Color blindness in children
Nowadays, color blindness is not uncommon. Its essence lies in the inability of a person to recognize (allocate among others) a certain color. Among the color blindness there are those who can not distinguish between several colors, and in severe cases, the patient may not have color sensation at all.
Colors that the color blind doesn’t recognize are gray to him. Not all moms and dads know how to recognize color blindness in children 3 years old, 2 years old, what are the causes of this disease and what measures should be taken by parents if their child has already been diagnosed.
Etiology
Most often, color blindness in a child occurs due to chromosomal mutation - even during fetal development. However, there are cases when the disease arose as a result of any ophthalmologic or neurological pathology.
Depending on the factors contributing to the development of this type of visual defect, it can be determined whether it is treatable with therapeutic or surgical methods. Hereditary color blindness is irreversible. It is known that mostly boys are subject to color blindness.
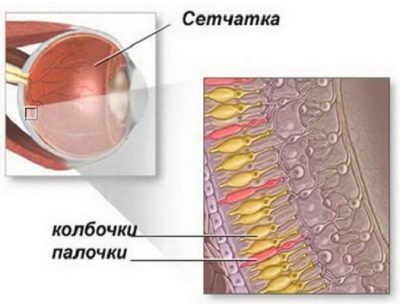
The mechanism of violation of color perception (full or partial) by the visual apparatus is the violation of the functional activity of color-sensitive cells (cones). They are located in the central part of the retina.
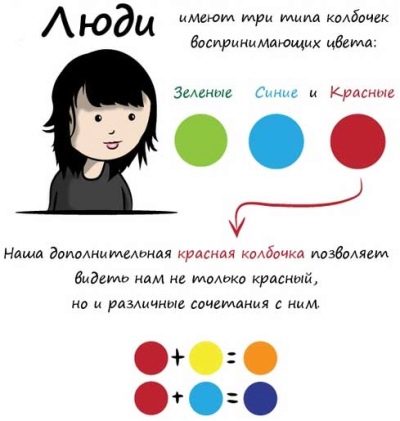
There are several types of cones, each of which contains a special protein pigment of nature, the presence of which determines the perception of a certain color:
- The first type of pigment perceives the red spectrum.
- The second type of pigment perceives the green spectrum.
- The third type of pigment perceives the blue spectrum.
In a healthy child, all color-sensitive cells have three types of pigment, so the visual apparatus of these children is able to correctly perceive information about all colors.
Clinical picture
The mechanism of development of the disease and the degree of visual disturbances associated with color perception are always very individual. Often recorded cases with partial violation of color perception, when the disease occurs in mild or moderate form. Cases with severe and complete lack of color perception occur quite rarely.
The most common form of manifestation of color blindness in children is a violation of the perception of the colors of red and green gamma. Less common cases of violation of susceptibility to blue-green shades.
The following ophthalmologic pathologies usually accompany severe forms of color blindness:
- low level of visual acuity;
- nystagmus (involuntary periodic movements of the eyeballs in a certain direction - horizontal or vertical).
Diagnostics
Children with impaired color perception begin to clearly name the colors of the objects around them much later than their peers. Parents try to teach the child to distinguish colors, repeating the name of each of them many times, and the child perceives some shades in a distorted way, but cannot determine this on their own. There are often cases when color blindness is diagnosed to a person already in adulthood, during a prophylactic eye examination.
Upon careful observation of the crumbs, the responsible parent still has the opportunity to check whether he has any color disturbances. To do this, you can use several simple tests to determine:
- Put in front of the baby a pair of equal in size and shape of candy. Wrap one of them in a motley wrapper, the other - in a nondescript, better gray.Children are greedy for everything that is colorful and bright, so a healthy child will probably prefer candy in a bright package.
A kid with color blindness will take it at random, and you will almost certainly notice it, which should be the reason for an immediate appeal to a specialist.
- Ask your child to draw a landscape from nature, using colored pencils or felt-tip pens. If the colors in the children's drawing do not sharply correspond to the real ones, then there is a reason to get worried. However, it happens that such a "technique of execution" is associated with the rich imagination of the baby and is not a sign of visual impairment.
