Causes and treatment of strabismus in children
In infants, the eyes are often pretty cute mowed And nothing terrible in this - at first glance. Not only that - it touches the parents. However, it takes several months, the child grows, and his eyes continue to mow, which can not but alert the adults. With suspicion of strabismus parents turn to ophthalmologists more often. This is the most popular reason for an unscheduled visit to a pediatric oculist. You will learn about the causes and treatment of strabismus in children by reading this article.
What it is?
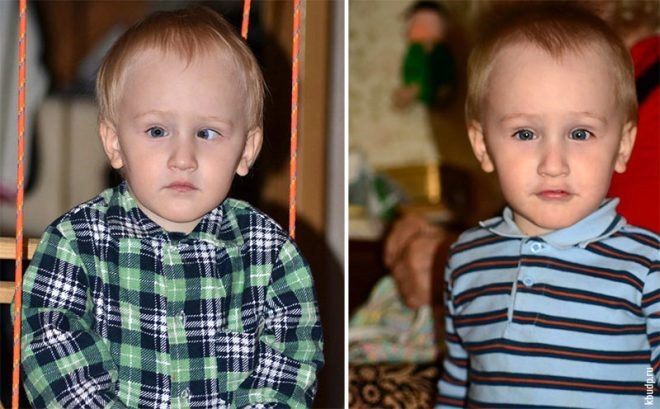
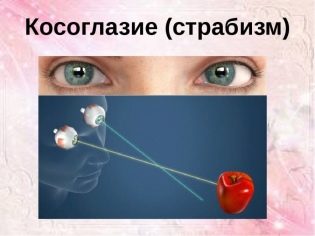
The disease, which is popularly referred to as strabismus, in medicine has rather complicated names - strabismus or heterotropy. This is a pathology of the organs of vision, in which the visual axes cannot be directed towards the subject in question. Eyes with differently arranged corneas cannot be focused at the same spatial point.
Quite often, strabismus is found in newborns and children in the first six months of life. However, in most cases, such strabism is physiological in nature and passes on its own within a few months. Often the disease is first detected at the age of 2.5-3 years, because at this time children actively form the work of visual analyzers.
Normally, the visual axes should be parallel. Both eyes should look at one point. With strabismus, an irregular picture is formed, and the child's brain gradually “gets used” to perceive the image from only one eye, whose axis is not curved. If you do not provide the child with timely medical care, the second eye will begin to lose visual acuity.
Often, strabismus accompanies eye diseases. More often it occurs as a concomitant diagnosis with hyperopia or astigmatism. Less often - with myopia.
Strabism is not only an external defect, a cosmetic defect, an illness affects the work of all the organs of vision and the visual center.
Causes
In newborns (especially premature) children, squint is caused by weakness of the eye muscles and the optic nerve. Sometimes such a defect is almost imperceptible, and sometimes it catches the eye immediately. With the active growth of all parts of the visual analyzers, physiological strabismus disappears. This usually happens closer to six months or a little later.
This does not mean that the parents of a six-month-old baby who mows his eyes need to sound the alarm and run to the doctors. Of course, it is worth a visit to the doctor, but only to make sure that the child does not have other pathologies of vision. If the baby sees well, the squint continues to be considered physiological. until they reach the year.
Strabism, which persists to one degree or another after a year, is not considered the norm, and it belongs to pathological disorders. The causes of pathological strabismus can be many:
- Genetic predisposition. If the close relatives of the child or his parents have a squint or had in childhood.
- Other diseases of the organs of vision. In this case, strabism serves as an additional complication.
- Neurological diseases.In this case, we can speak of dysfunction in the activity of the brain in general and subcortex in particular.
- Injuries to the skull, including generic. Typically, such strabism occurs as a result of acquired problems of the central nervous system.
- Congenital factors. These include intrauterine malformations of the organs of vision, which could have been formed as a result of mom's infectious diseases or genetic “errors”, as well as the effects of fetal hypoxia.
- Negative external influence. These causes include severe stress, jitters, psychological trauma, and poisoning from toxic substances, chemicals, or severe acute infectious diseases (measles, diphtheria, and others).
There are no universal reasons for explaining the occurrence of pathology in a particular child. Usually it is a complex, a combination of various factors - both hereditary and individual.
