B vitamins for children
The group of vitamins B includes several vitamin substances that perform different functions, but very important for the health of the child. The lack of any of these vitamins adversely affects the work of the organism as a whole. And therefore, all parents should know which vitamins belong to the B-group and how important they are for the child, as well as what foods and vitamin preparations they contain.
The value of B vitamins and the need for children
IN 1
The daily need for thiamine at different ages is:
|
Age |
Mg requirement |
|
Up to a year |
0,3-0,5 |
|
1-2 years |
0,7 |
|
3-6 years old |
0,9 |
|
7-10 years |
1-1,2 |
|
Teen girls |
1,1-1,3 |
|
Teen boys |
1,5 |
AT 2
Without a sufficient amount of vitamin B2, the adrenal glands are disrupted, and vision deteriorates, as riboflavin is a component of the pigment that protects the retina from the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation and is responsible for night vision.
A child needs riboflavin per day in such quantity:
|
Age |
Mg requirement |
|
Up to a year |
0,4-0,6 |
|
1-2 years |
0,8-0,9 |
|
3-6 years old |
1,1 |
|
7-10 years |
1,2-1,4 |
|
Teen girls |
1,3-1,5 |
|
Teen boys |
1,8 |
IN 3
This vitamin is called nicotinic acid, niacin or Vitamin PP. The main functions of this compound are to participate in the synthesis of hormones, the metabolism of nutrients and the formation of enzymes. Niacin is also important for the synthesis of red blood cells, the work of the central nervous system, heart and blood vessels.
The daily need for vitamin PP in children is:
|
Age |
Need in mg |
|
Up to a year |
5 |
|
1-2 years |
9 |
|
3-7 years |
12 |
|
8-11 years old |
12-15 |
|
Teen girls |
15 |
|
Teen boys |
17 |
AT 4
This vitamin is also called cholinesince it was first obtained from bile. Its main function is called participation in the metabolism of fats and liver work. In addition, this vitamin has a beneficial effect on such functions of the nervous system as attention and memory. Per day choline is required for a child in the amount of 100-350 mg.
AT 5
This vitamin is also called "Pantothenic acid". It is important for attention, heart function, fat splitting, wound healing, regeneration of mucous membranes and skin. Also, this vitamin is required to support hormonal levels and immunity.
Per day, this vitamin is required for children in such quantities:
|
Age |
Mg requirement |
|
Up to a year |
2 |
|
1-2 years |
3 |
|
3-6 years old |
4 |
|
7-11 years old |
5 |
|
Teenagers |
4-7 |
AT 6
This vitamin, another name is pyridoxine, is extremely important for amino acid metabolism. This compound also takes part in blood formation and hemoglobin formation, it affects the acid-base balance and blood glucose level.
Vitamin B6 stimulates the excretion of excess fluid from the body and improves the immune system.
Every day, the child needs to receive pyridoxine in such quantities:
|
Age |
Mg requirement |
|
Up to a year |
0,5 |
|
1-2 years |
1 |
|
3-6 years old |
1,1 |
|
7-11 years old |
1,4 |
|
Teen girls |
1,6 |
|
Teen boys |
2 |
AT 7
This vitamin, also called biotin or vitamin H, extremely important for the condition of the skin, since He is involved in the formation of collagen. A sufficient intake of such a vitamin ensures the normal condition of the nails and hair, and is also necessary for the metabolism of fats and the work of digestive enzymes.
The daily intake of biotin in childhood should be as follows:
|
Age |
Required in mcg |
|
Up to a year |
15 |
|
1-2 years |
20 |
|
3-6 years old |
25 |
|
7-11 years old |
30 |
|
Teen girls |
20-40 |
|
Teen boys |
50 |
AT 9
This vitamin is also called folic acid. It is very important for the formation of neurotransmitters, the production of gastric juice, growth and cell formation. This vitamin is required for normal blood formation, as well as protein metabolism.
Every day, children need folic acid in this amount:
|
Age |
Mcg need |
|
Up to a year |
25 |
|
1-2 years |
50 |
|
3-6 years old |
75 |
|
7-10 years |
100 |
|
Teenagers |
200 |
AT 12
This vitamin, called cyanocobalamin, required for normal division of germ cells, as well as cells in the bone marrow. Such a compound is involved in most physiological processes in the child's body, affecting metabolic processes, immunity, sleep, mental functions and much more.
Children's need for vitamin B12 every day is:
|
Age |
How many need in mcg |
|
Up to a year |
0,4 |
|
1-2 years |
0,7 |
|
3-6 years old |
1 |
|
7-11 years old |
1,4 |
|
Teenagers |
2 |
Read more about vitamin B12 in the program "Live Healthy".
Lack of B vitamins
Hypovitaminosis of compounds belonging to the group of vitamins B, quite often occurs in childhood and is manifested:
- Pale and dry skin.
- Eels or boils.
- Loss and dryness of hair.
- Decreased attention.
- Pain in the heart and shortness of breath.
