Causes, symptoms, treatment and effects of jaundice in newborns
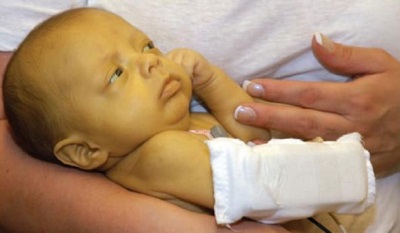
The skin of a newly born baby quite often acquires a yellow color in the first days of life - in more than 50% of full-term babies and in 70-80% of premature babies. Each mother will be alarmed by such changes, but the yellowness of the skin is not always the evidence of the disease. Why, then, can the skin turn yellow in the newborn and how can it be determined whether it is a normal stage of development or a disease?
What is it?
Acquisition of skin yellow shade called jaundice. This is not a disease, but only a symptom that in a newborn can occur both for physiological reasons and for various diseases.
The yellow tint of the skin is associated with an excess of bilirubin - a pigment formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin. In its free form, it is toxic to the body and is able to penetrate into the brain cells, therefore, in healthy people in the liver, such pigment is converted into a bound form (soluble in water), safely leaving the body with feces and urine.
The following video doctor Komarovsky explain in more detail why there is a children's jaundice.
Types of jaundice
Jaundice in infants of the first month of life is divided into physiological and pathological, caused by various pathologies. Given the cause of pathological jaundice is:
- Hemolytic. It is caused by the breakdown of a large number of red blood cells.
- Parenchymal. It is caused by liver diseases affecting hepatocytes.
- Conjugation. It is caused by bilirubin binding problems.
- Obturation It causes obstruction in the biliary tract.
Separately allocated jaundice, due to estrogen and special fatty acids in breast milk - it is called breastfeeding jaundice. It is not dangerous, appears in the second week of life and can last up to 2-3 months of age, manifesting itself only a yellow skin tone. A karapuz with such jaundice adds weight, sucks a breast with appetite and sleeps normally.
The reasons
The appearance of the physiological form of jaundice in babies on the second or third day of life is associated with:
- The collapse of a large amount of hemoglobin. We are talking about fetal hemoglobin, which was needed during fetal development, and after birth is replaced by normal (adult) hemoglobin.
- The immaturity of the enzymatic system of the liver, as a result of which it is impossible to bind all the pigment formed during the breakdown of hemoglobin.
- Long passage of fecal masses through the intestines and unformed microflora, due to which a part of bilirubin enters the bloodstream back.
Hemolytic jaundice in infants of the first days of life is most often caused by the incompatibility of the baby’s blood with the mother’s blood by the Rh factor or group.
The causes of parenchymal jaundice in a newborn are:
- A viral disease affecting the liver.
- Hereditary liver disease.
The causes of conjugation jaundice may be a hereditary disease, hormonal imbalance, or treatment of babies with some medicines.
Obstructive jaundice can cause mechanical damage to the biliary tract and diseases of the gallbladder, for example, genetic.
Factors that increase the risk of jaundice in newborns include:
- Prematurity
- Delayed fetal development.
- Reception future mum of many medicines.
- Significant weight loss after birth.
- Hemorrhages that appeared during childbirth.
- Asphyxia in childbirth.
- Intrauterine infection.
- Diabetes mellitus in the future mother.
- Rejection of breastfeeding.
Symptoms
The main symptom of jaundice in a newborn baby is yellowing of the skin. If jaundice is physiological, it appears on the second or third day of life and in most of the babies it does not fall below the navel (the head and upper part of the body turn yellow). The shade of the skin is bright, as pronounced as possible for 3-5 days of life, and then begins to turn pale.
In pathological jaundice, the skin can change its color even earlier (sometimes the child is already born yellow), and later, and the symptom may last longer and appear for periods (wave-like). On the possible obstructive jaundice may suggest a greenish skin tone.
Other manifestations of jaundice in the newborn are presented in the table:
When physiological | When pathological |
Overall health is fine | The child feels bad |
Sleep is not disturbed | Baby can sleep badly |
Good appetite | Appetite disturbances are possible |
The size of the liver and spleen is not changed | Liver and spleen may increase in size. |
The color of feces does not change | Feces may become discolored |
Urine has a natural color. | Urine darker than usual |
Treatment
In each case of jaundice in a newborn, the question of the appropriateness and tactics of treatment should be decided by the doctor. Physiological jaundice in most infants is not treated at all, as it passes on its own.
If the level of bilirubin is dangerously high, phototherapy is given to the child. This is the most common, simple and safe way to get rid of free bilirubin in the baby’s blood. It provides for staying under special lamps, the light of which converts toxic bilirubin into a harmless form.
Another treatment that can be given to an infant with jaundice is:
- Infusion therapy It is often prescribed in cases where the baby cannot breastfeed. The infant is given intravenous glucose, saline solutions, proteins and vitamins.
- Blood transfusion. This method of treatment is resorted to in a serious condition of the infant, for example, if the baby has a Rh-conflict.
- Medicines with choleretic effect. Usually prescribed for cholestasis and conjugation jaundice, when the liver does not cope well with its function to bind bilirubin.
- Sorbents to prevent the reabsorption of pigment from fecal masses.
- Surgical intervention in case of obstructive jaundice.
Possible consequences
One of the most dangerous complications of jaundice caused by an excessively high level of bilirubin is the defeat of the subcortical nuclei of the brain. This complication is called nuclear jaundice. At the first stage of its development, the baby becomes sluggish, sleeps a lot, refuses to suck the breast, bends, throws back the head.
If you do not take measures to reduce the level of bilirubin, the child increases the liver, body temperature rises, there are convulsions, a loud cry, tension in the muscles of the neck. In severe cases, the baby may die from apnea or coma. Children who have suffered nuclear jaundice may subsequently experience problems such as paralysis, deafness, and mental retardation.
After how many days does jaundice most often pass?
If the appearance of a symptom is caused by physiological reasons, as a rule, the yellowness of the skin decreases by 10-14 days of life of a full-term infant. In premature babies, jaundice lasts a little longer — on average up to 3 weeks.

Tips
- Often apply the baby to the breast, as breastfeeding promotes faster removal of bilirubin from the intestines.
- If the baby is already 2 weeks old, and his skin color remains yellow, show the crumbs to the doctor and analyze for bilirubin.
- Be sure to seek medical attention if your child with jaundice has deteriorated in general condition, body temperature has increased, sleep and appetite are disturbed.
Prevention
- The future mother should regularly visit the gynecologist and take all the necessary tests.
- Immediately after the birth of the child should be applied to the chest, so that the baby received colostrum.
- With the baby, you need to walk more, and at home to arrange air baths.
- Mom should watch her diet by eliminating foods that cause digestive problems.