Which is better to choose vitamin D for infants and how to give it?
Vitamin D is one of the key substances required for the full development of the child's body. It is prescribed to babies to prevent deficiency and the development of various pathologies. At the same time, parents should understand why their baby has vitamin D, which drugs include this vitamin and how to give them.
Purpose
For babies, enough vitamin D is essential. The lack of this vitamin threatens a child of the first year of life with a disease such as rickets. The treatment of the disease itself and its consequences is complicated, so it is easier to prevent such a problem by timely prescribing vitamin D in the form of medicines.
This vitamin is responsible for the metabolism of calcium as well as phosphorus. It affects the growth of bones in the children's body, the strengthening of the skeleton, the development of muscle tissue, and the development of teeth. Also, this vitamin is important for immunity, the nervous and cardiovascular system, skin condition, intestinal functioning and many other processes.
The following criteria affect the prescription of vitamin D in infants:
- Place of residence. Since the main part of vitamin D is produced in the skin under conditions of exposure to direct sunlight, in the southern regions its shortage is not a problem, but for children born in the north of the country, it is important to prescribe vitamin D in preparations almost from birth.
- Breast-feeding. If the baby gets breast milk, the focus is on enough vitamin D in the mother's body. Also, crumbs on HB are usually additionally prescribed prophylactic doses of this vitamin.
- Season. Appointment of vitamin D is justified in the autumn-winter period, when walks become shorter, and the sun's rays for the full production of vitamin in the skin is not enough.
- Artificial feeding. Appointment of vitamin D to babies who receive breast milk substitutes, adjusted to the presence of vitamins in the mixture. In winter, artificial crumbs are often given extra vitamin D.
There are also categories of children who are at increased risk of rickets, so vitamin D is almost always prescribed for them.
These categories include:
- Premature.
- Babies with dark skin color (their vitamin D production in the skin is reduced).
- Children who take medicines that affect the absorption of vitamin D.
Symptoms of vitamin D deficiency
The fact that the body receives less vitamin D can be judged by the appearance of such signs as:
- Increased sweating of the head and limbs.
- Hair loss.
- Decreased appetite.
- Bloating.
- Sleep disturbance
- Behavior changes - the child is often naughty and over-excited.
- The appearance of an itch.
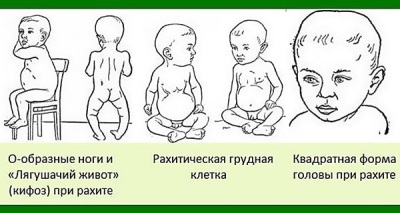
These are the first symptoms, and if left unattended, after a few weeks the growth of the skeletal system and the child’s teeth will slow down, and the work of the internal organs will break. Parents will notice the deformation of the bones and the delayed development of the crumbs.
Lack of treatment at this stage will lead to a slowdown in the development of the musculoskeletal system, an increase in the size of the head, muscle weakness, thickening of the ribs, a delayed closure of the large spring and softening of other parts of the skull, curvature of the spine and many other problems.
How old do you start giving?
Vitamin D preparations can be prescribed from birth, if the doctor sees for this purpose certain indications. Full-term infants, in most cases, are prescribed an additional dose of vitamin D from 1 month, and premature babies from two weeks of age. In some cases, babies start taking such supplements from 6 months of age.
Kinds
Vitamin D, which is given to babies for prophylaxis and for therapeutic purposes, comes in two different forms:
- The oily form of vitamin D.
- Water form of vitamin D.
The first is distinguished by better absorption and greater biological value, however, it is worse tolerated and more difficult to dose, and the second has no toxic effect and rarely causes allergies.
The aqueous form is often prescribed for prophylactic purposes, and when the first symptoms of rickets occur, the doctor usually prescribes an oil preparation.
If the child is premature, it is often prescribed an aqueous solution because of its more gentle action.
Prices
Buy drugs containing vitamin D, can be in each pharmacy. The cost of the funds will affect its manufacturer. Domestic vitamins are the least costly, for which you need to pay about 200 rubles. Drugs brought from abroad are more expensive - about 600 rubles. In some cases, the mother is given a privileged recipe, and she can get vitamin D for the baby for free.
