All about eggs: structural features, functions, quality and quantity
The knowledge of ova is minimal for many. Everyone knows that this is a female genital cell, without which it is impossible to conceive a child. Unfortunately, this is where knowledge ends. Even women themselves know little about their reproductive cells and what can affect them. Let's fill these "gaps" and learn a lot of interesting facts about the female egg.
What it is?
The egg cell is the female's sexual cell. Quite often it is called an oocyte. It is considered one of the largest in the human body, with the exception of certain nerve cells and smooth muscle cells. The egg cell is a unique living organism. This is a true masterpiece created by nature for the continuation of the human race.
It used to be thought that only the male germ cell, the sperm cell, was responsible for the formation of a human embryo. Now science and medicine have revised their attitude to the egg, recognizing that it participates in the formation of the embryo in the most direct way.
Oocytes are monogamous in nature. This means that its merging is possible with only one of the millions of spermatozoa that are moving along the female genital tract after ejaculation. Sometimes two or three sperm penetrate into the egg at once, but such an embryo is doomed to death - its genetic set cannot be normal.
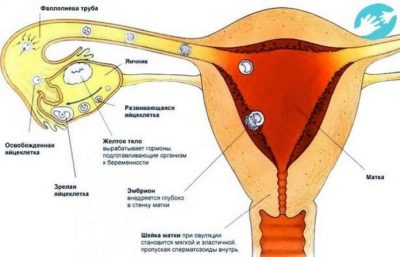
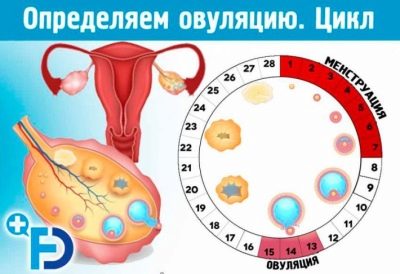
For the production of eggs are responsible ovaries - the female sex glands. First, they form a large number of primary cells - oogonia. Subsequently, significant changes at the intracellular level appear in the structure of these precursors. The third phase of development is the maturation of the egg. Only a mature egg can leave the follicle, this process is called ovulation.
Structure
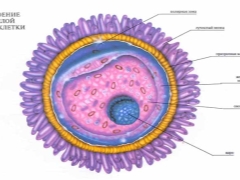
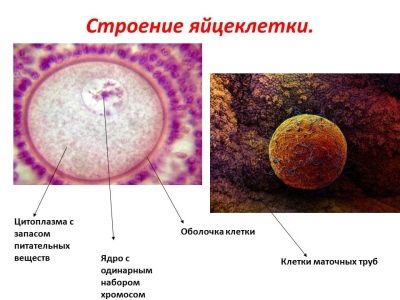
The structure of the female egg is very complex. Everything is provided in it in order to provide the best environment for the development of a new life. The size of the female reproductive cell is 0.1-0.15 microns. The large rounded cell is fixed. This feature facilitates the task of sperm. If the egg moved, fertilization would be more difficult.
In the structure of the cell, as can be seen in the diagram of the structure, the cytoplasm, nucleus and membrane are clearly defined. The outer shell of the cell has a multilayer structure. Each of the components performs its basic functions. The shells are designed in such a way that after one sperm cell penetrates into the cell, they become completely impenetrable to other male cells. At the same time, the shells have a sufficient margin of safety so that when the egg cell is transported through the fallopian tube into the uterine cavity after fertilization, the crushing cell does not suffer and is able to safely complete its “journey” and implanted.
In the egg nucleus there is a sufficient amount of proteins that can ensure the division and development of new life. The nucleus also contains the X chromosome set. If there is no chromosome in the egg, it is unsuitable for fertilization, such a cell is considered “defective”. The cell's protoplasm contains RNA and nutrients that are necessary at the crushing stage after fertilization.
How are they formed and developed?