That is why the occurrence of strabismus in each particular child is considered by the doctor individually. The treatment of this disease is also purely individual.
Symptoms and signs
Signs of strabismus may be visible to the naked eye, and may be hidden. Mow can one eye or both. Eyes may converge to the nose or be "floating." In children with a broad nose, parents may suspect strabismus, but in fact there may be no pathology, just the anatomical features of the structure of the child’s face will create such an illusion. As it grows (during the first year of life), this phenomenon disappears.
Symptoms of strabism usually look like this:
- in bright light, the child begins to "mow" stronger;
- the baby cannot focus on the object so that the pupils move synchronously and are in the same position relative to the corners of the eyes;
- to look at an object with a squinting eye, the child has to turn its head at an unusual angle;
- during crawling and walking, the baby stumbles upon objects - especially if they are located on the side of the squinting eye.
Children older than one year may have complaints of headache, frequent fatigue. Vision in strabizme does not allow to see the picture clear, it can be blurred or double.
Children with strabismus often have an increased sensitivity to light.
Kinds
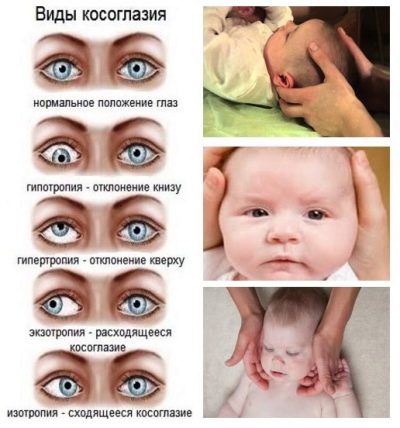
Squint can be congenital and acquired. Doctors talk about congenital pathology when clear signs of illness are visible immediately after the birth of the crumbs (or occur during the first six months).
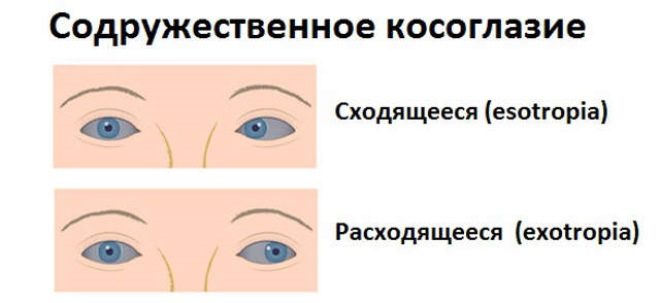
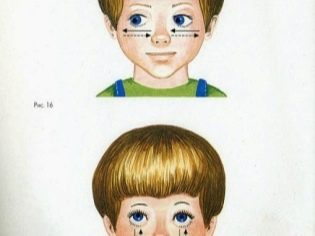
Usually pathology develops horizontally. If you mentally draw a straight line between the pupils through the nose, it becomes clear the mechanism for the occurrence of such a violation of visual function. If the eyes of the child tend to tend to each other in this straight line, it speaks of converging squint. If they tend in different directions in a straight line, then this is divergent squint.
Less commonly, pathology develops vertically. In this case, one or both organs of vision may deviate upwards or downwards. Such a vertical upward movement is called hypertropy, and downward - hypotropy.
Monocular
If only one eye deviates from the normal visual axis, then they speak of a monocular disorder. With it, the vision of the squinting eye is reduced in most cases, and sometimes the eye generally stops participating in the process of looking and recognizing visual images. The brain “reads” information from only one healthy eye, and the second “turns it off” as unnecessary.
Such a pathology is quite difficult to treat, and it is not always possible to return the functions to the affected eye. However, it is almost always possible to return the eye itself to its normal position, thereby eliminating a cosmetic defect.
Alternating
An alternating strabismus is a diagnosis that is made if both eyes are mowed down, but not simultaneously, but in turn.Either the right or the left organ of vision can change the axis both horizontally and vertically, but the angle and magnitude of the deviation from the line is always approximately the same. This condition is easier to treat.Since both eyes take part in the process of perception of images of the surrounding world, albeit alternately, which means that their functions have not been lost.
Paralytic
Depending on the reasons that triggered the formation of strabismus, there are two main types of strabismus: paralytic and friendly. When paralytic, as the name implies, paralysis of one or several muscles occurs, which are responsible for the mobility of the eyes. Immobility may be the result of violations of the brain, nervous activity.