Which vitamin D is better to choose?
Vitamin D a child can get from these drugs:
- Fish fat. For the youngest babies, it is produced in the form of an oil solution, while the modern forms of children's fish oil have a pleasant taste.
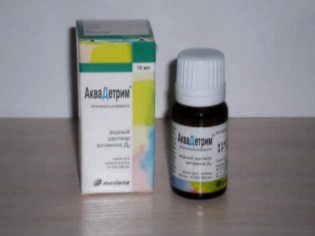
- Akvadetrim. This drug, which is an aqueous solution, provides the child’s body with 500 IU of vitamin D3 in each drop. Recommended from 4 weeks of age.
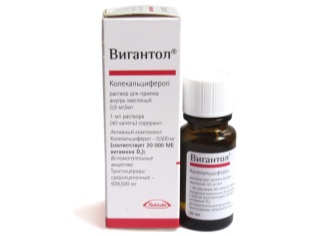
- Viganol. A drop of this oil solution contains 667 IU of active ingredient. The tool is discharged from 2 weeks of age.
- D3 Devisol Drops. This is a vitamin D preparation of Finnish production, which is often addressed in the winter to prevent hypovitaminosis. It is represented by an oil solution of vitamin D3.
Norms
All nursing babies are prescribed medication in the form of drops. The dosage of prescribed vitamin D in the drops in each case is calculated individually. The doctor takes into account the time of year, the type of feeding, place of residence, age and other factors. The standard dosage is one drop, which contains 500 IU of active ingredient.
Instructions for use
Both oil and water form of vitamin D is recommended to be taken in the morning - after breakfast. The drug is dripped into a spoon in the right dose, then add a little boiled water and give the child to drink.
What threatens overdose?
Excessive dosages of drugs with vitamin D cause poisoning, which affects the exchange of calcium and affects the state of the nervous, cardiovascular and digestive systems.It is manifested by poor sleep and appetite, vomiting, alternating diarrhea and constipation, dry tongue, difficulty breathing, bradycardia, the appearance of thirst, an increase in temperature to subfebrile numbers, loss of skin elasticity. Having noticed such symptoms in a baby, one should immediately consult a doctor, otherwise intoxication may result in convulsions, dehydration, arrhythmia and other dangerous conditions.
Opinion Komarovsky
A popular pediatrician considers the prevention of vitamin D deficiency as an important and simple task. He recommends the use of preventive measures from October to March, when the mother with the child does not dwell under the sun.
Breastfeeding Komarovsky recommends taking vitamin D to a nursing mother as part of a multivitamin complex or as an oil solution (1 drop every three days). A well-known doctor advises starting to give vitamin supplements to an infant from the moment when the supplement in the baby's diet has exceeded one third of the total amount of food per day.
Komarovsky offers to an infant to give two drops to a weekly basis, and only 1 drop to an artificial child - as vitamin D is added to milk formulas. If a nursing mother or baby was under the sun during the day, although it should be 30 minutes, Komarovsky does not recommend vitamin D in drops.
Watch the following video in which Dr. Komarovsky talks to parents about vitamin D.
Correct nutrition for vitamin D
In order to increase the dietary intake of this vitamin, as well as calcium and phosphorus, the following should be included in the infant diet:
- Cottage cheese
- Milk
- Cheese
- Butter
- Sea fish
- Cod liver
- Seafood
- Oatmeal
- Buckwheat groats
- Potatoes
- Parsley
If the baby is breastfed, such products should be present in the mother's menu so that enough vitamins pass into breast milk.
Reviews
Most parents are positive about the administration of drops with vitamin D and say that the drug did not give any side effects, and the child’s appetite and sleep improved. However, sometimes parents prefer to do nutritional correction and more often to be in the sun, refusing to give crumbs medicinal supplements.
Many are more supportive of fish oilthan to vitamins in drops. The same parents, who gave the children different forms of vitamin D, note that the kids like the taste of the oil more than the oil form.