When and how to do a pregnancy test after IVF?
A woman who, after long unsuccessful attempts to get pregnant, resorted to IVF, has high hopes for this procedure. And after the embryos obtained from germ cells under laboratory conditions are transferred to the uterus, the most difficult time comes for the woman, when the main question remains open: is it possible to get pregnant? The desire of a woman to understand this question as soon as possible is understandable. However, pregnancy testing after IVF has its own characteristics, which we will discuss in this material.
Terms of testing - features
In order not to waste nerves because of the “empty” tests and the money that will be spent on these same tests, a woman should clearly understand that to determine at least something is possible only if implantation takes place and the embryos take root.
The fetus after IVF does not take root immediately. For several days he is able to stay “in free swimming” in the uterine cavity, and only then he can attach to the endometrium. The earliest - it will happen after two or three days, in extreme cases - no earlier than 11-12 days after the transfer. Most often, implantation after in vitro fertilization occurs at 4-6 days.
If embryos in the blastocyst stage, the so-called five-day weeks, were introduced into the uterus, the chances for a faster implantation are higher than with the transplantation of the three-week days. And cryo-transfer can lead to a longer implantation.
After the fertilized egg is attached and embedded in the functional layer of the female reproductive organ, the chorionic villi begin to communicate with the mother's blood vessels. From now on, the fetus receives everything that it needs from maternal blood, and the chorionic villi themselves produce a special substance, which is called hCG.
In this abbreviation, the name of the chorionic gonadotropic hormone, which promotes the growth of the embryo at the initial stages of gestation, is “encrypted” and regulates the production of progesterone. And precisely: its quantitative value plays a crucial diagnostic role.
All rapid tests that women use with such pleasure are based on the detection of an increase in the quantitative indicator of hCG in the urine. But before the hormone enters the urine, it should be enough to accumulate in the blood plasma. That is why immediately after implantation, even if a woman knows by some miracle her exact date, standard and other tests will not show anything at all.
The number of human chorionic gonadotropin increases in waves - every two days, its amount increases about 2 times. Therefore, it is reasonable to conduct testing only when the real quantitative indicator of this substance reaches a sufficient value that is minimally necessary for recognition by existing test systems and laboratory markers in the biochemical study of a venous blood sample.
Needless to say, in the plasma structures of the blood, the desired substance is determined much earlier than in the urine that is excreted due to the work of the kidneys.
Given that on average, implantation occurs only at 3-6 days after transfer (DPP), the first traces of the hormone can be detected by laboratory technicians in a blood sample no earlier than 10 days after the replanting procedure. But given that in case of artificial insemination implantation is often late, it is recommended to start testing only a couple of weeks after the protocol ends, after the procedure of replanting into the uterus of cultured embryos.
Below we will justify these terms by presenting standardized numerical expressions for the amount of human chorionic gonadotrope after successful extracorporal fertilization for each day from the embryo replanting procedure and the official end of the protocol.
Rapid tests: when allowed
Inexpensive and very affordable tests for identifying an “interesting position” in the form of strips with a control zone, on which a reagent sensitive to HCG is applied, are very convenient and quick to use. But, applying them, it is extremely important to pay attention to the features that, when conceived in the traditional way (in bed and not in the test tube) are absent. To begin with, it should be understood and aware that pregnancy tests for self-diagnosis were created and are created for women who become pregnant in a completely traditional way.
If ecotransfer was performed in a stimulated in vitro fertilization protocol, during which a woman took hormones to grow follicles before receiving eggs, then shortly before follicle puncture she was administered a single dose of the chorionic gonadotropin preparation. Traces of hCG will be contained in the blood and urine of a woman for a long time. Therefore, tests made even the next day after the transfer will show 2 strips, which will be an absolute lie.
Women after hormonal stimulation, in general, are not recommended to do rapid tests, because there is a very high risk of receiving a false-positive result, in which the strips will be, but the pregnancy in fact will not occur. After stimulation and injection of one of the chorionic gonadotropin preparations in the protocol, it is best to conduct a laboratory blood test.
Sometimes it happens that hormone stimulation is not included in the protocol scheme, for example, when using embryos obtained earlier and having undergone cryopreservation. Their replanting may well be carried out in the natural cycle. In this case, the use of tests is quite acceptable, but again, adjusted for very likely late implantation, not earlier than 14-18 days after transfer.
Up to this point, tests can show a weak second strip, which women often call "ghost." Although such a strip of hope is usually not enough. Such a ghostly hope can manifest itself when using a poor, defective test. Often a slightly colored, non-intensive strip indicates that the embryo managed to implant, but then it stopped growing and died. Weak "ghosts" can appear on rapid tests with ectopic embryo attachment, which after IVF, although rarely, does happen.
