Astigmatism in children
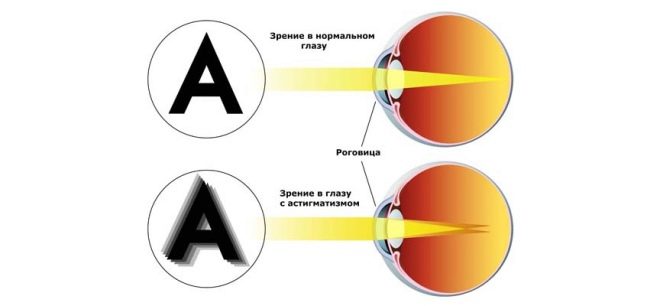
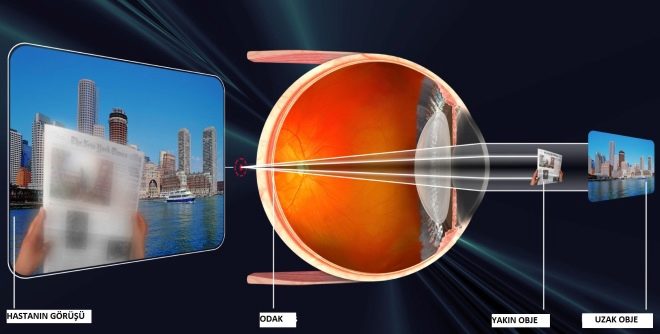
Astigmatism is a visual pathology that entails a significant reduction in visual acuity. This defect is a type of ametropia, that is, anatomical changes that disrupt the normal process of refraction of the beam, which should focus on the retina. In the presence of this disease, the child is not only unable to clearly distinguish between objects that are close or far away, but also perceives them in a distorted form.
Lack of treatment of astigmatism can trigger the development of other visual pathologies, and in particularly severe cases, lead to disability. What are the types of astigmatism in children? What techniques are used by modern ophthalmologists for the treatment and prevention of the disease? What will be the prediction for the future for a child suffering from astigmatism ?.
The mechanism of development of astigmatism and its types
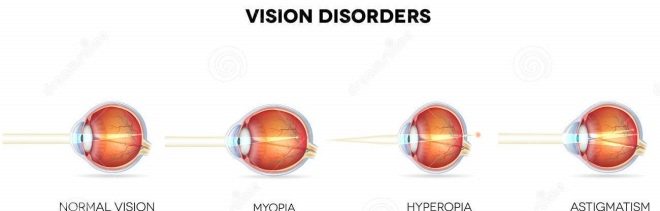
The group of visual disorders, including astigmatism, is called refractive errors. This is ranked:
- myopia (myopia);
- hyperopia (farsightedness);
- presbyopia (aging of the lens).
Astigmatism is found in both children and adults. This is mainly a congenital defect, but the disease can also develop as a result of mechanical trauma or surgery. Statistics show that almost 58% of the total adult population of the Earth has astigmatism ≥0.25 D. With astigmatism, there is a change in the refractive index, sphericity and curvature of the eye components.
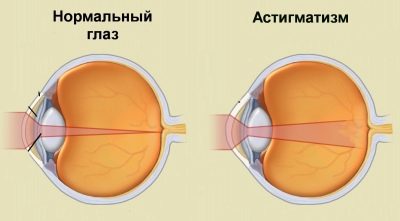
Also, a violation of the eye alignment mechanism relative to each other can be the cause of visual disturbances, in which rays of light passing through the transparent medium of the eye and having parallel trajectories are focused on two different focal lines perpendicular to each other, instead of focusing at one focal point.
Not so long ago, a series of clinical studies were conducted, during which a link was established between the process of autosomal recessive inheritance and the development of astigmatism. Due to impaired refractive ability of the eye There are several types of astigmatism:
- corneal;
- lenticular;
- ophthalmic (ocular).
Next, we consider in more detail each of these types of violations.
Corneal
The cornea is one of the transparent media of the eye, which is located in front of it. In addition to its primary conductor function, the cornea is involved in protecting the eye from mechanical damage and ingress of infectious agents.
In children with astigmatism, it is usually slightly oval instead of normal spherical. Such an anomaly leads to the fact that the focusing of light rays occurs at two points instead of one.
In modern ophthalmology has not yet formed a clear concept of the etiological factors that provoke the abnormal formation of the cornea.
It is proved that a genetic predisposition has a certain influence on this mechanism. A child with one of the parents suffering from this anatomical defect has an increased chance of inheriting it. Therefore, a child with such a family history should be examined for refractive anomalies as soon as possible.