Friendly
Common strabismus is the simplest and most common form of pathology, which is usually characteristic of children. The eyeballs with it retain the full or almost complete range of movements, there are no signs of paralysis and paresis, both eyes see and are actively involved, the image of the child is not blurred and does not double. Mowing the eye can see somewhat worse.
Friendly squint can be accommodative and non-accommodative, as well as partial. Accommodation pathology usually appears in early childhood - up to a year or 2-3 years. Usually it is associated with high or significant nearsightedness, farsightedness, and also with astigmatism. Treating such a “childish” eye disorder is usually quite simple - wearing glasses, prescribed by a doctor, and sessions of hardware therapy.
Partial or non-accommodative visual impairment also appears at an early age. However, myopia, hyperopia will not be the main and only reasons for the development of strabismus of these types. Surgical methods are often chosen for treatment.
Strabismus in children is permanent and impermanent. Non-constant diverging are often found, for example, in infants, and it does not cause great concern among specialists. Constant divergence is almost always the cause of congenital developmental abnormalities of visual analyzers and requires serious treatment.
Hidden
Hidden squint is difficult to recognize. With him, the child sees normally, with two eyes that are perfectly positioned and are not deflected anywhere. But it is necessary to “turn off” one eye from the perception of visual images (for example, close it with a hand), as it immediately begins to “float” horizontally (to the right or left of the bridge of nose) or vertical (up and down). To determine this pathology requires special ophthalmic techniques and devices.
Imaginary
Imaginary strabismus arises due to quite normal features of eye development in one or another child. If the optical axis and the visual line do not coincide, and this discrepancy is measured by a rather large angle, then slight false strabismus may occur. With it, the vision is not disturbed, they see both eyes, the image is not distorted.
The alleged strabism does not need correction and treatment at all. Cases in which a child begins to mow a little because of certain structural features of not only the eye, but also of the face, for example, because of the size of the orbits, cut eyes or wide nose bridge, can be attributed to false squint..
Treatment
It is possible to correct such a visual defect in almost all cases, the main thing is for parents to contact an ophthalmologist in a timely manner, without delaying a visit to the doctor. If after six months of a year the squint in a baby has not passed, it is necessary to begin treatment.
It is not necessary to be afraid of therapy, in most cases it is possible to do without surgery. Surgical intervention is prescribed only when all other methods are unsuccessful.
Modern medicine offers many ways to correct strabismus.This includes hardware treatment, physiotherapy, and special gymnastics to strengthen the oculorotatory muscles and the optic nerve.
The treatment schedule is prescribed strictly individually - taking into account all the circumstances and reasons that led to the development of strabism. ABOUTHowever, each therapeutic plan includes key moments and steps that need to be passed in order to correct the defect of the organs of vision most successfully:
- First stage. Includes treatment of amblyopia. The goal at this stage is to improve eyesight, increase its sharpness, bring sharpness values to the norm. To do this, usually use the method of wearing glasses with a sealed lens. In order not to frighten the child with such a medical device, you can use special child seals (occlusions). At the same time, several courses of treatment are prescribed.
The squint itself at this stage does not pass, but the vision is usually significantly improved.
- Second phase. Includes procedures that are aimed at restoring synchrony, communication between two eyes. To do this, use special devices and apparatus, as well as corrective computer programs.
- The third stage. It consists in the restoration of normal muscular balance between the organs of sight. At this stage, surgical treatment can be prescribed if the muscle damage is sufficiently pronounced. However, in children's practice, it is often possible to do with techniques that parents can practice at home - gymnastics, exercise for the eyes and procedures that the physiotherapy rooms of the clinics can offer.
- Fourth stage. At the final stage of treatment, doctors will try to do everything possible to fully restore the stereoscopic vision of the child. At this stage, as a rule, the eyes are already symmetrical, occupy the correct position, vision can be improved, the child is able to see clearly without glasses.
Based on such a sequence, the doctor will individually select a program for the correction.
After 2-3 years of treatment according to the prescribed scheme, the doctor will be able to conclude whether the child has managed to cure - or he is shown a surgical operation.
More details about some modern methods of strabismus treatment can be found below.
