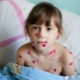
Possible complications after chickenpox in children
Most parents find chickenpox to be a fairly mild illness. Such an opinion about chickenpox is associated with a mild course of this infection, which is noted in the majority of sick children. However, chickenpox is not always harmless, because in adolescents and adults it goes much harder. In addition, complications after chickenpox are also found in childhood.
What could be the consequences of such a childhood infection and how to prevent them? What symptoms suggest that complications have started? Can chickenpox give complications to the heart or pose a danger to a child's life? These questions concern any mother, because with chickenpox, almost everyone is at risk.
How is chickenpox transmitted
The causative agent of varicella, which belongs to the herpes viruses, is transmitted from sick children to previously ill people with varicella by airborne droplets. The child becomes infectious from the last day of the incubation period and releases the virus with droplets of mucus through the respiratory organs throughout the entire period of eruption. It is possible to get an infection from a sick baby even within five days after the last rash appeared on his body. Next, the child with chickenpox becomes non-infectious.
Why complications may arise
The most susceptible to the pathogen of chickenpox children aged 2-7 years. It is in them that such an infection proceeds quite easily - with a slight rise in temperature and not too heavy rash. However, chicken pox is sick and kids up to a year, and adolescents in 14-16 years, and adults who have not had this disease in childhood.
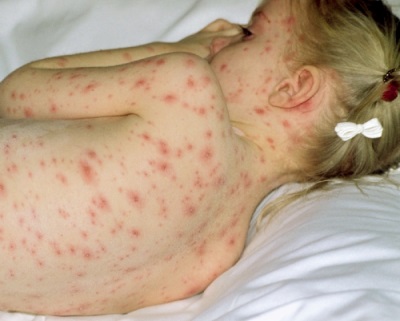
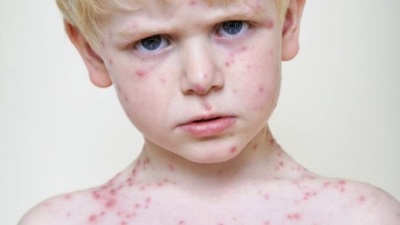
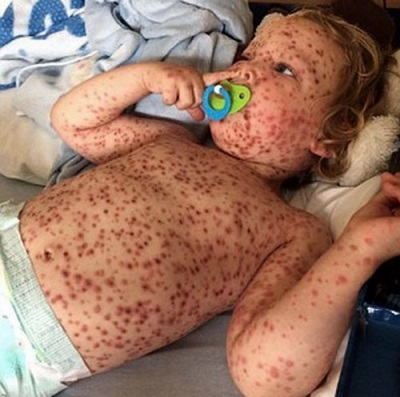
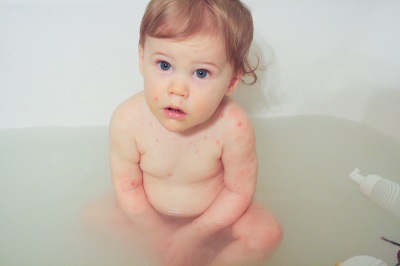
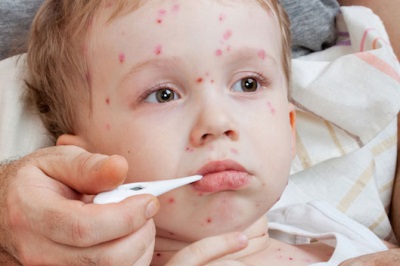
All these categories may have a severe course in which the body temperature rises to 40 ° C and the rash is represented by a very large number of bubbles. It is in such people that various complications of chickenpox are possible. A major role in their development is played by a decrease in immune defense and the presence of chronic diseases.
All complications provoked by chickenpox are of two types:
- Viral - caused by the toxic effect of the pathogen. To prevent their development in severe chickenpox, antiviral drugs are used, for example, acyclovir.
- Bacterial - when a microbial infection joins due to reduced immunity. To avoid such complications, you can follow the rules of hygiene (bathe the child after reducing the temperature, regularly change clothes, shortly cut nails, distract) and use antipruritic drugs.
Chickenpox Pneumonia
Inflammation of the lungs is one of the frequent complications of severe chickenpox. It is characterized by the appearance of chickenpox cough and shortness of breath, blue skin, hemoptysis. Children and adults with such symptoms should be immediately hospitalized, since they increase the risk of pulmonary edema and respiratory failure. In addition, before treating the pneumonia-induced pneumonia, its nature is ascertained, since it can be caused by both the chickenpox virus and the bacterial flora that have fallen into a weakened organism.
Chickenpox encephalitis
A child or adult with severe varicella is always at risk of getting encephalitis. Such a dangerous complication can be identified by the following symptoms - very high body temperature, vomiting episodes, severe headaches, the appearance of convulsions, tremor of the limbs, shaky gait and impairment of consciousness.
Treatment of varicella encephalitis is necessary in the hospital, and the mortality rate with this complication reaches 10%. In addition, 15% of those suffering from encephalitis with chickenpox have consequences in the form of epilepsy, paresis, and other lesions of the nervous system. In addition to encephalitis, chickenpox may be complicated by meningitis, polyneuritis, or inflammation of the optic nerve.
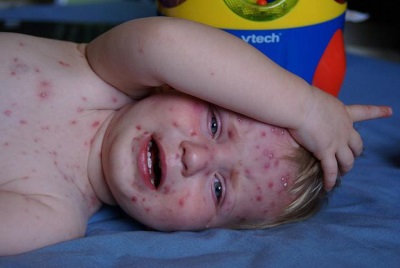
Skin complications
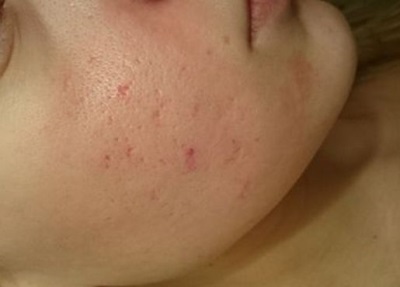
These are quite common effects of chickenpox, which are associated with scratching itchy bubbles. When pathogenic bacteria get inside the wounds, this causes purulent inflammation. It is not life-threatening, but after healing, there are “marks” in the form of scars and scars on the skin. Remove them hard enough and sometimes impossible.
Other complications
In more rare cases, the effects of chicken pox are such problems:
- In some patients, nephritis is possible, which develops at the end of the rash period and manifests itself in abdominal pain, headaches, and vomiting.
- Sometimes with chickenpox, the liver is affected with the development of hepatitis.
- It is also possible damage to the heart (myocarditis), representing a danger to the patient's life.
- The appearance of a rash in the oral cavity can lead to stomatitis, and in the ear - to otitis.
- When the lesions go to the area of the larynx and pharynx, a life-threatening complication such as chickenpox is possible.
- Chickenpox eruptions on the genitals in girls can cause vulvitis or vaginitis, and in boys cause inflammation of the foreskin.
- If bubbles form on the mucous membrane of the eyes and bacteria enter them, this leads to bacterial keratitis, which ends with cicatricial corneal opacities and a decrease in visual acuity.
- Chickenpox can also cause myositis, arthritis, bursitis or thrombophlebitis.
You can learn more about chickenpox from Dr. Komarovsky’s program.