When a mother wears a girl under her heart and still does not realize that her fetus is female, the baby in the ovaries already develops cells that are the precursors of the eggs. They are called first order oocytes. The female fetus has tens of millions. But these cells do not differ in strength and vitality, and therefore the overwhelming majority of them die. By the time a girl is born, about two million cells remain in her ovaries, and by puberty their number reaches only 400-500 cells. Their number does not change in their entire life.
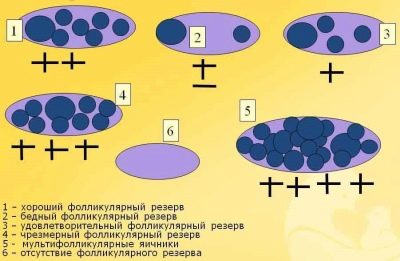
This stock of oocytes is strictly defined; it cannot increase or decrease. Further cells of the first order develop in the follicles. Hormonal background, sensitivity to its changes allow the follicles to independently regulate these processes. During puberty, the follicles increase under the action of the female sex hormones, some eggs mature, and the development of others is artificially slowed down so that the stock does not quickly run out.
One egg grows in one follicle. In the first phase of the menstrual cycle, several follicles grow, but only one of them becomes dominant. From it, the mature sex cell “hatches”, ready for fertilization. The older a woman becomes, the less number of immature eggs she has. After 40 years, the stock is almost exhausted. Some of the oocytes matured and left, and some underwent degeneration, the precursors of the eggs died.
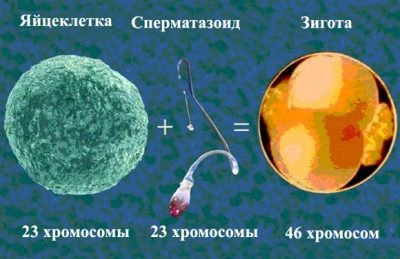
With the onset of puberty in a girl, first-order oocytes are transformed into second-order oocytes with a half set of chromosomes. 23 pairs - this is the “contribution” that a woman makes at the time of fertilization. Exactly the same pair of chromosomes "gives" the male reproductive cell.
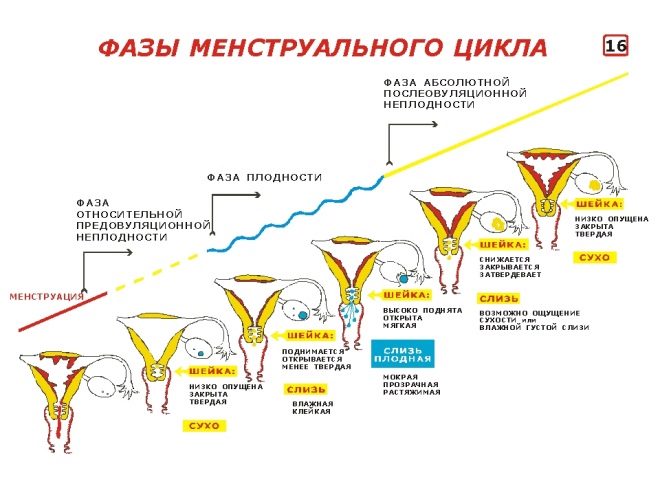
By the time of ovulation, the size of the egg reaches its maximum, the follicle is torn and the egg leaves the fallopian tube. There, she can wait for the sperm for 1-2 days, after which, if fertilization has not taken place, the cell dies, after two weeks the woman begins her period. The process in the new cycle is repeated.
Ovulation
The process of the egg from the follicle, which is called ovulation, usually occurs in the middle of the woman's menstrual cycle. If from menstruation to menstruation takes 28 days, then ovulation usually "falls" for 14 days, if the cycle is longer - ovulation shifts proportionally. Conception is possible only on the day of ovulation or days later, while the egg cell remains viable.
If sexual intercourse took place 2-3 days before ovulation, fertilization is possible in the first minutes after the release of the egg. Sperm cells are more enduring, they can “wait” for the female cell in the fallopian tube for about 3-4 days. Sexual intercourse on the day of ovulation or the day after it is also more likely to end with the onset of pregnancy.