Hardware
Apparatus treatment accompanies virtually all stages of strabismus treatment, starting from the first, aimed at improving vision, and ending with the last - the development of stereoscopic vision. There is a large enough to correct the problem. the list of devices on which the child can work in the clinic or at home - if the parents have the opportunity to buy such equipment:
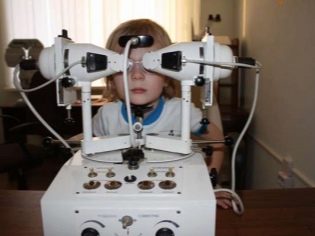
- The device "Ambliokor". Used to improve vision. It is a monitor and sensor system that captures nerve impulses during the work of the organs of vision. The child simply watches a movie or cartoon, and the sensors make up a complete picture of what is happening inside its visual analyzers. Special video programs allow sending “correct” impulses to the brain and restoring visual function at the subtlest (nervous) level.
- The device "Sinoptofor". This is an ophthalmological apparatus that allows a child to view parts of pictures (both two-dimensional and three-dimensional) and combine them. This is necessary for the development of binocular vision. Exercises on such a device train eye muscles well. In each eye, the child receives only parts of the image, attempts to combine them and will be an effective correction for strabismus at one of the final stages of treatment.
- Ambliopanorama. This is a simulator with which you can begin to treat strabismus, even in infants, because no effort is required from the child. It is enough for him to look at a disk with dazzling fields, wearing glasses prescribed by a doctor with corrective lenses, and try to examine objects.From time to time there will be a so-called retina glare. The simulator is very useful in the initial stage of strabismus treatment.
- The device "trickle". This unit can very well help at the stage of training the eye muscles and learning to control accommodation. The child will have to keep track of the eyes as they approach and move away, as well as make various movements with their eyes, since the light points will flash in different directions of the field.
Apparatus treatment can be carried out in the clinic, and at home.
Typically, a child at the initial stage is prescribed 3-4 courses, each of which includes at least 10 sessions. At subsequent stages of strabism treatment, the duration and feasibility of hardware treatment courses are determined solely by the doctor.
In connection with the emergence of a large number of private clinics and ophthalmologic offices that offer paid hardware treatment - however, they practically do not examine the child, many negative reviews have appeared about such treatment. Parents claim that the procedures and training did not help the child.
This once again proves that any therapy should be prescribed by the attending physician. If he sees that the extent and nature of the damage to the eye is such that hardware treatment is not enough, he will definitely choose other methods for the child.
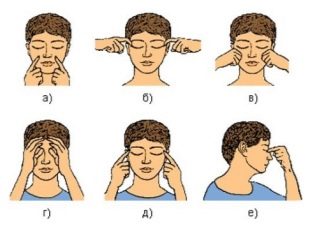
Eye gymnastics and exercises
In some cases, with a slight squint of non-paralytic origin, special exercises help at the stage of strengthening the oculomotor muscles. This is a treatment that does not require large expenditures, but requires the obligatory and strict observance of the principle of systematic training.
Gymnastics with a child is best done in the daytime, in daylight. Exercises are best performed with glasses. Gymnastics should be daily, it is desirable to repeat a set of exercises with the child 2-4 times a day. The duration of each lesson is from 15 to 20 minutes.
It is impossible to explain the essence of gymnastics to the smallest patients, and therefore it is recommended to simply play with them - moving balls, bright cubes and other objects in front of them, tying one or the other eye.
For older children, use occlusion or eye patch is desirable only if the squint is monocular. Children over 3 years old are invited to look for differences in pictures every day. Today on the Internet there are many such tasks that parents can print on a color printer and offer their child. For a start, it is recommended to take simple pictures with a small number of differences, but gradually the complexity of the puzzle should increase.
Children of kindergarten age with squint are helpful every day to solve maze tasks. These are drawings. The kid is invited to take a pencil and hold the bunny to the carrot, the dog to the booth or the pirate to the ship. Such pictures can also be downloaded from the Internet and printed.
Gymnastics for the eyes in the treatment of strabismus is very useful at the stage of the formation of stereoscopic vision. To do this, you can use ready-made programs compiled by Professor Shvedov or a psychology doctor, an unconventional healer Norbekov. However, it is absolutely impossible to choose a technique on your own. Incorrectly chosen and used exercises can lead to loss of vision.
Any gymnastics should be discussed with the doctor.
Many of the exercises that are suitable for a particular child, an ophthalmologist will show and teach them to do.