Corneal astigmatism can also be associated with any pathologies of the fibrous membrane of the eye, including acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, mechanical injuries, keratoconus, keratoglobus, pterygium, and other causes of hypertrophic changes in the structure of the cornea.
Lenticular
The lens is a kind of organic lens, which is located behind the iris. Any of its structural damage or violation of its refractive power leads to a decrease in vision. Most patients with lens astigmatism have a normal cornea shape.
Often the cause of this disease becomes dislocation or subluxation of the lensthat happen as a result uneven distribution of the tension of the zinn bondchanging its spatial position. Also, this type of astigmatism may be a consequence of mechanical injury to the eye or cataract.
Systemic diseases such as diabetes mellitus or hypertension, lead to disruption of the normal blood circulation process in the eye vessels, because of this, the shape and size of the lens is gradually deformed.
Ocular
Ocular astigmatism is quite rare among other types of congenital astigmatism. It may develop as a result of swelling of the optic nerve, pathological changes in the posterior ocular pole, orbit, or other nearby facial bones.
Clinical picture
There are several degrees of this disease, which differ depending on the level of violation of light refraction:
- weak - up to 3 D (the most common form, successfully compensated);
- medium - 3-6 D (less common, correction or surgical treatment is possible);
- high - above 6 D (registered quite rarely, treated only by surgery or with the help of laser correction).
The main symptoms of astigmatism:
- blurred or distorted vision at different distances from objects;
- photophobia (increased sensitivity to light);
- frequent headaches;
- eye strain (it happens when you have to focus on something for a long time, for example, when reading or working at a computer);
- increased fatigue.
When making a diagnosis in young children and especially babies, it is difficult to determine astigmatism, since the child can not always notice and explain that he has begun to see worse. In such cases, the care of parents helps: they may notice that the baby has often squinted, and also tilts his head to the side, examining an object.
In ophthalmology, there is a special concept - "Physiological astigmatism"in which there is a weak degree of violation of light refraction (not more than 0.5 D), because of which it is difficult to diagnose. It must be borne in mind that even a weak degree of development of astigmatism in a child needs to be treated, since the lack of adequate therapy for such a serious visual impairment can lead to serious consequences.
If a child for a long time perceives an image in a distorted form, then this provokes the degradation of the entire visual apparatus (in particular, cells of the visual cortex), and this in turn leads to the formation of stable amblyopia.
Treatment methods
Among all children and adolescents suffering from astigmatism, the majority have a weak degree of disturbance of light refraction, which is not always noticeable to parents in the initial stages of the development of the disease. Therefore, the child must regularly undergo preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Depending on the degree of development and the type of the disease, the ophthalmologist may elect one of the following areas of astigmatism treatment:
- vision correction with glasses;
- vision correction contact lenses;
- surgery and laser technology.
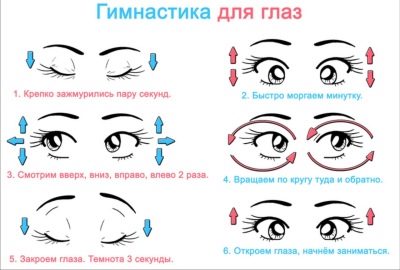
Additionally, the child must periodically take a course. hardware treatment and physiotherapy. Also he is shown a special visual gymnastics. Thanks to special exercises during charging for the eyes, it is possible not only to increase visual acuity, but also to avoid the development of concomitant disorders (for example, strabismus). Eyeglass or contact corrections are designed to correct improper light refraction.
Wearing contact lenses is undoubtedly more effective in astigmatism, since this method allows one to take into account the individual characteristics of defects in the structure of the eyeball.
Contact correction does not provide for the presence of a vertex distance between the eye, which, with an eyeglass correction, averages 12 mm. Constant wearing of contact lenses is advisable with a weak and moderate degree of refractive disorders in children.
Methods of correction for types of astigmatism
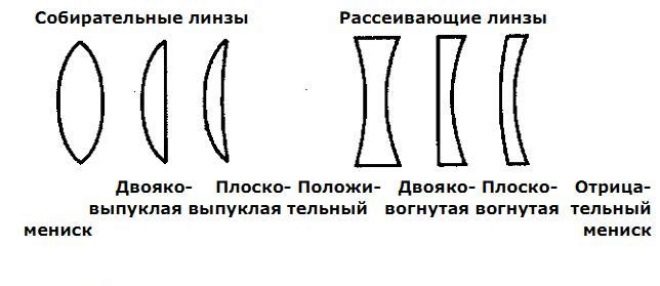
The first attempt to correct this type of refractive anomaly was made by an Englishman. George Biddel Airy in 1872. He created a cylindrical lens 4 D minus to compensate for the astigmatism of his own left eye. The main quality that distinguishes cylindrical lenses from spherical lenses is that the cylinders focus the light beam in a straight line, not a point.