Ovulation in women is often accompanied by certain sensations on the physical level. Nature has foreseen everything so that a woman who cannot see the processes at the cellular level can feel the most favorable period for the continuation of the race, because time is very short. Often, a woman experiences increased sexual desire before ovulation and on the day of the egg's release. Allocation becomes more abundant, there is a feeling of heat and moisture in the perineum. The hormone secretions become more viscous, less acidic, so that male germ cells can survive in a different environment and get to the egg cell.
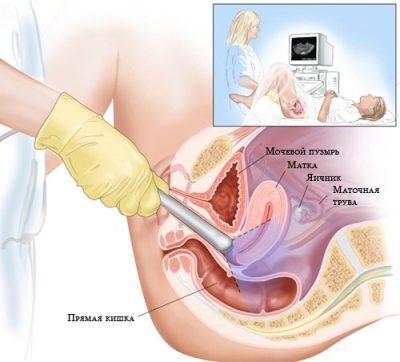
From time to time, even in a healthy and procreative woman, anovulatory cycles are observed in which there is no release of the egg.It is impossible to determine such cycles by yourself. This can only be done with ultrasound. If their number is large, they talk about ovarian dysfunction and anovulatory infertility.
Sometimes a woman matures at the same time two or three eggs. In this case, fertilization of them all is possible, and then twins or triplets are born.
Fertilization and implantation
Sperm cells begin to move toward the location of the egg immediately after ejaculation. They do not have the intelligence to understand where to swim, but they have a very developed apparatus that analyzes the chemical composition of the environment. There, where the acidity is lower, they need to get. The fallopian tube, where the meeting with the egg cell should take place, is reached only by the strongest and strongest of the premiums.
They begin to "attack" the transparent shell of the egg, trying to find a "gap" and get inside. In some sources one can come across the assumption that the egg itself chooses the one who can be allowed to penetrate by screening out defective spermatozoa. This assumption is not confirmed by scientific evidence, moreover, the insolvent male germ cells simply do not get to the egg. The sperm head secretes special substances capable of dissolving shell structures.
As soon as one sperm has penetrated inside, the command about the accomplished conception is spread throughout the body, the hormonal background changes rapidly, progesterone is produced in large quantities, which is necessary to preserve pregnancy and the development of the embryo. Sex chromosomes occur in the egg. It is at this moment that it is decided who the child should be - a boy or a girl. At the same time, almost everything is determined - what color the baby’s eyes will be, his height, who he will be more like - his father or mother, what his health will be.
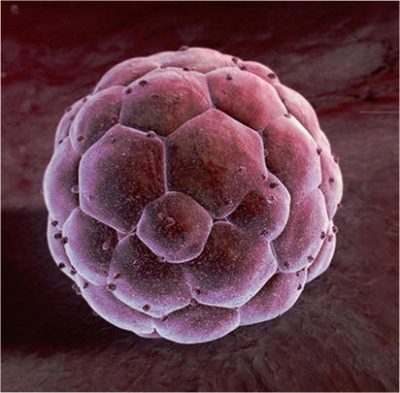
The egg cell becomes a zygote. Despite the fact that the female sex cell looks clumsy and immobile, it begins to show activity. Now, with every hour, it will slowly move into the uterine cavity. It is mobilized by the villi that cover the inner part of the fallopian tube. This path takes an average of 7-8 days, after which implantation occurs.
On the fifth day after the start of crushing, the cell changes its status and becomes a blastocyst. It differs from a zygote by a large number of cells and a spherical shape. In the uterine cavity, the blastocyst is released from the shiny shell, which provides it with better and closer contact with the walls of the uterus. The cell literally grows from the tissue of the inner wall of the uterus.