A poorly colored control strip is able to peek out even when the test is conducted incorrectly, the result waiting limit is exceeded, and then when the embryo has attached itself late, and the hCG quantitative indicator is not yet so large that the strip becomes more brightly colored.
Usually the striped ghost does not reassure anyone and in the “interesting position” does not convince, only gives hope, but it can be more painful to be a disappointment. Do not worry so nervous and for the result, which can not be considered reliable.
Tests, despite the statements of manufacturers, quite often can give a positive or negative result erroneously.Therefore, it is much easier and even cheaper (if you count all attempts to “soak” the strips) to refuse the pharmacy tests and go to the clinic to investigate the level of hCG in the blood, the main thing is to do it in the timeframe your repromatologist recommended.
Laboratory analysis
Stimulated IVF protocol is over. After that, you should not immediately run to the clinic with the requirement to find out if everything went well. Recall that in order to stimulate ovulation in the middle of the cycle, you were given a shot of chorionic gonadotropin, which allowed the oocytes to ripen faster. Because of him, the quantification of hCG will be increased.
The optimal period is 14-15 days after embryogenesis.
At the end of the IVF protocol in the natural cycle, without stimulation, it is permissible to visit the clinic and go to the clinic and do research as early as 10-11 days after embryos transfer.
The cost of medical services is low (500-600 rubles), the analysis is done quickly (from several hours to a day), many clinics and medical centers provide such services, and therefore finding an institution that does this analysis next to the house will not be difficult.
Before analysis, a woman should be excluded from the diet of fatty foods for 2 days, since the study is carried out by a biochemical method. Blood is taken in the morning on an empty stomach. Blood sampling is performed under the conditions of the most ordinary procedural room, 20 ml of biomaterial is quite enough for biochemical examination.
After the transfer - how does the hormonal level change?
At the end of the protocol, given the unstable and rather “scattered” terms of engraftment, it is rather difficult to determine what the quantitative indicator of the hormone produced by the chorion will be, with a successful protocol. In this matter, the decisive role of implantation - the earlier it occurred, the higher the hCG. However, there are average standards for diagnosing an “interesting position” on the quantitative value of hCG in connection with the time elapsed after transplantation and the age of the embryos. But in practice, the values obtained may differ.
Different medical laboratories can indicate different results, you should not expect a match to the number. In addition, circumstances that are not dependent on the patient themselves can tell their weighty “word”.
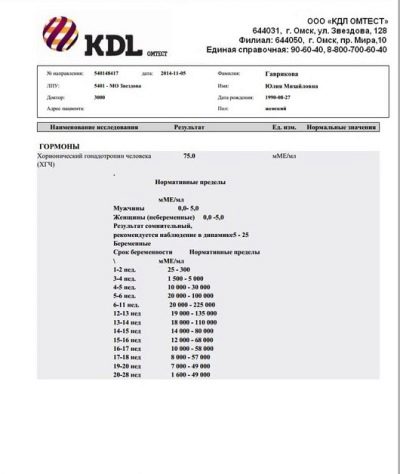
Chorionic gonadotropin - three-day embryos.
DPP (day after transplanting) | Germ age, days | Lower threshold, mU / ml | Average rate, mU / ml | Maximum threshold, mU / ml |
4 | 7 | 2,0 | 4,0 | 10,0 |
5 | 8 | 3,0 | 7,0 | 18,0 |
6 | 9 | 3,5 | 11,0 | 18,5 |
7 | 10 | 8,5 | 18,0 | 26,5 |
8 | 11 | 11,4 | 28,6 | 45,0 |
9 | 12 | 17,4 | 45,0 | 65,6 |
10 | 13 | 22,2 | 73,7 | 105,5 |
11 | 14 | 29,3 | 105,0 | 170,5 |
12 | 15 | 39,0 | 160,6 | 270,0 |
13 | 16 | 68,0 | 260,5 | 400,6 |
14 | 17 | 120,5 | 410,0 | 580,6 |
15 | 18 | 220,7 | 650,7 | 840,6 |
16 | 19 | 370,0 | 980,9 | 1300,4 |
17 | 20 | 520,6 | 1380,0 | 2000,6 |
18 | 21 | 750,6 | 1960,5 | 3100,6 |
19 | 22 | 1050,6 | 2680,0 | 4900,0 |
20 | 23 | 1400,6 | 3550,5 | 6200,5 |
Hrionic gonadotropin - five-day embryos.
