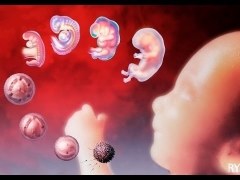
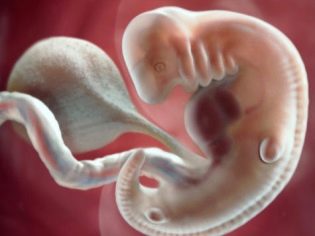
The development of the embryo on days after transfer during IVF
Women who are being treated for infertility by IVF, as well as those who are still thinking about joining the protocol, are interested in finding out how the fetus develops after it is transferred to the uterine cavity. Embryo transfer is considered the final stage of the protocol, and after it remains only to wait for confirmation of pregnancy, if it comes.
We will tell about what happens to the embryo in this difficult and filled with anxiety and expectation period in this material.
About the beginning of life
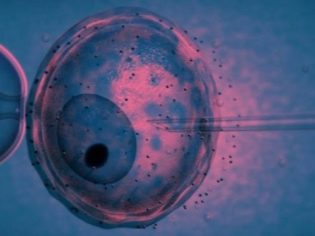
From the moment when the reproductive cells of the male and female sex cells are at the disposal of a new and interesting stage begins. The egg must be fertilized. During in vitro fertilization, doctors can arrange a meeting with the spermatozoon in a special laboratory Petri dish, or they can conduct a more complicated procedure, ICSI, in which a separate spermatozoon is injected directly into the cytoplasmic fluid under the oocyte membranes.
Anyway, in a few hours, if fertilization took place, the embryological stage of your baby’s life begins. The very next day after the collection of oocytes, a woman can find out the first results - how many embryos are obtained.
The embryos are placed in a nutrient medium, where they develop for several days under the supervision of an embryologist.
The doctor assesses the rate at which each fertilized egg, which has already passed to the zygote stage, is crushed. The appearance of the cells, the thickness of the walls and the intercellular membranes, the correct number of nuclei in the size of two is important. As a result, at this early stage, all embryos are divided into four categories:
- germs of category A (excellent quality);
- Category B (good quality) germs;
- category C embryos (of satisfactory quality);
- embryos of category D (poor quality).
Embryos of excellent and good quality are recommended for transfer to the uterus. If these could not be obtained, category C germs may be allowed as an exception, but germs of unsatisfactory quality for transfer are not recommended. The higher the category, the more likely the embryo is to implant.
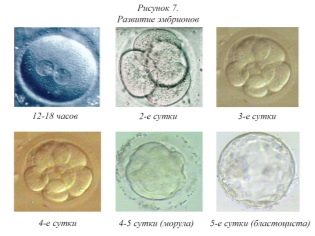
On the second day after fertilization, the zygote has from 2 to 4 blastomeres. Depending on the exact number, the embryos receive their first “name” - they are designated as follows: 4B or 2C. If they call you such alphanumeric combinations, it means the following:
- 4B - a category “B” embryo was obtained and on the second day he already had 4 blastomeres;
- 2C - an embryo of category “C” was obtained and on the second day he had 2 blastomeres.
There may be other options - 4A, 2A, 4C, 2B, etc. In any case, the number will indicate the number of blastomeres, and the letter will indicate the quality of the embryo. The best will be recommended for transfer to the uterus, which not only have a high category, but also rather quickly break up, increasing the number of blastomeres.
The third day of embryonic development is considered crucial in many ways. By this day, the development of embryos with gross anomalies in the genome usually spontaneously stops.
Doctors place the embryos “three days” in the woman's uterus only if the embryos are not of the highest quality, for example C.This is due to the fact that in the natural environment of the uterus in the embryo will be more likely to further development.
On the fourth day, the zygote becomes a morula - this is a qualitatively new stage in the development of your future baby. Morula already consists of 10-16 blastomere cells. Externally, the morula looks like a blackberry berry. If a woman becomes pregnant naturally, on the fourth day the morula may well go into the uterine cavity, and it can still pass the mouth of the fallopian tubes.
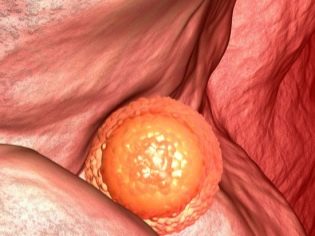
A day later, on the fifth day, the morula becomes a blastocyst. From this period, embryos are considered completely ready for implantation. For this reason, often the transfer of viable embryos of good and excellent quality is usually carried out on day 5.
