Blepharitis in children
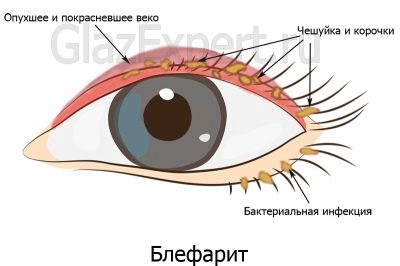
The term "blepharitis" in ophthalmology is used to denote inflammation of the eyelids. This disease can be caused by a number of reasons and have a different nature of the course. Often, blepharitis is diagnosed in children, including newborns and infants.
Classification
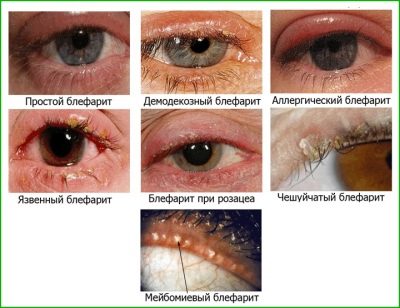
According to the characteristic clinical picture and the conditions of occurrence of blepharitis, ophthalmologists There are several types of it:
- scaly, or plain. Manifested by hyperemia and increasing swelling at the edges of the eyelids. A distinctive feature of this form of blepharitis is the formation of peculiar scales, which are particles of desquamated glandular epithelium;
- ulcerated. There is a purulent inflammatory process, localized in the hair follicles of the eyelashes. Pathology is characterized by the formation of ulcers along the edge of the eyelid;
- Meibomian In this form of the disease, the specific sebaceous glands of the eyelids (meibomian) produce an increased amount of fat secretion, while its outflow slows down, which becomes the cause of the blockage of the gland and, as a result, its pathological increase;
- Rosacea. The form of blepharitis, which is characterized by the appearance on the centuries of small grayish-red nodules, crowned with pustules. These symptoms can also be combined with pink acne;
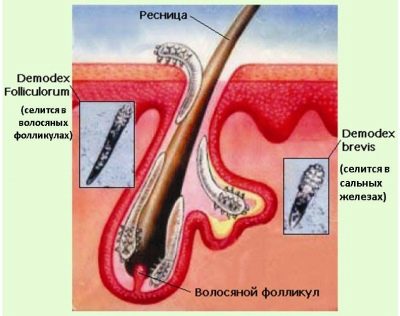
- demodectic Typically, the causative agent of this form of blepharitis is a parasite - iron mite. Its habitat is the sebaceous and meibomian glands of the eyelids, as well as hair follicles. Most often, young children suffer from this disease due to non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
Etiology of the disease
The most common cause of the inflammatory process in the thickness of the eyelids in children is the excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands located in the thickness of the eyelids. Drops of the secreted substance accumulate at the edges of the eyelids, creating favorable conditions for the reproduction of pathogenic microflora.
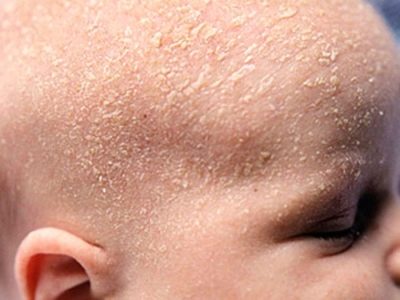
Often seborrheic joins blepharitis dermatitis. This condition is manifested peculiar stratification of dry skin on the face and scalp. There may also be a number of signs of an allergic reaction.
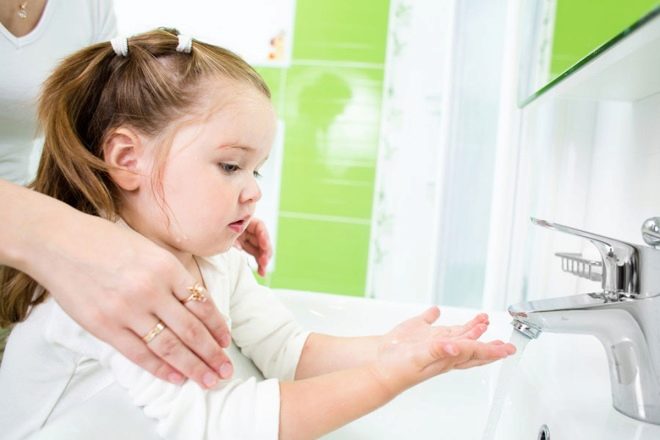
In addition, the causes of inflammation of the eyelids in children often become elementary non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, eyebrows, illiterate treatment of functional visual disorders, chronic anemia of various etiologies, lack of vitamins, inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx, chronic inflammatory processes in one of the gastrointestinal sections tract.
Also, blepharitis may be one of the signs of the presence in the child's body of infection or helminthic invasion.
Not only the symptoms, but also the tactics of further therapy depend on the type of pathogen of the pathological process.
