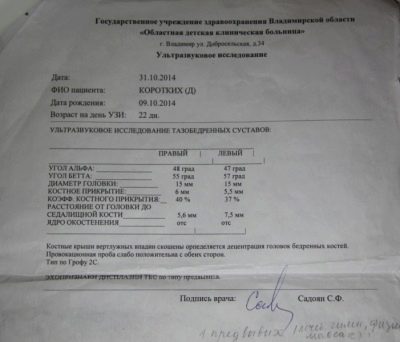
The position of the joints and the femoral head is not only visually assessed. To determine their condition, a special angle measurement is used according to the Graph table. There is an alpha angle and a beta angle.
- Alpha refers to the development of the bony part of the vetsel fossa.
- Beta describes the cartilage space inside the vein cavity.
For healthy children, it is considered normal if the Alpha angle is more than 60 degrees, and the Beta angle is less than 55 degrees.
A slight excess of the norm of 55 degrees is permissible, such a joint is considered normal, mature. But if the Beta angle is 77 degrees, the doctor will imprison the suspicion of dislocation or subluxation. Also the pathology is indicated by the angle Alpha, which is in the range of 43 degrees.
The norm of the angles in the table is as follows.
Angle "Alpha" | Beta Angle | Bone protrusion | Conclusion |
More than 60 degrees | Within 55 degrees | Flattened | Healthy mature joint |
50-59 degrees | Less than 55 degrees, tight on the thigh | Rounded | Physiologically immature joint |
50-59 degrees | Less than 55 degrees | Round, almost flat | Ossification delay |
43-49 degrees | Less than 77 degrees | Flattened | Adverse prognosis |
43-49 degrees | More than 77 degrees | Flattened or flat | Initial decentralization |
Less than 43 degrees | Does not cover the head | Flat | Decentration, total immaturity of the joint |
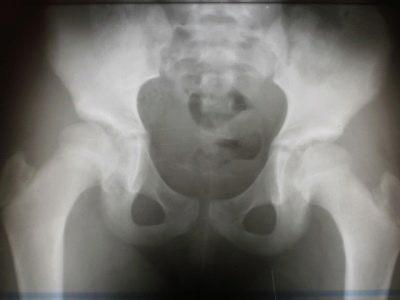
During the growth of the child, the indicators may change, this is what the doctor will take into account during the ultrasound. If the child is already four months old, the most accurate and accurate method of examination will be an x-ray.
If problems are found, doctors try to examine the pelvic bone structure at the same time. Quite often, the pathology of the hip joint is reflected on it.
In conclusion, the doctor may be laconic and would prefer to limit himself to the alphanumeric designation of the type of joint found in the child. Remember that a healthy joint is always referred to as 1A or 1B.
If the conclusion states that a joint 2A or 2B has been found, this means that the child has signs of physiological immaturity, which will pass on its own with great probability, but still will require observation from a pediatric orthopedist.
Joint 2C - a joint with signs of pre-dislocation. Obligatory observation of a doctor and implementation of all his recommendations is required. 3A and 3B - subluxation joints. The most severe pathology is a joint of 4 types. This is how the hip joint with signs of dislocation (dysplasia) is indicated.
General recommendations
Many mothers who are faced with diagnoses such as the immaturity of the hip joints in a newborn, note that there should be no reason for panic. In the overwhelming majority of cases, only a systematic orthopedic visit is required for monitoring. Ripen joints independently.
Most mothers say that a massage prescribed by a doctor, special therapeutic exercises and calcium supplements helped to cope with the problem detected by ultrasound at an early age. His mothers give their babies with breast milk, that is, they increase the dose of calcium in their own diet, they begin to take calcium preparations specially.
Children are recommended widespread swaddling, wearing diapers more than the size required, so that the legs are more often in a divorced state.
Parents often point out that ultrasound scan of the TBS is closely related to the phenomenon of overdiagnosis: doctors are often “reinsured”, revealing the physiological immaturity of joints in almost every second child during screening.
For more information about the method of ultrasound examination of the hip joints for newborns and infants, see the following video.