What is embryo cryopreservation and why is it needed?
About cryopreservation of embryos to ordinary couples, as a rule, little is known. This concept is faced by those who are going to do in vitro fertilization. A lot of controversy arises around the freezing of embryos, including religious and moral ethical ones. But sometimes you can not do without cryoembryos. In this article we will explain in detail what is cryopreservation of embryos, and why it is done.
What it is?
With the prospect of in vitro fertilization, couples encounter who cannot conceive a child in a natural way and whose causes of infertility cannot be eliminated by other methods. During the procedure, the biological materials of partners are taken - sperm and egg. Fertilization does not occur in the maternal organism, but in a test tube. After this, a fertilized egg is transplanted into the uterine cavity of a woman. If the blastocyst is successfully implanted into the uterine wall, then it is said that the pregnancy has begun.
IVF without hormonal stimulation is done infrequently because of the low chances of successful implantation. Usually couples do IVF with hormonal support. In the course of preparation, under the action of a hormone in the ovaries of a woman, not one or two eggs mature, but a much larger number of them. The punctured eggs fertilize the sperm of the husband or donor (if the cause of infertility is total male infertility).
The more eggs received, the greater the chances of success. The more oocytes will be successfully fertilized by the male reproductive cells, the more opportunities the reproductive doctor will have - he can only choose the strongest and strongest embryos for replanting from the uterus.
Usually try to plant 2-3 eggs. The question arises: what to do with the remaining embryos? Most often, with the consent of the couple, they undergo cryopreservation. If the first IVF attempt fails, then these embryos can be used for a second attempt.
In addition, a couple after a successful IVF attempt may well want another child in a few years. Then she, too, can take advantage of frozen embryos. Then the woman will not need long preparation for IVF - the cryo-transfer will be done within the framework of the cryo-protocol.
How does this happen?
Usually they try to freeze an embryo at the zygote stage when they are a two-year, four-cell or eight-cell organism. Cryopreservation, by the way, can be carried out at almost any stage of the early development of a fertilized egg. The reproductologist carefully assesses the quality of the embryos - inferior, the weak may not survive freezing and thawing.
There are two main ways to save life in the embryo, temporarily stopping all cellular processes. In the first case, the embryos are frozen slowly and immersed in a cryoprotectant solution with certain drugs. The cells surrounded by such a composition are more protected, and the liquid inside the cells does not crystallize during freezing, does not turn into ice and does not break the cell wall, which becomes vitreous. This allows all its structures to remain viable.
The second method is called windification.This is a rapid, rapid freezing, in which the crystallization stage does not pass under the laws of physics. Cooling is performed using liquid nitrogen or its vapors. Frozen embryos are stored at minus 196 degrees Celsius in special tubular containers. They can be stored up to 10 years.
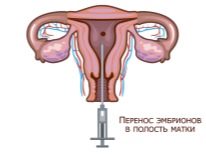
If necessary, the embryos are extracted from nitrogen, thawed at room temperature, and then placed in a special nutrient medium. After the doctor is convinced that the embryos are alive and they have resumed the process of cell division, they can be transferred.
Statistics say that about 20% of embryos unfreeze, unfortunately, die. At the same time, after ultrafast freezing with the method of windification, the survival rate is higher - it is more than 80%, and with slow freezing with a replaceable cryoprotective solution, the survival rate of embryos is estimated at about 50%.
Advantages and disadvantages
Cryopreservation of embryos “in reserve” allows the couple to increase the chances of IVF success. If one protocol to get pregnant did not work, you can do the second. After an unsuccessful IVF with a simple (fresh, fresh) embryo, the cryoembryonic protocol very often gives a quick positive result.
If the first IVF is not crowned with success (and this is a rather likely outcome), the preparation of the second protocol will not require aggressive hormonal stimulation of the woman’s ovaries, which means that the harmful effects on her body will be minimized.
With cryoembryos, it is also possible to conduct IVF in the natural cycle, if the woman is not disturbed by the menstrual cycle.
The presence of frozen embryos in a cryobank significantly reduces the cost of subsequent IVF attempts for spouses. And besides, it gives them the opportunity to use the right to transfer them into the mother’s womb even after several years. Frozen embryos can be used for surrogate motherhood if a biological mother is contraindicated for a number of reasons, or she does not have this possibility (age over 45, absence of a uterus, total dystrophic changes of the reproductive system, endured cancer
A married couple whose IVF is crowned with success in one of the attempts have the right to decide the fate of the embryos remaining in the freeze, whose biological parents they are. They can pay for their storage for several years in advance, donate them as donor to other sterile couples, and also allow science to use them for study and experimentation or allow their disposal.