- Problems with the digestive system (reduced appetite, flatulence, nausea, and others).
- Frequent conjunctivitis.
- Weakness
- Anemia
- Vision problems.
- Stomatitis.
- Insomniac
- Increased irritability.
We recommend to watch the video, which describes in more detail the symptoms of hypovitaminosis in children:
It is especially important to pay attention to the intake of B-vitamins in sufficient dosages for such groups of children:
- Nursing babies.
- Teenagers.
- Children with chronic illnesses.
- Babies who are malnourished.
- Often sick kiddies.
- Children attending sports clubs.
Why vitamin B deficiency is called the problem of the XXI century, see the next video.
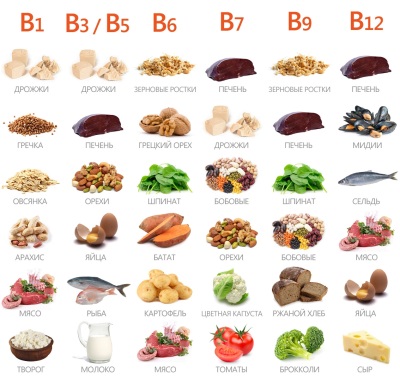
Products
Sources of vitamins included in group B are:
The name of the vitamin | Where is contained |
IN 1 | Whole Grain Products, beans, cereals, peas, liver, nuts, meat, bran, yeast |
AT 2 | Spinach, eggs, green peas, dairy products, offal, yeast, mushrooms, buckwheat, rosehip, oatmeal, meat, rye flour, tea |
IN 3 | Offal, chicken, eggs, pork, nuts, porcini mushrooms, cereals, fresh vegetables |
AT 4 | Egg whites, bran, liver, nuts, soybeans, green tea, trout, sunflower seeds, dairy products |
AT 6 | Porridge, nuts, yeast, chicken and rabbit meat, garlic, tomato, fish, lamb, cabbage, potatoes, raisins |
AT 7 | Offal, egg yolks, yeast, peanuts, almonds, oatmeal, peas, fish, chicken, rice, cottage cheese, cabbage, plums, grapes |
AT 9 | Fish, offal, yolks, hard cheese, caviar, cheese, buckwheat, millet, rolled oats, green vegetables, berries, avocado |
AT 12 | Meat products, eggs, fish, offal, dairy products, hard cheese, soybeans, sea kale |
Vitamin supplements
Vitamins B1, riboflavin, pyridoxine and vitamin B12 can often be seen in vitamins for children, since these are the most important compounds for the life and growth of the child's body.
Pediatricians argue about the need to introduce vitamin complexes in the diet of children. For example, the authoritative doctor Komarovsky does not see them as necessary, but he sees the Union of Pediatricians of Russia. See the following videos for details.
Overdose
Dangerous only one-time use of a large dose of such vitamins, which can lead to intoxication and digestive problems.
The best drugs and their names
To prevent vitamin B deficiency in childhood, you can use these vitamin complexes:
- Multi-tabs. In the line of these multivitamins, group B is presented in additions Kid for children 1–4 years old and Junior for children 4–11 years old. These drugs are chewable tablets containing 7 vitamins of group B. There is also group B in the multivitamins Teenager and Imuno Kids, where biotin is also present (there are a total of 8 B-group vitamins).
- Pikovit. The Pikovit 1+ complex, represented by syrup for babies older than a year, contains 5 basic vitamins of group B. Pikovit 3+ chewable tablets for children over three years old, complexes for children over 4 years old (Pikovit 4+ tablets and Pikovit D tablets), and also Pikovit Forte tablets for children over 7 years old include 7 vitamins of this group. Biotin is additionally present in the Pikovit Plus chewable tablets.
- Alphabet. A feature of such vitamin preparations is the separation of vitamins and minerals into 3 single doses, which take into account their compatibility and absorption. In one dose (sachet №1 Our baby) vitamins B12 and B9, as well as pantothenic acid are presented. In the yellow tablet Kindergarten and white tablets Schoolboy and Teen, they are supplemented with biotin. In another dose (sachet number 2 Our kid, orange tablets Kindergarten, Schoolboy and Teenager) contains vitamins B2, B6 and B3. The third dose (sachet number 3 Our baby, pink tablets Kindergarten, Schoolboy and Teenager) contains folic acid and vitamin B1.
- Vitamishki. In these vitamins in the form of cute bear cubs recommended from 3 years of age, group B is represented in Focus + complexes (contains riboflavin), Multi + (contains choline, vitamins B1, H, B5, B12, pyridoxine, folic acid and biotin) and Bio + ( contains vitamins B1, B6, biotin, choline and niacin).
- Vitrum Junior. This preformed complex for children over 6 years old contains 8 essential vitamins of group B.
- Jungle. Such a children's vitamin complex in chewable tablets, approved from 2 years of age, contains vitamins B1, B2, B6, B9, niacin and B12.
- Kinder Biovital. Such a popular multivitamin preparation in the form of a sweet gel includes 6 basic vitamins of group B.