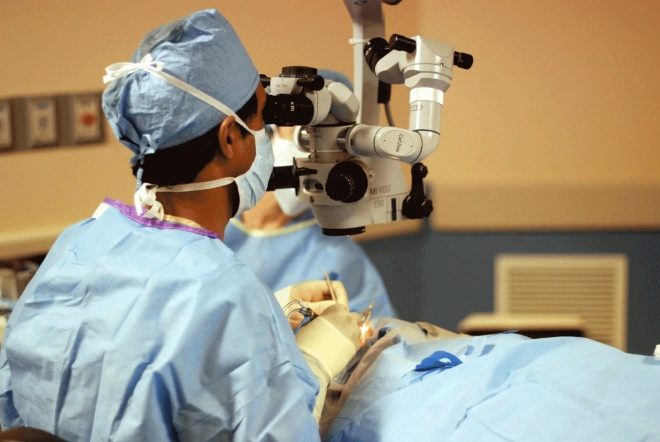
Surgical method
It is necessary to resort to the help of surgeons when conservative treatment was not crowned with success, when there is a need to restore the normal position of the eye, at least cosmetically, as well as at the treatment stage, when there is a need to strengthen the muscles responsible for eye movements.
Squint intervention options are not many: operating way, either they strengthen the weak and poorly holding the eyeball muscle, or relax it, if it stably fixes the eye in the wrong position.
Today, most of these operations are performed using laser systems. This is a bloodless and benign method that allows you to leave the hospital room the next day and go home in a familiar and child-friendly environment.
Small children are operated on under general anesthesia.
Older boys and girls - under local anesthesia. The most effective surgical intervention is considered to be at the age of 4-6 years; at this age, correction with the help of operating techniques provides the best results.
During the rehabilitation period, children are prohibited from swimming (for a month). Almost at the same time extends the ban on other sports. After the operation, for several weeks you cannot rub your eyes with your hands, wash your face with water, the quality and purity of which causes great doubts.
Return to the children's team (in kindergarten or school) a child after such an operation can only 2-3 weeks after discharge. During the crescent, all prescriptions and prescriptions must be carefully observed, including daily instillation of antibiotics or other anti-inflammatory eye products into the eyes.
Prevention
Preventive measures that will help protect the child from strabismus, can not be put off until later. They should start on the same day when the child was brought home from the maternity hospital. You need to do the following:
- You should make sure that the room where the baby is to live is well lit, that there is enough artificial lighting in the evening time of the day.
- Do not hang toys in a crib or stroller too close to the face of the baby. The distance to the eyes should be at least 40-50 cm. Another big parental mistake that often leads to the development of strabismus is a single bright toy suspended in front of the child in the center. It is best to hang two toys - right and left, so that the baby can switch his gaze from one to the other, thereby training the oculiatory muscles.
- Small toys are not suitable for infants, not only because he can choke with them. He will definitely try to examine them, and for this he will have to reduce his eyes to the bridge of his nose, bend low over the toy or bring it too close to his face. For the eyes of such children's experiments are not useful.
- Too earlier, learning, writing and reading (up to 4 years) can also lead to the development of strabismus, since the unformed visual apparatus is very tired during classes that require maximum concentration and concentration.
- If a child is sick with a flu, scarlet fever or another infection, you should not read it, draw or cross-stitch. During such diseases, the risk of complications from the most diverse organs and systems of the human body increases.
- In the diet of the child must be present products and vitamins necessary for the formation of normal vision. To do this, you should choose foods and vitamin complexes that contain a large amount of vitamins A, B1 and B2, as well as PP, C, and E.
- One should be attentive to the fears and experiences of the little man, since the psychological factor is far from the last among the causes of the development of pathology. It is very important that the baby grows up in a friendly atmosphere, so that parents can protect it from all the frightening factors. Avoid too sharp movements near the small child.
- Children should severely limit the time spent at the computer and at the TV, and also ensure that they do not use the gadgets uncontrollably - especially when traveling by bus or in the car.
- If there is a genetic predisposition to strabismus, the child should be shown to the oculist more often, visiting the doctor’s office not only during planned visits (at 1, 6 and 12 months), but also between these periods - to make sure that the pathological process has not started .
For more information about strabismus, see the next edition of Dr. Komarovsky’s program.