The decision on the transfer is made by two doctors collectively: an embryologist who monitors the development of the embryo, and a fertility specialist who knows the exact answer to the question of whether the endometrium of the woman’s uterus is ready for the upcoming implantation.
In some cases, a later transfer by the totality of evidence from these two specialists is recommended. However, six-day and seven-day embryos take root much worse.
At 6-7 days of development, the embryo is already called a gastrula. If it is located in the uterus, implantation may already begin, since the membranes of the gastrula already release certain enzymes to dissolve the functional layer of the endometrium and introduce it into it.
After embryo transfer
The development of embryos after transfer may differ somewhat, it depends on the age of the embryo and the favorable circumstances for its development. Let's look at all the options for embryonic development after the IVF protocol is completed.
"Three days"
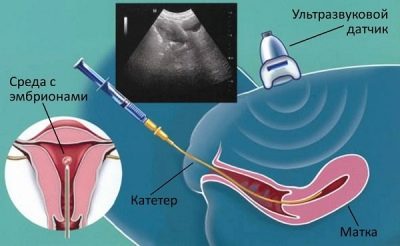
The zygote, which is the fertilized egg at this moment, consists of 6-8 cells. Zygotes are inserted into the uterus using a soft and flexible catheter through the cervical canal of the cervix. It is advisable to replant at the end of the third day, because it is during this period that the so-called “developmental block” often arises - some of the embryos cease to break up and stop growing because of the presence of gross genomic anomalies. It is the genome that “dictates” the rules of development. It contains all the information about which cells should divide and how to differentiate and how.
If the quality of germ cells was high enough, the chances of getting embryos with a full-fledged genome are higher. But even in the case of the fusion of perfectly healthy germ cells (normal oocyte and high-quality spermatozoon), they do not guarantee that some genomic anomalies will not arise during the fertilization process. That is why it is important for the embryologist to make sure that on the third day of development the embryo does not have a “developmental block”.
It is not excluded that development will stop even after the transfer, but in this case the reasons may be not so much genetic as physiological: the endometrium was not ready to accept the embryo, the hormonal balance of the woman is not favorable enough due to other factors.
So, a three-day planting was done. During the first days after the transfer, the embryos cannot consolidate even theoretically, they freely “float” in the uterine cavity. The embryonic period of their development continues. The embryo transfer procedure itself does not affect the embryo if the procedure is carried out correctly. Zygotes are introduced into the uterus along with a small amount of nutrient medium in which cultivation took place.
The day after the transfer, the embryos in the uterus go to the morula stage. Forms of the embryo become more even, intercellular bonds - more dense. At the end of the first day after the transfer, a hollow space appears inside the morula, it expands.
The process, which in embryology is called “cavitation”, starts: blastomere cells begin to divide into two parts.Each of the groups of cells will be assigned its own nature by nature, because very soon the intensive laying of organs and systems of the fetus will begin.
The second day after the embryo-three-day embryo transfer procedure corresponds to the fifth day of embryonic development. On this day, the morula becomes a full-fledged blastocyst. Inside it, the process of cavitation continues, the cavity inside expands.
If the process takes place in favorable conditions, within a day after the start of the blastocyst stage, the embryo will leave the enlarged cavity and will be able to begin the implantation process. If conditions are not too favorable, the process may be delayed for a couple of days or stop altogether, and then the pregnancy will not come.
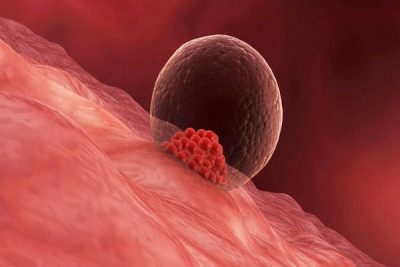
The implantation process begins immediately after the embryo leaves the blastocyst cavity. The first stage is adhesion. The embryo simply sticks to the endometrium of the uterus. Immediately after this, its membranes begin to produce special enzymes that gradually dissolve the cells of the functional layer of the uterus. The fetus "buries" in the endometrium, strengthens in it, this stage is called invasion. On both stages of implantation takes an average of 3-4 days. All this time, the process of separating cells according to functionality in the baby’s body does not stop, the number of blastomeres is rapidly increasing.
On the completion of implantation after the transfer of three-day embryos, thus, it is possible to speak only on the 6-9 day after the transfer. Norms do not exist, implantation may be later if the embryos are transplanted in the cryoprotocol.
On days 6–9 after the transfer, the embryo that managed to implant already produces chorionic gonadotropin: this hormone produces chorionic villi, with which the embryo attaches to the uterus.
From the moment of attachment, your crumb already receives oxygen and nutrients from the maternal blood. At the site of attachment of the chorion to the 12th week of pregnancy, a full-fledged placenta will be formed.