From this point on, cons begin. The decision on the utilization of embryos is given to many couples is not easy. Some religions (for example, Orthodoxy) consider this a great sin - infanticide, abortion.
That is why the couple needs to discuss with the doctor in advance the possibility of fertilizing a small number of eggs so that they are maximally used for their intended purpose.
If there is a high probability of developmental pathologies of embryos, it is better to agree to the procedure for cryopreservation of eggs and fertilize the thawed oocytes each time before replanting. But in financial terms, it is much more expensive.
The death of frozen embryos in the process of defrosting is also a clear minus of the cryoprotocol. It may happen that only one out of three thawed embryos will survive, or none at all, and then the replanting will have to be postponed to a later date.
Indications
Cryopreservation of embryos any couple can choose consciously of their own accord. Such services are provided by clinics specializing in IVF. But there are situations in which the freezing of fertilized eggs is strongly recommended by doctors.
This happens in the following situations:
- participation in the surrogacy program;
- several unsuccessful IVF attempts using “fresh” embryos;
- when stimulating the ovaries, a woman showed hyperstimulation syndrome and re-stimulation is contraindicated;
- changed circumstances (the couple passed the biomaterial, but for some reasons decided to get pregnant a little later, at a more appropriate time for this);
- individual history of women, if there are diseases that significantly reduce the likelihood of pregnancy after the transfer, (for example, chronic illnesses), which may worsen before the procedure; in this case, frozen embryos can “wait” until the expectant mother recovers and heals to increase the chances of success.
How does freezing affect the embryo?
Many future parents, thinking about the proposal of the doctor about cryopreservation of embryos, are worried that the process of freezing and thawing will harm the child, will later affect his development and health.
In this matter, over 40 years of observation, doctors have come to the unanimous opinion - staying in suspended animation in a frozen state does not affect the further development of the baby. Do not be afraid of deformities, pathologies, developmental disorders. Freezing and subsequent defrosting are dangerous only by themselves, since the embryo may not survive them. If the thawed cells are crushed, then nothing will happen to the child who grows out of them.
Some doctors even claim that cryo-children are stronger, they have stronger immunity, they are less likely to get sick. Is there any connection with cryopreservation, it is difficult to say, because initially there are no weak and painful among embryos suitable for vitrification. The development of such kids meets all age standards, and sometimes even ahead of them.
Replanting of the thawed embryo can take place on the same day, if the embryo was frozen (cryopreserved) in the crushing stage (2, 4, 8 cells). If freezing was carried out at the stage of two pronuclei, then doctors will need a few more days to observe the development of embryos.
The success of replanting in cryoprotect
The use of frozen embryos does not reduce the likelihood of implantation and the onset of pregnancy. Therefore, as in the case of other types of IVF protocols, the likelihood of pregnancy after cryopreference is about 30%. Much depends on how the spouses managed to prepare for the protocol. If they normally have all the tests, if there are no reasons that can negatively affect the implantation process after the replanting, the probability increases.
The age of the future mother also plays a role: after 35 years, the probability of getting pregnant is about 25%, and at 40, the probability of a successful protocol decreases to 18%. The older the woman, the less likely the pregnancy.
The probability of becoming pregnant is reduced after infectious diseases, flu and ARVI, as well as after a previous miscarriage or missed abortion. After diseases and complications, it is important to wait for the time recommended by the doctor so that the woman's body can recover.
Re-freeze
Sometimes there is a need to re-freeze the thawed embryos. This can happen if all thawed embryos were alive, if the woman could not attend the transplant (emergency, unforeseen circumstances).
Theoretically and practically repeated freezing of already thawed embryos is possible. But there is an important condition - the primary freezing should have been carried out at the earliest stages of embryo development. After repeated defrosting, the probability of death of such embryos is higher. The success of the protocol with the use of twice thawed and frozen embryos does not exceed 10%.
That is why it is not worth risking and freezing the embryos again, if there is at least the slightest opportunity to replant as planned.
About what cryopreservation is and why it is needed, see the next video.