Day after transfer | Embryo age, days | Lower bound, mU / ml | Average rate, mU / ml | Maximum threshold, mU / ml |
2 | 7 | 2,0 | 4,0 | 10,0 |
3 | 8 | 3,0 | 7,0 | 18,0 |
4 | 9 | 3,5 | 11,0 | 18,5 |
5 | 10 | 8,5 | 18,0 | 26,5 |
6 | 11 | 11,4 | 28,6 | 45,0 |
7 | 12 | 17,4 | 45,0 | 65,6 |
8 | 13 | 22,2 | 73,7 | 105,5 |
9 | 14 | 29,3 | 105,0 | 170,5 |
10 | 15 | 39,0 | 160,6 | 270,0 |
11 | 16 | 68,0 | 260,5 | 400,6 |
12 | 17 | 120,5 | 410,0 | 580,6 |
13 | 18 | 220,7 | 650,7 | 840,6 |
14 | 19 | 370,0 | 980,9 | 1300,4 |
15 | 20 | 520,6 | 1380,0 | 2000,6 |
16 | 21 | 750,6 | 1960,5 | 3100,6 |
17 | 22 | 1050,6 | 2680,0 | 4900,0 |
18 | 23 | 1400,6 | 3550,5 | 6200,5 |
As it is easy to see from the presented tables, the quantitative value of hCG will be quite sufficient for research and detection of the “interesting position” after IVF only for at least 9-10 days after transferring the cultured three days and for 7 days after the introduction of five-day embryos into the uterus.
However, if late implantation is taken into account, the results of the study are quite capable of being lower than the diagnostically important control level, and then the laboratory technician can establish the absence of pregnancy in its actual presence.
In order not to undermine the state of the nervous system (its safety and emotional balance contribute more to implantation and to a healthy pregnancy), one should heed the advice of a fertility specialist, and not try to establish the truth within the first two weeks. If everything is done correctly, the result will be 99.5% reliable both in a successful protocol and in an unsuccessful one.
In addition to establishing the fact itself, the laboratory conclusion, repeated several days later, will provide an opportunity to assess how the baby grows. And if two embryos have stuck, all values will exceed the standard exactly twice.
Signs and symptoms - can you trust?
Even specific recommendations on the timing of testing for an “interesting position” often fail to convince women not to try to find out about the possible successful outcome of the protocol at the very beginning.
Whether the appearance of any symptoms and signs within two weeks after the embryo-transfer procedure is real, the question is ambiguous. From the standpoint of classical fundamental medicine, symptoms characteristic of pregnancy should not be. Theoretically, the female body immediately responds to the accomplished implantation of metamorphosis at the hormonal level.
At first, these changes are so small that only very sensitive women can feel them. After 4-5 days after implantation a slight swelling of the breast, a change in the sensitivity of the mammary glands is possible. This is due to an increase in the hormone prolactin, which is also a consequence of the beginning endocrine adjustment.
There can be no classic symptoms of toxemia at all, and they should not be expected at such an insignificant period of gestation. But some changes may well begin within five to six days after the successful introduction of the ovum into the endometrium. Therefore, some patients note that body temperature has begun to rise.
Every day in the afternoon, in the evening, the temperature rises a little above the subfebrile value of 37.0 degrees, there is a chill, or “throws into heat”, the face may blush and “burn cheeks”.
Quite often at this stage it seems to women that they are sick, caught a cold. This impression is complemented by a light runny nose. It is not associated with colds or viruses, but with the effect of progesterone, which after implantation becomes larger, on the mucous membranes. They are under the influence of this female hormone become more friable, edematous.
Runny nose such a treatment is not necessary, it is the physiological rhinitis of pregnant women. However, all signs and symptoms cannot be considered reliable and clinically important. The only reliable information is the results of a blood test for chorionic gonadotropin.
Tips
According to numerous histories of female patients of reproductive clinics, sometimes tests even after two weeks show a negative value, and already resigned to the fact that this time there was a “span”, the upset patient went to the ultrasound, where an attached embryo was found. In no case should you despair. Statistics, of course, does not add optimism, because only a little more than a third of women according to the results of IVF become pregnant. But it has long been known that each subsequent protocol increases the likelihood of successful long-awaited pregnancy.
To increase the likelihood of success, a woman is recommended to lead a calm and measured lifestyle, not to lift weights, not to jump and not to bend down sharply, not to charge yourself with the whole load of homework. It is equally important to avoid psychosomatic disorders by the implantation process; for this, you should remain calm, tune in to the good, but be prepared for the fact that the protocol may not be crowned with success.
This attitude will help you to more easily survive the failure, if it happens, and the woman can quickly start preparing for the next attempt.
About how long the pregnancy test shows the correct result, see the next video.