"Five Days"
Many of the processes described above embryo, which is five days old, does not take place in the mother's body, but in the nutrient medium in the laboratory. It enters the uterine cavity already at the blastocyst stage, ready to exit its expanded cavity and start the implantation process. It is for this reason that embryo transfer on day 5 is more common and is considered more effective. In fact, the embryo immediately enters the uterus, and within a few hours it is ready to begin its consolidation.
The day after the ECO transfer in the uterus, the woman already lives not the blastocyst, but the gastrula, and with favorable circumstances, adhesion has already begun. Two days after the transfer, the invasion process starts, and in another day the implantation may well end. Although in the case of five-day embryos, late implantation is possible.
Every minute in a small organism (this is not just a set of cells and genes, but a full-fledged new life), the most important and intensive processes take place:
- biochemical (production of enzymes, hormones by chorionic villi);
- biophysical (cells continue to break up, their differentiation into destination is already beginning);
- there is a metabolism (the crumb already eats, receiving necessary substances from my mother's blood);
- anatomical (the laying of the first organs begins, which so far represent certain groups of cells, the first cells responsible for the formation of the heart are laid already 5 days after IVF).
Uterine period
An embryo or several embryos behave approximately equally after implantation and develop at approximately the same rate.
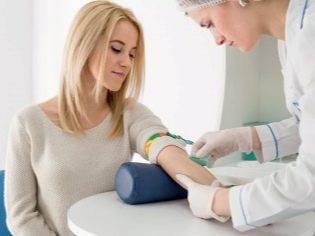
Two weeks after embryo transfer, a woman can already know about her pregnancy: a blood test will show it, since plasma hCG will accumulate in sufficient quantity. 21 days after the transfer, you can and should do the first ultrasound.
All this time, the baby will grow rapidly. When the mother comes to donate blood, he will have all the embryonic structures formed, and after two weeks the heart will beat, this touching moment can be overcome by doing an ultrasound at the end of the 6th week of pregnancy (this will be exactly 4 weeks after the embryo transfer).
The development of crumbs by the day after IVF actually repeats the entire evolutionary process, only the changes that occurred to a person over ten thousand years, happen to your embryo within 24 hours. A woman should understand that it depends on her lifestyle and compliance with the recommendations how successful the development of the embryo will be in the first days after replanting.
Recommendations
After embryo transfer, a woman receives a sheet or table of appointments and recommendations that will help her create the most favorable conditions for the implantation of babies (baby). A woman cannot fundamentally change something in the thin cellular processes that occur inside her uterus. But to create optimal conditions for achieving the effect, she must.
- Observe bed rest for 1-2 days after transfer. Do not lie down in bed for a long time, as this may lead to impaired blood circulation in the pelvic organs.
- Do not lift weights eliminate intense training, running, jumping, any hard physical work.
- Avoid contact with chemicals., poisons, paints and varnishes, gasoline, acetone.
- Eat a balanced and sufficient. Preferred after the transfer is considered to be a diet rich in proteins.
- Observe medication intake. After embryo transfer, progesterone therapy is very often prescribed. This is important to increase the chances of implantation and the preservation of pregnancy in the earliest terms.
- Beware of viral infections. If it is cold during the year, take a sick-list (there is such an opportunity) and exclude visiting large stores, markets, public transport trips to minimize the risk of getting influenza or ARVI, which at this stage can have a disastrous effect on the embryo, even if he will be able to implant.
- Do not take any medications., if your health care provider did not give consent to them. There are no harmless painkillers or antipyretics. For any drug you need to ask permission.
- Do not have sex. With sexual arousal and the body, the smooth muscles of the uterus contract, the uterus comes to tone, the intensity of the blood supply to the main female reproductive organ changes. Tonus is likely to prevent implantation of the ovum.
- Exclude alcohol intake, do not smoke.
- Do not be nervous. Calmness is of paramount importance, because stress hormones block sex hormones, and a normal endocrine background is the key to success of the IVF protocol. Eliminate quarrels and conflicts, worries about pregnancy, do not buy pharmacy tests and begin testing within a day after embryo transfer. This will not give the right result, but will cause a severe psychological state, which is now completely unnecessary.
The main thing that you need to understand is that the success and effectiveness of IVF can not be one hundred percent.
Doctors even in the most optimistic cases do not give certain predictions. The average probability of pregnancy after IVF is 30-45%.
What is important is the age of the woman, and her state of health, and the reasons for which she turned to reproductive medicine for help.
How to behave after the transfer of embryos, experts say in the next video.