If the implantation is successful, a new stage in the development of the embryo begins. Now he is where he is to spend the coming months. During pregnancy, at this stage, the work of all organs and systems of the female body undergoes colossal restructuring. If, for some reason, transportation fails, the zygote will continue to develop in the fallopian tube or in the cervix. And then the pregnancy will be ectopic.
Signs of implantation many women are also able to feel. After 7-8 days after ovulation, they may have a slight pulling pain in the lower abdomen, as well as weak spotting, which indicate a violation of the integrity of the inner layer of the uterus during implantation. Such secretions are called implant bleeding, they usually stop within a few hours or the first day. Such symptoms do not always accompany implantation and for many it goes completely unnoticed.
Aging
After 35-36 years, the quality of the eggs is noticeably reduced in a woman. The impact of the overwhelming nature, which every month does not allow the entire stock of eggs to ripen at the same time, environmental factors, harmful effects, food habits, alcohol, chronic and acute diseases affects.
The X chromosome also undergoes aging, which is why women who decide to become mothers after 35 years old have higher risks of having a child with chromosomal pathologies and anomalies. The greater the age of the expectant mother, the higher these risks. However, age is not a sentence, and many successfully give birth after 40 years.
When there are no suitable eggs for maturation in the ovaries, menopause occurs. At this stage, conception is impossible, monthly menstruation is absent, since the body no longer needs to release the uterus from the dead eggs as an unsuitable biomaterial.
How much is left?
A woman’s fertility directly depends on how many percent of normal and immature eggs remain in her body. In men, spermatozoa are produced continuously, the composition of sperm is updated every three months, the woman has to be content only with the stock that she has, new oocytes are no longer produced, their updating is impossible.
The number of remaining cells depends on the age and state of health. In a newborn girl, 100% of the cells are alive and well; by the age of 10, their number reaches 70%. In 20 years, the girl has 37% of the eggs from the stock of a lifetime, in 25 years - 22%. At 30 years, a woman has only 12% of a large supply of eggs, 35–7%, at 40 years old - about 4%, and at 45% only 2%.
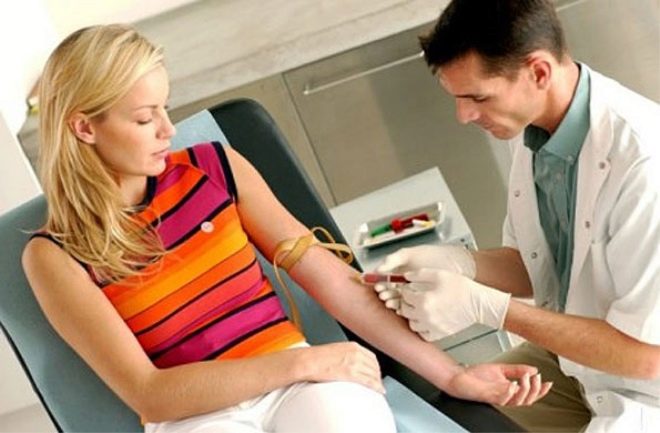
Find out how many eggs left, allows a special analysis. This is an uncomplicated hormonal test, which is called the "egg timer". Such an analysis is very useful for women who are planning a pregnancy after having undergone a previous course of chemotherapy, long-term treatment with antibiotics or hormones, as well as for those planning to conceive after the age of 35 years.
Qualitative characteristics
Usually, women who are undergoing fertility treatment, who are shown to be conceived by in vitro fertilization (IVF), are faced with an assessment of the quality of the eggs. Their eggs are laboratory and genetic research, during which deviations from normal characteristics can be identified. A defective egg will be considered to be a violation of the state or structure of at least one of the organelles.
The hormones FSH and AMH also indicate ovulatory stores and quality of female reproductive cells, the concentration of which is determined in the blood of a woman by laboratory methods. But to establish exactly what the defect is, only a microscopic puncture of the resulting egg cell allows.