Contact lenses that correct astigmatism are almost impossible to make completely cylindrical, so a spherocylindic or, as it is also called, toric form is created for them. With their regular use it is necessary to strictly adhere to all requirements of operation, especially with regard to hygienic rules.
There are many types of contact lenses, depending on the design, including: rigid glass-plastic, polymer gas-tight, soft silicone, etc. The rules for their use depend on the type of specific lenses.
Lenses for the correction of astigmatism are distinguished by the presence of certain marks on their surface that indicate the correct position in the eye (at a certain angle).
Methods of surgical treatment of astigmatism
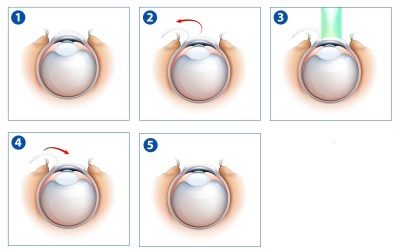
The most effective method of correcting astigmatism is laser correction. Currently, there are several types of it:
- laser keratomileuse (LASIK);
- super LASIK;
- epi-lasik;
- Femto LASIK (Intra LASIK);
- laser epithelial keratomiliasis (LASEK);
- photorefractive keratectomy (PRK).
These techniques differ in the degree of impact and the method of processing the surface of the cornea. However, in essence, they have a common principle: with the help of a laser, the shape of the cornea is changed to spherical, taking into account the individual characteristics of the eye. Such operations can be performed not only for patients with a corneal type of astigmatism, but also with lens-like ones, since the degree of refraction of the light beam changes when correcting the shape of the cornea.
However, this procedure has a number of contraindications:
- the presence of diabetes mellitus (as in this case, astigmatism is a secondary disease and first of all the therapy of the underlying disease is necessary);
- the presence of severe immune diseases, such as lupus, HIV, etc., (due to the high risk of complications during the postoperative period);
- treatment of certain groups of drugs (corticosteroids, certain types of antibiotics, isotretinoin, etc.);
- high severity of astigmatism (above 5 D).
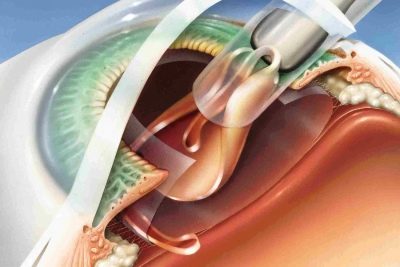
If for some reason it is impossible to apply laser correction to a patient with corneal dysfunction of light refraction, then keratoplasty can be performed for him (partial or full replacement of the cornea with an artificial or donor).
The procedure of refractive lens replacement is widely used to correct astigmatism according to the lens type of light refraction. Its essence consists in removing the damaged lens through a micro-section and replacing it with an intraocular toric lens.
Myopic
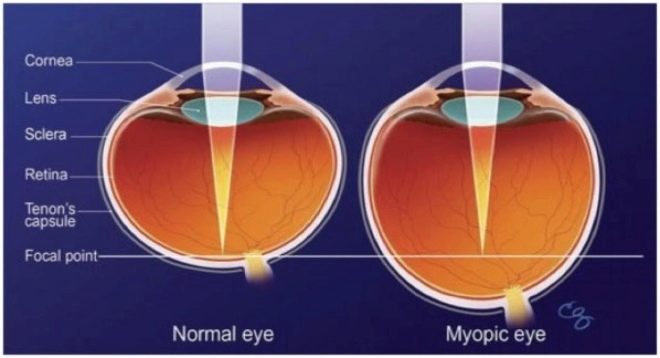
As already mentioned, with astigmatism, the cornea has an irregular shape.It can be of several types, which makes it possible for ophthalmologists to classify astigmatism in more detail. The myopic (myopic) astigmatism of one or both eyes is a type of refraction anomalies in which the eye prevails myopia.
This means that if, in a healthy eye, light rays, passing through transparent media, are focused on the retina at one particular point, then in the astigmatic eye it occurs simultaneously at several points, while some part of the “picture” is focused in front of the retina (which is typical for myopia), and the other - on it. Also, the light beam can be focused at two points in front of the retina.