For the diagnosis of color blindness in a child, an ophthalmologist may use Special color schemes with pictures and Rabkin tables. They will allow not only to identify the disease, but also to determine the type of violation of color susceptibility.
Treatment methods
Unfortunately, at the moment congenital color blindness in children, due to a genetic trait, cannot be fully cured or prevented. Some types of acquired color blindness can be eliminated by acting on their root cause.
If the disturbance of color perception is associated with a cataract or other organic pathology of the visual apparatus, then you can get rid of color blindness adequate therapy or surgical correction of the primary disease. Systematic intake of certain groups of drugs may trigger the occurrence of such visual disorders. In such cases, the doctor will correct the plan of drug treatment.
There are ways to correct violations of color vision in children. These include:
- Wearing special glasses or contact lenses for color blind. They can increase the recognition of certain colors, but they can distort the shape and size of some objects.
- Wearing glasses or contact lenses blocking bright light. Such glasses are not only a means of correcting color disturbances, but also a high-quality therapeutic agent. With their help, a child with a color blindness can orient himself much better among multicolored objects.
- Wearing special glasses with shields on the periphery. It is shown to children with a complete lack of normal color perception.
Due to the dimmed light, additional stimulation of the color-sensitive cells occurs.
Some facts
If you focus on the statistics, it can be noted that 10% of all inhabitants of the planet Earth to some extent suffer from color blindness. Numerous studies of specialists in this field confirm that the probability of occurrence of this disease depends on many factors. Among them are genetic predisposition, gender, age category, place of residence. There is a hypothesis that this visual impairment was the physiological norm for the ancient man.
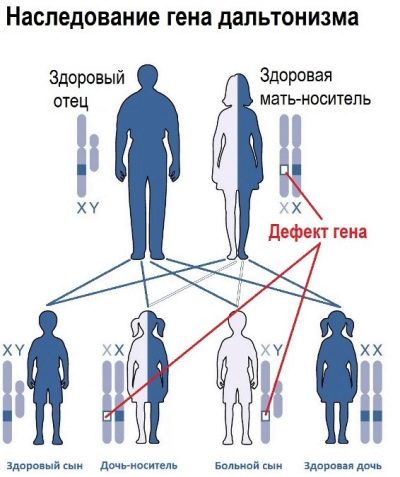
It is proved that hereditary color blindness arises due to a violation of the structure of the X chromosome. The acquired form of the disease may develop as a result of traumatic brain injury, neurological or ophthalmic organic disorders, stroke, some infectious diseases with a severe clinical course.
In world clinical practice, there are cases when color blindness was a sign of degenerative processes in the visual apparatus associated with aging of the body. A vivid example of this is the famous artist Ilya Repin. Being already quite an elderly man, he decided to remake his famous painting "Ivan the Terrible and his son Ivan." However, in the process of work, his friends and colleagues began to notice that an experienced painter had distorted the color palette of the entire composition, which clearly indicated a violation of his color perception.
Color blindness manifests itself predominantly in men, but more often this defect handed down to the child inherited from the mother, not from the father.
Among all color blind people, a very small part of people (0.1%) suffer from an absolute lack of color perception. It is much more common pathology in which a person can not distinguish between certain colors.
This is usually not a fallout from the sight of any color, but a significant weakening of its clear perception.
There are three types of partial color perception:
- Protanopia - a weakened color perception of a red range of shades.
- Deuteranopia is a weakened color perception of a green range of hues.
- Tritanopia - poor color perception of the blue-violet range of colors.
An interesting fact from the history: during the Second World War, there were frequent cases when the military, suffering from color blindness, quickly recognized their comrades among the leaves as camouflage. This curious fact was the subject of research for many scientists. In the course of their work, it was found out that color-blind people who have difficulty in recognizing red and green colors are well oriented among other shades. This may be due to the mechanism of visual compensation.
Ophthalmologist Smirnova Irina Yuryevna answers the questions about color blindness in the next video.