The reasons for which a woman develops low-quality germ cells can be very diverse. Most often, doctors associate them with hereditary factors, because the health of future eggs is determined when the female fetus develops in the womb. However, do not underestimate the influence of external factors. These include bad habits - the systematic use of alcohol or drugs, smoking. The reason for the deterioration of the quality of eggs can be improper diet, the tendency to eat fast food. A large number of preservatives and dyes in food causes slow mutations of germ cells.
The extra weight that a woman may suffer causes changes in the hormonal background, namely, hormones regulate the life cycle of the eggs. Sometimes excess weight is generally an obstacle to conception, and only by dropping interfering kilograms does a woman acquire the possibility of finally becoming a mother.
In our crazy age, when both men and women do not feel sorry for themselves, they work at night, often the eggs lose their basic functions due to chronic fatigue, stress, overwork.
Long-term courses of treatment, chemical and radiation effects on the body of a woman, her work in hazardous production, where there is contact with toxins, nitrates, heavy metal salts, varnishes and paints, can affect egg health.
It is not possible to increase the number of oocytes, but medicine may well fight for the quality of the eggs. Women are prescribed appropriate therapy designed to improve the quality of germ cells. This includes vitamins, dietary supplements to improve women's reproductive health, as well as a radical change in lifestyle, the elimination of all bad habits and correction of nutrition.
To improve the quality of the eggs are often prescribed dietary supplements such as "Ovariamin", "Inositol." A woman is recommended to take folic acid, sometimes, if the cause of cell failure lies in hormonal disorders, the endocrinologist, together with the gynecologist, prescribes hormonal preparations for the woman to regulate the menstrual cycle and improve cell quality.
The characteristics of the eggs are restored gradually, you should not expect a quick result.
A normal full night’s sleep is recommended for a period of treatment for the woman - at least 8 hours a day. To do this, sometimes you want to give up work on the night shift. Meals should be healthy and balanced, you should also bring your own weight back to normal. Useful walks in the fresh air, sports, active lifestyle.
To improve the quality of the egg after 40 years, it takes even more desire and effort, because natural aging and changing structures are almost inevitable. But it is also possible. A woman is advised to completely give up bad habits, as well as to acquire a healthy habit of being less nervous.
Under stress, the female body is enriched with stress hormones, many of which block the work of sex hormones. That is why you need to monitor your mood and psychological state, to study well the peculiarities of your body in order to prevent psychogenic infertility.
The reproductive's verdict about low quality of oocytes is not unshakable and irreparable. In most cases, a woman with the observance of medical recommendations can improve the quality of their germ cells. Problems can occur only with autoimmune forms of infertility, when antibodies and antigens interfere with the fusion of sperm and egg. But even in such cases, doctors can offer several effective treatment regimens that will increase the chances of the couple to conceive a baby.
If a woman's eggs do not ripen to the desired condition, ovulation does not occur, methods of stimulating ovulation with hormonal drugs are widely used in medicine. In the first phase of the cycle, hormones are usually administered to promote the growth and development of the egg, and then drugs are injected that cause the follicle to rupture.
Improvement feedback
Women who have gone through their own experience through the procedure of improving the quality of the eggs, are urged to be patient, because this is quite a long and consistent process. According to women, the main treatment prescribed by a doctor does not interfere and even auxiliary treatment with folk remedies contributes.
Thus, fish oil is very useful in improving eggs. It is taken both in liquid form and in capsules. Only edible fat is used, which has significant differences from other types of product. Cod liver and fatty sea fish are added to the diet. Cinnamon is also good for women. It is taken in capsules.
The course of treatment is often prescribed just before IVF, in order to get the best quality eggs for fertilization. But even to conceive naturally, women are often recommended to take vitamins and dietary supplements.
Those who wish to become pregnant, especially after 30 years, have to abandon coffee and strong tea, because caffeine negatively affects the state of the eggs. Women have to change the whole usual way of their life in order to achieve the goal and become mothers.
About the features of the structure, functions and quality of eggs, see the following video.