Congenital cataracts in children
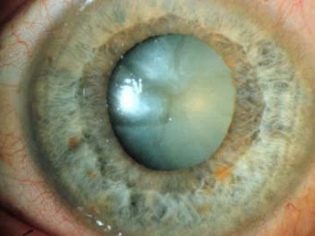
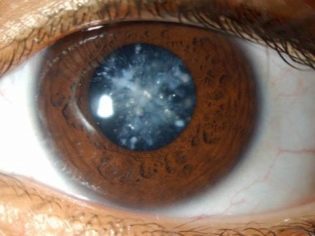
A cataract is a clouding of the lens. Unfortunately, it happens that a similar pathology is diagnosed in newborns. The cataract can cause a sharp decline. of view, which can be returned to normal values only promptly. Without appropriate therapy, this condition can lead to disability. What are the main symptoms of congenital cataracts, and what treatment is most suitable for children, will be discussed in this article.
Etiology of the disease
Statistics show that annually congenital cataract is diagnosed in 0.5% of all newborn children. At the same time, most often the degree of lens opacification is such that other methods of treatment, besides operative, will not be effective. It happens that the turbidity affects only the peripheral region of the lens and does not affect the quality of the central vision. In such cases, you can do with drug therapy.
Causes of congenital cataracts:
- genetic predisposition (disruption of the normal formation of the structure of the protein during embryonic development);
- metabolic disorders (including diabetes mellitus);
- the use by the future mother of certain types of drugs (eg, antibiotics);
- intrauterine infection (rubella, measles, cytomegalovirus, chickenpox, simple and shingles) herpes, poliomyelitis, influenza, Epstein-Barr virus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis and others).
Sometimes congenital cataracts are diagnosed in older children, but the causes of its occurrence remain the same.
Varieties
There are several types of congenital cataracts, depending on the localization of the pathological process in the structure of the lens:
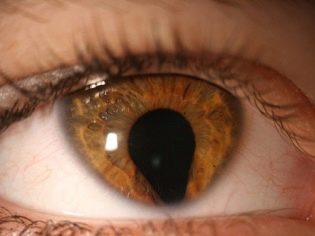
- Anterior polar cataract. Point cloudiness is localized in front of the lens. This type of disease is associated with a genetic predisposition. It is considered a mild form of cataract, since it has almost no effect on the visual acuity of the child and does not require surgical treatment;
- Rear polar cataract. In this case, the pathological process is localized in the back of the lens;
- Nuclear cataract. This is the most common type of cataract. Here, the turbidity is localized in the central part of the lens;
- Laminated cataract. This is also a common form of this disease. Opacification of the lens is localized in its central part around the transparent or cloudy nucleus. With this pathology, vision can be reduced to the minimum;
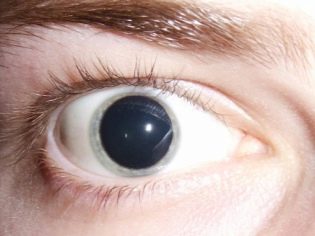
- Complete cataract. Blurring applies to all layers of the lens.
Clinical picture
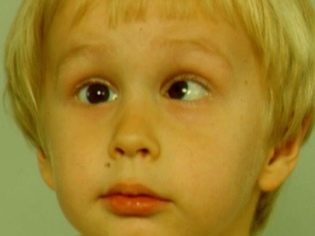
The first thing to look out for is the appearance in the pupil of a small area of discoloration. During a routine examination, an ophthalmologist may notice the development of strabismus in one or both eyes, as well as nystagmus (uncontrolled periodic movement of the eyeballs).
A newborn baby from about two months old begins to fix its gaze on objects and people surrounding it. If this does not happen, then most likely the baby’s vision is significantly reduced. At an older age you may notice that Every time a child tries to look at an object, he tries to turn to him with the same eye.
Without timely treatment, cataracts can trigger education. amblyopia ("lazy eyes"). Such a violation of the visual function in a child inevitably leads to the emergence of certain problems in the development process.
Therefore, it is important to undergo all the ophthalmologic examinations required for a newborn child (especially routine check-ups for children under 1 year) in order to take effective measures to solve this problem in the event of the presence of such a pathology.