Simply put, this pathology can be regarded as a kind of synthesis of astigmatism and myopia.
Myopic astigmatism is simple and complex. They can be differentiated during an ophthalmologic examination by identifying the main meridians of the eye. There are two types of myopic astigmatism:
- Plain. It is characterized by the fact that in one of the main meridians of the eye myopia is observed, and in the other - normal vision. In this case, a certain part of the rays focuses on the retina (as occurs in a healthy eye), and the other part - in front of it (which is typical of myopia);
- Complicated. Myopia takes place here in both main meridians of the eye, but it has a different degree in each of them. In this case, the light rays are focused at two points in front of the retina.
The clinical picture of myopic astigmatism is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- reduced visual acuity;
- double vision as well as other types of image distortion;
- headache;
- tearing during long focusing on a particular object.
With this type of astigmatism, the child is forced to come as close as possible to the subject in order to see it clearly. The “picture” can be doubled or blurred. If we are talking about myopic astigmatism of a weak degree (less than 3 D), then these symptoms may be absent. The child may not notice reduced vision or simply get used to the perception of a distorted image.
In this case, parents should pay attention to the fact that the child quickly began to tire after a long visual load or complains of a headache.
The main cause of myopic astigmatism is hereditary factor. In rare cases, the disease develops as a result of previous injuries, surgeries or infectious diseases.
Myopic astigmatism can be difficult to differentiate from myopia, since the clinical picture of these diseases is quite similar. It is especially difficult to make a correct diagnosis when vision is reduced in both eyes.
If the child was not diagnosed in time, as a result of which he did not receive adequate treatment, then at a more advanced age he may develop more serious defects of the visual apparatus, such as amblyopia, or "lazy eye" - pathology, which is very difficult to correct. Therefore, you must seek qualified help in the early stages of the disease.
To do this, the child must regularly undergo preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist, and parents must respond promptly to the appearance of any signs of reduced vision. Treatment of myopic astigmatism, of weak and moderate degree, primarily includes the use of spectacle and contact correction, apparatus treatment, and visual gymnastics.
Additionally, instillations of therapeutic eye drops can be prescribed, as well as regular intake of a complex of vitamins. Sometimes an ophthalmologist may consider the question of surgical treatment.
In case of a high degree of myopic astigmatism, an operation is considered to be the best way to solve a problem. In this case, the constant wearing of glasses or contact lenses can be cause regular headaches and dizziness. There are several methods of correctional surgery for high degree myopic astigmatism.
Astigmatic keratotomy
On the surface of the cornea, micro incisions are made in the corresponding meridian. In the process of their healing, there is a gradual change in the curvature of the cornea along the axis, which contributes to the weakening of the stronger meridian.
Photorefractive keratectomy
With the help of a laser, a kind of "grinding" of the corneal surface is performed. Due to this, its curvature changes. During the operation, the surface layer of the cornea (epithelium) is removed, other structures of the eye remain undamaged.
The recovery period usually lasts no more than a week. At this time, the patient may feel pain and a burning sensation in the eye, photophobia (increased photosensitivity) and tearing. At this time it is necessary to wear special protective contact lenses.
Photorefraction keratectomy is not performed immediately in both eyes, and there is also the risk of turbidity in the central optical zone of the cornea. After such an operation, vision is restored no later than six months later;
Laser keratomileusis
At the moment, this procedure is very popular. Laser keratomileusis is a very effective way to correct myopic astigmatism. Its essence is to change the shape of the cornea by removing its middle layers, which, unlike photorefractive keratectomy, avoids the threat of corneal opacity and pain in the recovery period.
The operation is performed by a laser. This procedure allows you to achieve the highest possible visual acuity, which in the future will not need to be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Unfortunately, for such a manipulation there is a list of contraindications and possible side effects. All possible risks, as well as arguments in favor of the operation, should be discussed in detail with an ophthalmologist, which will help make an informed decision. Laser keratomileusis results are irreversible..
In special cases, if there are absolute contraindications to the implementation of the above methods for treating myopic astigmatism, the ophthalmologist may recommend more radical methods such as implantation of a phakic intraocular lens, lens replacement or cornea transplantation.
Farsighted
Difficult long-sighted astigmatism develops under the condition that the cornea’s normal surface structure is disturbed: it becomes toric with an uneven curvature, and the eyeball acquires a slightly oblate shape. Various factors can provoke such changes in the visual apparatus. For long-range visions, or hypermetropic astigmatism, the focusing of light rays occurs behind the retina. The disease can have a simple or complex form.