The clinical course of blepharitis in children
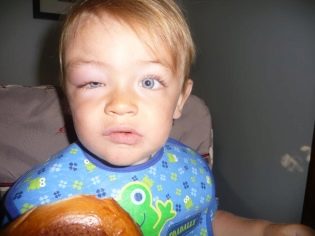
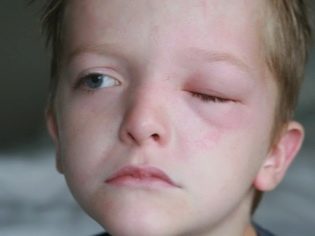
One of the main symptoms of blepharitis is severe itching in the eyelids. Parents may notice that the child constantly scratches his eyes, despite repeated requests from adults not to do this. Objectively, you can notice redness and swelling of the edges of the eyelids, as well as constant tearing. The child will constantly complain of severe itching or say that he has a speck in his eye.
When scaly blepharitis in the zone of growth of the eyelashes may appear the appearance of small scales. The skin below them will have signs of inflammation.
For ulcerative forms of the disease is characterized by the formation of purulent crusts on the eyelids. If the child tries to comb them, he will remove the scales along with eyelashes, and in the place where there was a crust, a small ulcer will appear that may bleed.
In addition to local symptoms, the child may have signs of general malaise. If he is not timely provided with qualified assistance, then in the future the disease can become chronic and have a negative effect on vision baby Also, the inflammatory process can spread to neighboring organic structures and provoke the occurrence of more serious ophthalmic pathologies.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by the ophthalmologist on the basis of the subjective complaints of the child, an objective examination of the eyelids, collection of anamnesis and detection of associated diseases, as well as the results of laboratory tests. Held in parallel visometry and eye biomicroscopy. In addition, the attending physician may order a study of the refractive capabilities of the child's eye to identify the possible latent form of hypermetropia (farsightedness), myopia (myopia), and astigmatism.
If a specialist suspects a baby with demodectic blepharitis, then the child’s cilia are subjected to detailed laboratory analysis.
To confirm the blepharitis of infectious nature, bacteriological smear from conjunctiva is performed. In order to refute or confirm helminthic invasion as a possible cause of the development of the disease, a sample of a child's feces for worms is examined.
Sometimes, a child suffering from this disease requires consultation of narrow specialists, for example, an immunologist, a gastroenterologist, an endocrinologist, an otolaryngologist, and others.
If there is a chronic course of blepharitis, which is accompanied by hypertrophy (pathological growth of tissue) of the eyelid margins, then a specialist should be allowed to have a malignant neoplasm in the patient's body, such as squamous and basal cell carcinoma of the century. To confirm or deny this diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct biopsy followed by histological examination of the biopsy.
How to treat blepharitis in children?
For the treatment of disease using modern methods that are most effective. Tactics of treatment is always determined only by an ophthalmologist. To do this, it is necessary to establish the exact cause and form of the disease.
It must be remembered that treatment of blepharitis should not be limited only to the primary withdrawal of symptoms. It is impossible to voluntarily stop taking the drugs without first consulting an ophthalmologist, so as not to provoke the development of relapses and the transition of the disease to the chronic form.
During therapy, the doctor may raise the question of the appropriateness of using not only local antibacterial agents, but also general antibiotic therapy. This is usually associated with the appearance of abscesses (fibrous capsule with purulent exudate). In this case, the following drugs may be prescribed: oxacillin, ampicillin, sulbactam, amoxicillin and others. It may also be necessary surgical opening of the abscess.
With a protracted course of the disease, tetracycline tablets are administered orally, the course of treatment is usually 1-1.5 months. In addition to the main therapeutic effect - the destruction of the infectious agent, it is also possible to note its effect on the secretory activity of the meibomian glands. Any antibacterial agents are applied strictly on the recommendation of a doctor after preliminary identification of the source of the pathogen, therefore self-medication with antibiotics "blindly" will most likely not bring the desired result.
Topical medications that contain corticosteroids in their composition are not used for long periods in order to avoid side effects.
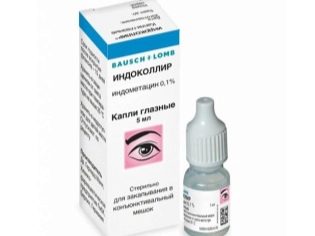
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used when there is evidence of chronic blepharoconjunctivitis of a non-infectious nature. Most often in this situation drugs are prescribed. indokollir or diclofenac.
Well-known in Russia, pediatrician Komarovsky devoted one of his programs to this topic.
Anyway, the key to successful treatment of blepharitis is strict adherence to all medical recommendations. Remember do not self-medicate or experiment with various questionable methods of traditional medicine.
As you know, the best cure for the disease - its prevention. The main thing - the observance of personal hygiene.
The pediatric ophthalmologist will talk about the causes of eye inflammation in children under one year in the next video.