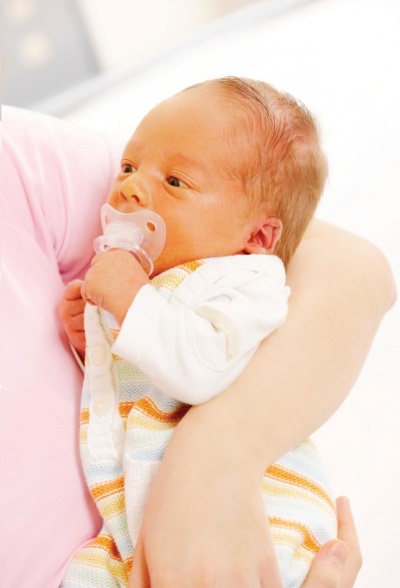
Hemolytic jaundice in newborns
The skin of more than half of newborns in a few days after birth becomes yellow due to physiological jaundice. However, jaundice in a newly born infant is not always caused by physiological reasons. Sometimes the doctor diagnoses hemolytic jaundice in the baby, which, unlike the physiological one, must be treated.
The reasons
The main cause of hemolytic jaundice in newborn babies is the conflict between the mother’s blood and the blood of the crumbs. Such a conflict may be in the blood group, but most often it occurs on the Rh factor. With him, the baby has antigens received from the father, and in the mother's body, in response to them, the production of antibodies begins.
Antibodies can begin to be synthesized even during pregnancy, threatening the process of gestation, but in many cases they appear before or during delivery. Through the placenta, they get to the baby and destroy the red blood cells in the baby's blood, that is, provoke their hemolysis (this causes the name of jaundice).
More information about jaundice and its forms can be found in the following video.
Symptoms
Due to the destruction of red blood cells in a child develops anemia and jaundice appears. If the disease is severe, the infant may be born with a yellow skin or edema, but this is rarely the case. Most often, hemolytic jaundice develops after birth, while the earlier onset and more pronounced jaundice distinguish it from the physiological one.
The spleen and liver in a baby with hemolytic jaundice is usually enlarged, the urine becomes darker, and the color of the feces does not change. If the baby has severe anemia, then it will be pale. With a high level of bilirubin, there is a risk of damage to the brain tissue (nuclear jaundice may develop).

Treatment methods
Phototherapy is the most preferred and widely used treatment for hemolytic jaundice. The child is kept under special lamps, the light of which makes bilirubin water-soluble, as a result of which the pigment leaves the body more quickly with physiological functions. Phototherapy is carried out continuously, pausing only for feeding.
Depending on the condition of the child, they may also be given this treatment:
- Intravenous infusion of glucose and other therapeutic solutions (salts, proteins, vitamins). They are prescribed when breastfeeding is impossible.
- Exchange blood transfusion. Appointed in a serious condition of the baby.
- Removal of antibodies from the child’s blood, as well as erythrocyte breakdown products using extracorporeal methods, which include hemosorption and plasma exchange.
Tips
In order to prevent the development of hemolytic jaundice, a mother should regularly attend an antenatal clinic and carry out all necessary research during the infant's period. This will help in time to identify the conflict in Rh or blood type, as well as take the necessary measures to protect the health of the crumbs.
Hemolytic jaundice should not be an obstacle to breastfeeding, on the contrary, the child should be breastfed more often, as this contributes to a more rapid excretion of bilirubin with feces. Studies have shown that antibodies entering the baby’s digestive tract with human milk are destroyed by the action of gastric juice. If the infant cannot breastfeed, they feed it with expressed milk.