How many days does an egg live after ovulation, and on what factors does its viability depend?
The biological development cycle of female germ cells is rather complicated. Every month a fertile woman matures with one egg, which should participate in conception. This article will tell you how many days the egg lives after ovulation, as well as the factors that may determine its viability.
Life cycle features
In order to understand the biological process of egg maturation in the female body, it is very important to touch upon the basic knowledge of their development. Initially, each woman has a certain number of female germ cells, bestowed on her by nature. Approximately 1-1.5 million follicles are already present in the body of a newborn girl. Immediately after the birth of the girl, her follicles are not active. Maturation will begin much later - during puberty.
The appearance of the first menstruation is a signal of the female body that the maturation of the follicles has begun. On average, the first menstruation occurs in girls at the age of 10-13. The time of their appearance is a very individual parameter. In some girls, they may appear first and much later - by the age of 14-16.
From the moment of menstruation and until their complete cessation with the onset of menopause, a woman is reproductive, that is, capable of having children. This period is called the time of reproduction. In the reproductive woman's body, the eggs mature each month. This process is ongoing. It is conceived by nature so that a woman can become a mother in a natural way and continue the race.
The entire menstrual cycle of a woman can be divided into several successively successive phases:
- Menstruation. The first day of your period is the first day of the new menstrual cycle. The previous day before the month ends the previous menstrual cycle. The time interval between menstruation in each month and determines the total duration of the menstrual cycle. According to statistics, it is on average 28-30 calendar days.
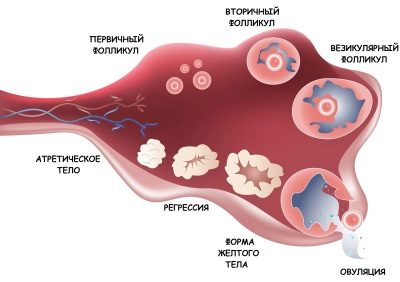
- Follicular. Characterized by egg maturation. Lasts immediately until the rupture of the follicle.
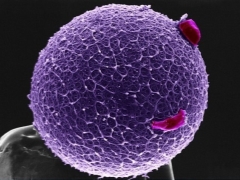
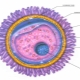
- Ovulation. Accounted for, as a rule, in the middle of the menstrual cycle. On this day, the dominant follicle bursts, and the ripe egg leaves the abdominal cavity.
- Luteal. Begins after the release of the egg from the follicle. In place of a bursting follicle in the female body, a special formation appears - a yellow body that produces progesterone. If the egg remains unfertilized, then the corpus luteum is subsequently reduced.
Female genital cell life expectancy
Ovulation is a very important day of the menstrual cycle from a biological point of view. All hormonal processes occurring in the female body throughout the entire menstrual cycle are largely necessary only for the egg to fully mature and to be prepared for a meeting with the sperm cell.
With a 28-day menstrual cycle, the day of ovulation usually falls on the 13-14 day.Unfortunately, it is not always possible to correctly determine the final maturation of an egg by a simple calendar counting method.
Special pharmacy tests, folliculometry, as well as measurement of basal body temperature, help to determine ovulation more accurately.
A couple of days before the onset of ovulation, the dominant follicle, in which the maturation of the egg occurs, increases. Usually by this time its dimensions are 18-20 mm.
In order for the dominant follicle to burst, hormones are needed. The growth of the follicle during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle is influenced by FSH - follicle-stimulating hormone. It acts in such a way that the dominant follicle grows approximately 2 mm each day.
The day before ovulation, the concentration of luteinizing hormone (LH) rises rapidly in the blood. Under its influence, the dominant follicle is ruptured and the mature egg cell leaves it.
The female reproductive cell first enters the abdominal cavity, and then is “absorbed” by the villi of the fallopian tube. It should be noted that the egg practically does not carry out independent movement, in contrast to the spermatozoon. It moves through the fallopian tube due to the special peristalsis of its wall. The movement of the egg through the fallopian tube can not be called fast.
If the confluence of germ cells has occurred, then a new biological element, the zygote, is formed. It is a fertilized egg cell whose cells are beginning to actively divide. Subsequently, a small embryo is formed from the zygote, which is attached to the inner wall of the uterus. From the moment of fertilization and pregnancy begins.
It also happens that in the female body matures several eggs. In this case, during ovulation, both of them can come out of the ovaries. This situation increases the likelihood of conceiving twins or twins.