Symptoms of hypermetropic astigmatism:
- burning eyes;
- blurred vision;
- diplopia (double vision);
- eye fatigue during visual loading of various kinds (reading, working at a computer, watching TV, etc.);
- feeling of tension in the eyes.
In most cases, the etiology of hypermetropic astigmatism is associated with heredity, but it happens that the disease develops as a result of the influence of external factors.
There are several types of long-sighted astigmatism:
- Simple form. In one of the two main meridians of the eye, vision is normal, and in the other - farsightedness;
- Complicated form. In both main meridians of the eye, hyperopia of different degrees is present.
With complex hypermetropic astigmatism, the ophthalmologist determines its degree, which is characterized by the length of the distance between two foci. There are only three degrees of complex long-sighted astigmatism:
- Mild - up to 2D;
- The average degree is 2-3 D;
- High degree - from 4 D.
In children under the age of 1 year, complex hypermetropic astigmatism is considered the physiological norm. Statistics show that physiological hypermetropic astigmatism occurs in 25% of the Earth, where the refractive difference of light rays is 0.5 D. Such a defect does not have a significant effect on visual acuity and does not provoke other symptoms, so there is no need to correct it.
In children of younger preschool age, the most frequent complex hypermetropic astigmatism of the left eye occurs. In this case, when selecting glasses, the astigmatic glass is inserted into the frame only on the left side, and for the right eye they put simple glass. This type of astigmatism in children is effectively amenable to therapy with the help of hardware treatment and charging for the eyes.
Visual defects are corrected with the help of special cylindrical glasses. With this diagnosis, the child is put on the dispensary account, and he is shown constant wearing glasses.
With the implementation of all the recommendations of the ophthalmologist by the age of 12-13, visual acuity can be brought to normal values without the use of corrective surgery. If for some reason (a high degree of complexity of the refractive anomaly, neglected pathology, etc.) visual impairment does not respond to spectacle or contact correction, an ophthalmologist may be prescribed a surgical correction of the defect.
There are several types of such operations:
- Laser thermokeratoplasty. With this method, the shape of the cornea is changed. The surgeon applies several burns to the surface in the periphery area with a laser, due to which an active reduction of the collagen fibers occurs, which contributes to the change of the shape of the cornea;
- Thermokeratocoagulation. In fact, the method is similar to the previous one, only here burns are applied with a thin metal needle heated to a certain temperature;
- Laser keratomiles. It is considered the most successful method of surgical treatment of hypermeptropic astigmatism. With the help of an excimer laser, a kind of “evaporation” of a certain part of the surface layer of the cornea occurs, as a result of which its shape changes.
Mixed
Mixed astigmatism is considered the most severe form of refractive errors. With this type of visual impairment, the child is deprived of the opportunity to clearly see objects that are both close and far away. Also significantly distorted the shape of objects. Mixed astigmatism is characterized by the presence in the same eye along two main meridians myopia and hyperopia.
This is the main difficulty in the selection of correction, since the optical power in one meridian must be strengthened, and in the other - weakened.
The main reason for the formation of mixed astigmatism is a hereditary factor. If a newborn child has a congenital refractive anomaly of this type to a certain extent, then as it grows up and approaches one year old, it will decrease (approximately to 1 D), which is the physiological norm. This kind of astigmatism does not affect visual acuity and does not need special treatment, or in the selection of corrective means. If the mixed astigmatism of the child is not diagnosed in time and does not prescribe the appropriate treatment, then the baby’s visual abilities will not develop.
In addition, without proper therapy, after some time, vision will rapidly begin to deteriorate, and as a result, other pathologies of the visual system, such as amblyopia and strabismus, may form.
Therefore, parents need to be especially attentive to the child, and when the first signs of visual impairment appear, contact an ophthalmologist.
Symptoms of mixed astigmatism:
- eye fatigue;
- recurrent headaches (especially in the superciliary arches) and dizziness;
- difficulties in recognizing printed text;
- difficulties with long-term focusing on objects that are at a certain distance (for example, on a blackboard);
- the child, trying to look at an object, tilts his head from different angles and squints his eyes.
The human visual system ends up being formed at about 14-16 years old, so if a child is diagnosed with mixed astigmatism, treatment should be started immediately so that the visual skills that he has are not reversed. Children with this pathology are shown to constantly wear glasses or contact lenses.
Surgical methods for correcting this refractive anomaly in childhood are rarely used because of changes in the shape of the eyeball as the child grows up.
How to treat astigmatism in children, see the next video.