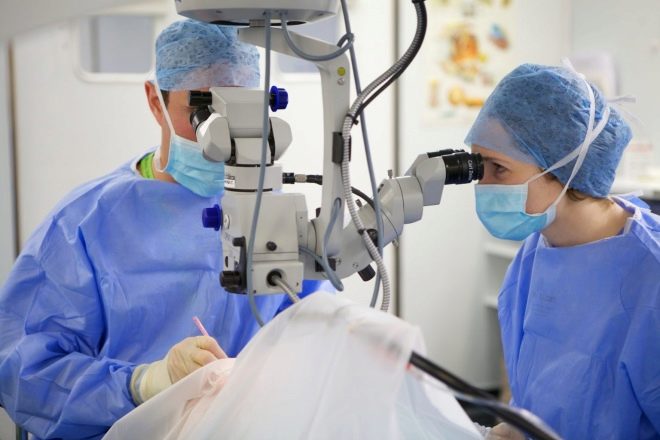
Surgical treatment
If the degree of opacification in the lens does not have a negative impact on the formation of central vision, then this pathology does not require a radical solution and the child is put on medical records. If the area of turbidity in the lens is extensive enough and adversely affects the central visual acuity, then an ophthalmologist raises the question of cataract surgery.
Of course, any surgical intervention is a certain risk of complications associated primarily with the effects of general anesthesia on the children's body. Also, such manipulation can trigger the development of secondary glaucoma, which is characterized by a persistent increase in intraocular pressure.
It is believed that the most optimal age for surgical removal of congenital cataracts is from 6 weeks after birth to 3 months.
One of the main conditions for the full development of the visual apparatus in a child who has undergone cataract surgery is correct spectacle or contact vision correction. If the parents and the ophthalmologist come to the conclusion that wearing contact lenses for a particular child is the most appropriate method of correction, in most of these cases lenses are assigned for long-term wearing. Increased demand for them is associated with simplified operating rules.
The timing of implantation of the artificial lens, after removing the clouded, is set for each child individually, as there is a chance that the intraocular lens will create additional difficulties in the process of growth of the eyeball.
It is rather difficult to calculate the exact optical power of the lens due to the increasing eyeball, and, accordingly, its changing refractive power. But, if you still managed to correctly determine this parameter, then you can avoid the development of postoperative complications, such as aphakia (complete absence of the lens in the eye)
Also among the likely complications after surgical removal of cataracts include:
- change in the normal shape of the pupil;
- strabismus;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- secondary cataract;
- retinal damage;
- development of severe inflammation in any part of the eye.
Such phenomena occur quite rarely, however, in the event of the occurrence of one of the above symptoms, another operation is performed, with the help of which the appeared defect is eliminated.
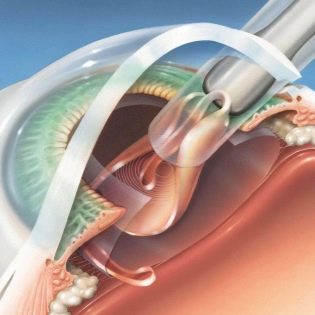
A microsurgical operation is performed to remove a clouded lens in a child, which is performed under general anesthesia. Laser correction for the treatment of pediatric cataracts is not used.
Recovery postoperative period
For some time after the operation, the child will need to correct vision, which is the correct focusing of the light rays on the surface of the retina. This can be achieved by several methods:
- constant wearing of glasses;
- constant wear of contact lenses;
- implantation of an artificial intraocular lens.
Eyeglass correction is the easiest and most affordable way to improve visual acuity in a child with a removed lens. Wearing glasses after surgery will have to constantly, because without them the baby will not be able to clearly see objects and freely navigate in space. Wearing glasses is an ideal method of postoperative correction for children whose lens is clouded in both eyes.
An ophthalmologist can assign multifocal (allowing to clearly distinguish objects at far, middle and close distances) or bifocal (allowing to see objects at a distance and near) glasses.
If the baby was operated on only with one eye, then the ophthalmologist will most likely prescribe an artificial intraocular lens implantation or contact correction. So-called "breathing" contact lenses are quite popular. They possess powerful optical power and remain invisible when worn.
For proper selection of lenses, you should consult with an ophthalmologist., which will determine the exact parameters of the lenses and help with the selection of the optimally suitable model for your child. In addition, he should explain in detail and show how to properly wear and remove the lenses, as well as tell about other nuances of operating these optical products, since the child will have to wear them all the time.
As the baby grows up, he will need to replace contact lenses.
An artificial intraocular lens can be implanted during the operation itself to remove the clouded natural lens or some time after it. It must fully compensate for the refractive function of the natural lens.
The artificial intraocular lens has a rather powerful refractive ability, due to which it does not require replacement as the eyeball grows.
About what kind of cataract in children, see the following video.