After ovulation, the egg remains viable, usually within 12-24 hours. If the female reproductive cell has not met with the spermatozoon and fertilization has not occurred, then it dies. In a woman's body, the next phase of the menstrual cycle begins.
Causes of death
Scientists have found that in most cases the unfertilized germ cell dies while in the distal part of the fallopian tube. The remains of the dead egg will be removed from the body during the next menstruation.
Much less often, the death of an unfertilized egg occurs directly in the abdominal cavity. As a rule, this contributes to any pathology of the fallopian tube. The presence of adhesions or congenital anomalies of the fallopian tubes can become obstacles for the physiological movement of the egg, and hence for the onset of pregnancy.
It is conceived by nature that an unfertilized egg cell dies. This is due to its special structure. The egg cell has only a haploid (half) set of chromosomes. Such a set of "includes" 22 normal and 1 sex chromosome. With such a half set, a cell cannot fully exist. Synthesis of proteins essential for the activity of the germ cell is possible only with diploid set of chromosomes.
Unfortunately, in practice, eggs do not always mature every month. Even a healthy woman can have menstrual cycles when ovulation does not occur. They are called anovulatory.
Such cycles develop for many reasons.
If anovulatory menstrual cycles are repeated in a woman too often, this is already a consequence of the presence of pathology. In such a situation, it is imperative to establish the cause, which contributes to the violation of ovulation. Frequent anovulatory cycles can cause infertility.
There are also clinical situations when the date of ovulation is shifting. As a rule, they develop due to the presence of any gynecological or endocrine pathologies in a woman.In this case, the follicle usually develops slowly, but on the expected date of ovulation it does not open.
Insufficient levels of LH can also affect the opening of the follicle. An unopened follicle in the future may simply decrease in size or turn into a follicular cyst over time.
Factors affecting vitality
For quite a long time, scientists tried to establish on what factors the viability of the egg after ovulation depends. This knowledge is necessary in order to understand how to plan pregnancy for couples who have difficulties with the natural conception of a baby.
Investigating the stages of development and maturation of female germ cells, scientists concluded that the following factors affect their viability:
- safety and functional suitability of genetic material contained in chromosomes;
- the amount of protein particles inside the cytoplasm of the egg, accumulated during the pre-ovulatory period;
- individual characteristics of the female body.
Experts note that younger eggs are the most viable. It is believed that the chance to conceive a child in 40 years much lower than 25. This decline in fertility with age is due to numerous factors. Psychoemotional stresses, unhealthy lifestyles and bad habits, concomitant diseases, hormonal disruptions, the effects of miscarriages and abortions and many other causes have a negative effect on the maturation and development of the eggs.
It has been scientifically proven that ionizing radiation also has a negative effect on the viability of oocytes. Radiation has the most adverse effect, leading to rapid death of germ cells.
Scientists believe that at a younger age, the egg is able to maintain its viability for 36 hours. After 30 years, this time is already reduced to 12-24 hours. In women after forty years, even when ovulation is preserved, the life of the egg is significantly lower and may even be 4-6 hours. If at the same time the woman has any related gynecological diseases, then the chance of natural conception decreases many times.
Pregnancy planning
Terms of viability of ovules after ovulation help many couples to plan the conception of the baby. Knowing the exact date of ovulation, you can purposefully plan fertilization. Experts recommend on the day of ovulation to perform several sexual acts. This will increase the likelihood of possible fertilization.
It is important to remember that the egg after leaving the follicle may remain viable throughout the day. If the sperm are healthy and active, then at this time the chances of conceiving a baby increase dramatically. Healthy sperm can be stored in the female genital tract for several days. At this time, the risk of conception is also quite high.
Some women, in order to provoke ovulation in them, resort to taking special medicines that stimulate the ovaries. Doctors do not recommend it themselves. It is extremely dangerous to resort to the reception of such funds for women with gynecological diseases or dishormonal disorders. Any prescription of drugs that stimulate ovulation should be done only by a gynecologist.
In order to increase the potential viability of the eggs, it is very important for the woman to look after her health. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, eliminating bad habits, a normal 8-hour sleep and a balanced diet are the basis for maintaining fertility for many years.
In the event of adverse symptoms on the part of the genitals, it is not necessary to postpone a visit to the gynecologist for a long time. Early treatment of gynecological diseases in the early stages will help to maintain reproductive health in the future.
How an egg develops can be found in the following video.