Norm of bilirubin in newborns and what to do when it is elevated
The appearance of the jaundice in the newborn crumbs is a very common problem associated with increased bilirubin level. Every expectant mother should find out what kind of compound it is, why it appears in the blood of a newborn and causes yellow skin color, as defined in the children's body, and what is being done to improve performance.
What is bilirubin?
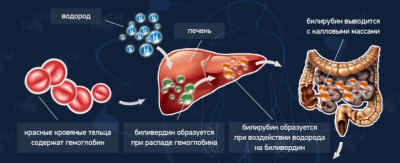
Bilirubin is a pigment whose formation in the human body occurs during the breakdown of hemoglobin. Normally, it binds to the compounds produced in the liver and is excreted in the urine, as well as in the feces. Such a pigment is always present in human blood in small quantities.
Types
Allocate bilirubin:
- Indirect. This fraction is also called free or unbound. This bilirubin is not soluble in water and is quite toxic. It easily penetrates the cells and disrupts their metabolic processes.
- Straight. Since this fraction of the pigment is bound in the liver with glucuronic acid, it is also called bound. After binding, this bilirubin becomes water soluble, making it easy to leave the body.
- Overall. This indicator shows the total amount of bound and free bilirubin.
A broader description of the types of bilirubin is disclosed in the video:
How is the analysis done?
Immediately after birth, the baby takes cord blood to determine the level of bilirubin and some other indicators. Also, newborns can be tested for blood taken from the heel. Prior to blood sampling, it is advised not to feed the baby for four hours. The blood is placed in a special tube, and then examined, determining the level of total bilirubin, and if necessary, its fractions.
The rate of bilirubin in newborns by day in the table
|
Age |
The maximum rate in µmol per liter of blood |
|
First hours after birth |
60 |
|
Second day |
149 |
|
Third to seventh day |
205 |
|
Three weeks |
20,5 |
Why is the rate of change so strong?
These indicators are associated with increased formation and slow removal of bilirubin from the child's body. In the erythrocytes of a fetus residing in the womb, for better oxygen transfer, hemoglobin has a different structure than hemoglobin in adults and children already born. Such hemoglobin is called fetal. As unnecessary after childbirth begins its destruction with the release into the blood, where it is converted into bilirubin. This causes a high concentration of bilirubin in the first weeks of life.
The reasons for the increased level
The appearance of an increased level of bilirubin is caused by:
- Baby prematurity.
- The development of diabetes in the future mother.
- Acute illness of a pregnant woman.
- Hypoxia in the infant during gestation.
- Asphyxia in childbirth.
- Premature onset of labor.
- Increased amount of estrogen in human milk.
- Incompatibility of the blood type of mom and baby.
- Rhesus-conflict during gestation.
- Rejection of breastfeeding immediately after childbirth.
- Big weight loss in the first days after childbirth.
- Pathology of intrauterine development.
- Infectious liver disease.
- Mechanical type of jaundice.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- The destruction of red blood cells due to genetic diseases.
- The use of drugs to stimulate childbirth.
- Hepatic dysfunction in the infant.
- Hormonal malfunction at karapuz.
Types of jaundice in accordance with the indicator
Most babies have jaundice, which is called physiological. It appears after the penetration of bilirubin into the superficial layers of the skin, which occurs when the level of this pigment is above 120 µmol / l in healthy full-term babies and above 85 µmol / l in infants born prematurely.
With an increase in bilirubin level in a full-term newborn, more than 256 µmol / l, and in premature infants over 172 µmol / l, the diagnosis of pathological jaundice is made. The increase in the level of bilirubin in this state is more than 5 µmol / l in one hour, while in physiological jaundice such an increase does not exceed 3.4 µmol / l per hour.
The main symptoms of physiological jaundice and its differences from the pathological are presented in the table:
|
Physiological jaundice |
Pathological jaundice |
|
Starts from 2-5 days of life |
It can start from the first day of life, and after 14 days of life |
|
Lasts an average of 2-3 weeks |
Lasts longer than 2 weeks |
|
From the 4th day of life, the intensity of jaundice and the level of bilirubin decreases |
Differs in wave-like flow. |
|
Yellowing begins with the face and upper body |
The body turns yellow below the navel, the feet and palms are orange. |
|
The child's well-being is not broken. |
The child may be too excited or there are signs of depression of the nervous system. |
|
Coloring feces and urine is normal |
Sometimes the feces become light and the urine darkens. |
|
The work of the liver is not broken |
Possible violation of the liver |
Treatment: How to lower the rate?
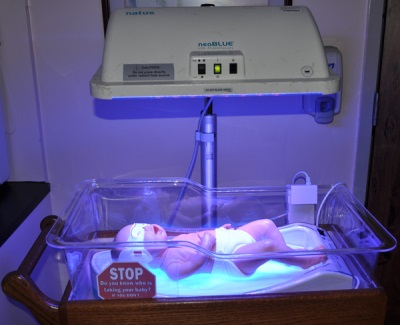
Phototherapy is the most simple, affordable and harmless way to treat jaundice in newborns. A child with the risk of increasing bilirubin to toxic indicators is placed for a certain time under special lamps, the light from which transforms indirect bilirubin into a non-toxic substance called lumirubin. Within 12 hours, bilirubin leaves the body of the baby with feces and urine.
Phototherapy is carried out with breaks for feeding. The baby should lie 20-40 cm away from the lamp, and its genitals and eyes should be covered with a non-transmissive cloth. Side effects of such treatment can be diarrhea, sunburn, fever, dehydration and peeling of the skin. To eliminate them in the body of a newborn, it is important to maintain a constant water balance.
It is equally important to attach the baby to the breast as soon as possible and feed frequently. because it stimulates the removal of meconium from the intestines of a child containing large amounts of bilirubin.
For pathological jaundice, such treatment is connected to:
- Infusion therapy. Special solutions are administered intravenously to the child, and if the condition of the baby is complex, the blood is poured into the crumbs.
- Enterosorbents. Baby is given smectum, enterosgel and other drugs to prevent bilirubin from being absorbed from the intestines.
- Specific treatment depending on the revealed pathology.
What could be the consequences of high bilirubin?
The main danger of an increased amount of bilirubin in the baby’s blood lies in its negative effect on the nerve cells and other organ systems of the child. The result can be encephalopathy, an enlarged spleen and liver, increased drowsiness, lower blood pressure, seizures, developmental delays, hearing problems, and even paralysis.
Opinion Komarovsky
Famous pediatrician confirms that physiological jaundice occurs in almost half of newborn babies and in most cases passes by 10-14 days of life without a trace.
A popular doctor also notes that many babies have breastfeeding jaundice. With her, the condition of the baby is not broken and the crumb normally gains weight. To identify this type of jaundice can stop feeding for 1 day, resulting in the level of bilirubin immediately decreases.
Prevention
- Woman should pay attention balanced nutrition and in the period of carrying a babyand after childbirth.
- Immediately after giving birth, you need apply to my mother's chest.
- Also, already born baby will help prevent the development of jaundice sun baths. Keep the baby under the sun should be no longer than 10 minutes.