Neonatal jaundice of newborns
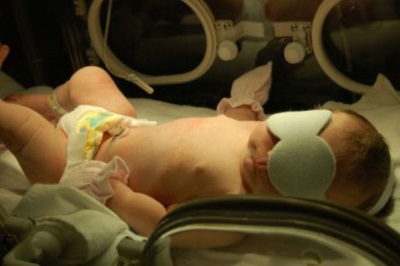
In half of newborn babies (and with prematurity - in about 70-80% of babies), skin becomes yellow for 2-3 days of life. This condition is called neonatal jaundice.
What it is?
This is the name for jaundice occurring in the first days after birth, due to hyperbilirubinemia in newborns. In most cases, this condition is physiological, so it soon passes away on its own, but in some babies this jaundice becomes pathological (approximately 10% of children).
You can learn more about neonatal jaundice of newborns in the following videos.
The reasons
Yellowness of newborns due to:
- Rapid disintegration of fetal hemoglobin in the first days of life, resulting in a large amount of bilirubin circulating in the baby’s blood.
- The immaturity of the liver, which is not active enough to bind the formed bilirubin.
- Reverse absorption of bilirubin from the feces in the intestine due to slow progress, which may be due to rare attachment to the breast or lack of breastfeeding.
With the influence of such factors as prematurity, hypoglycemia, hypoxia during childbirth, low weight and some other conditions, jaundice becomes pathological and may be complicated by bilirubin encephalopathy.
Symptoms
- With physiological jaundice, the baby's skin color changes from top to bottom - first the face turns yellow, then the body and at the very end the limbs turn yellow, although in most cases the yellowness does not fall below the navel.
- The color of the feces and urine remains natural, the general condition of the toddler does not deteriorate, and the spleen and liver are not enlarged. Already by the end of the first week of life, the intensity of skin coloration begins to decrease in the reverse order. The limbs first turn pale, then the body and finally the face turns pale.
- If jaundice is abnormal, the baby’s skin, along with the appearance of jaundice, may become pale or greenish. The general condition of the baby deteriorates, the stool may become discolored, and the urine becomes dark.
- Encephalopathy due to the toxic level of bilirubin is manifested by drowsiness, lethargy, depressed sucking reflex, lethargy, which are then replaced by muscle hypertension, increased irritability, a loud cry, sometimes elevated temperature. In the worst cases, the baby has cramps, stupor, apnea and coma.
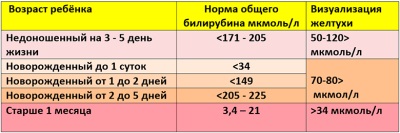
Norm bilirubin
Normally, the level of this pigment in the blood of a child of the third day of life does not exceed 205 µmol / l. At the same time, jaundice becomes visible when the level of bilirubin in the blood of a premature infant is greater than 85 μmol / l. The skin of full-term babies turns yellow with an index of more than 120 µmol / l.
Pathological jaundice is judged by the following indicators:
- In full-term babies, bilirubin levels exceed 256 µmol / L.
- In premature babies, this figure exceeds 172 µmol / L.
- Hourly increase in bilirubin exceeds 5 µmol / l.
Treatment
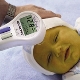
The most common and highly effective method of treating neonatal jaundice is phototherapy. The babies are kept under special lamps, the light of which converts toxic bilirubin into a harmless isomer capable of being excreted with physiological items.In severe cases, the child is prescribed infusion therapy, including blood transfusion.
When does it take place?
In most cases, neonatal jaundice after the onset of 2-3 days and the increase of symptoms during the third or fourth day of life then begins to subside and disappears completely by the end of the second week of life. With prematurity, the duration of neonatal jaundice (physiological) often increases to three weeks.
Pathological jaundice may begin earlier than the second day of life or increase later than on the third or fourth day of life. Its duration often exceeds 3 weeks.
Tips
- For a more rapid decrease in the level of bilirubin, the crumb should often be applied to the breast - at least 8-12 times a day, without interrupting feeding during a night's sleep. If the baby sucks the breast badly, it is fed with expressed milk.
- It is equally important to provide the newborn with daily walks, sun and air baths. At home, the crumbs should be left undressed on the diaper for up to 30 minutes depending on the room microclimate and time of year.