How to distinguish a milk tooth from a molar tooth?
The process of the appearance of teeth in a child is always interesting to parents, so they keep track of which milk ones have dropped out and which permanent ones have come out. However, there are situations when it is not clear, it is still a baby tooth in the mouth of a karapuz or already a molar one. How do they differ and by what signs can they be recognized?
What is the difference?
Dairy
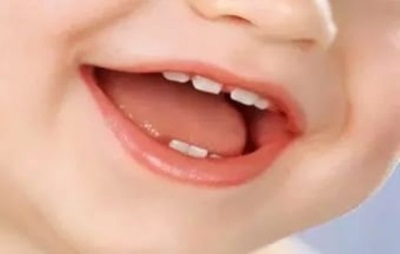
So called the first teeth that appear in a child under the age of 2.5-3 years. They begin to cut through in most babies at 6 or 7 months, when the first central incisor “pecks” on the lower jaw of the baby. Soon his “partner” comes out, after which incisors on the upper jaw are cut, the lateral incisors are below, the first molars, canines and the second molars, until the child has 20 teeth.
This number will remain until about 5-6 years, after - the time comes for the eruption of the first molars.
Indigenous
So called permanent teeth, which begin to cut at an average of 6-7 years of age. The first molars erupt from the molars take the sixth place in the dentition, and only after this the baby teeth begin to fall out, and in their place their permanent replacement begins to cut. At the same time, there are more molars - 32 in total, although in childhood only 28 of them are incised in most cases.
The last four (“wisdom teeth”) appear later than the others, sometimes even over the age of 30-40 years.
How to distinguish milk from root?
You can determine whether a tooth is dairy or indigenous, you can by its:
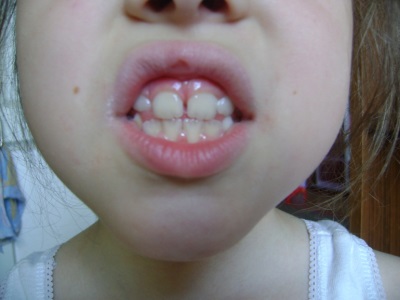
- The magnitude and form. Temporary - small in size and more rounded, and indigenous - larger.
- Coloring. The color of dairy is often white with a non-expressed blue tint, and the permanent ones, due to the presence of more mineralized tissues, are distinguished by a yellowish tinge of enamel.
- Location. The growth of milk occurs vertically, while the indigenous ones slightly guide their crowns outward to the lips and cheeks.
Let's take a closer look at how to understand a baby tooth in a baby’s mouth or is already permanent, taking into account its serial number in the dentition (the number is calculated from the centerline out):
- If the tooth is sixth or seventh, then it is a root one, because there will only be five teeth on each side of the jaw.
- If you are looking at the fourth and fifth teeth, pay attention to the crown. Milk teeth on this place are distinguished by wider crowns and the presence of four chewing hillocks. If these are already permanent teeth, which are called premolars, they will differ in a smaller number of hillocks (there are only two on each tooth) and narrower crowns. In case of a controversial situation, the tooth is compared with the similar one on the other side of the dental arch.
- When deciding whether a third tooth (canine) is permanent or milky in a child, its shape and size should also be considered. Milk canines differ in smaller sizes, and by the time of physiological change their sharp tips are abraded. Permanent fangs are longer, and their tubercle has a distinct pointed tip.
- Looking closely at the incisors (first and second teeth), first of all they also take into account their size.If they are temporary, their width is about 4-5 mm, and the height is about 5-6 mm. In permanent incisors, the width of crowns is greater - about 10 mm in the central and about 6-8 mm in the lateral ones. In addition, at the age of eruption of permanent incisors, their cutting edges are uneven (with small tubercles), and for milk incisors the edge will always be smooth and even by this age.
Do all dairy change to indigenous?
In order for a child to have indigenous, absolutely all baby teeth must fall out. Some mothers think that milk molars, because of their large size, are permanent and do not fall out, but this is not so. They will also fall out in due time, making it possible for permanent premolars and molars to cut through.
Is the wisdom tooth native or milky?
Four teeth are called “wisdom teeth”, which are cut last. By their location in the dentition, they are also called "eights". Since they are the 29th, 30th, 31st and 32nd teeth in a person’s mouth, they can’t be milky, because there are only twenty milk teeth. In addition, they are cut over the age of 17, when no baby tooth in the child’s mouth should normally remain.
What if the dairy grows root?
The situation when the molar tooth has already “spiked”, and the milky one is in no hurry to fall out - not uncommon. In this case, you should wait for some time, giving the milk tooth a chance to loosen and leave the dentition.
If more than three months have passed since the appearance of a permanent tooth, and the milky remains in the gum, you should go to the dentist with the child.
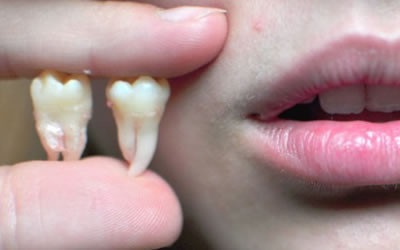
Can the root stay in the gum?
Since the age of five, the roots of milk teeth begin to dissolve. This process takes quite a long time, for example, the root of each incisor resolves within two years, and it takes about three years to completely dissolve the roots of the molars. However, all the roots sooner or later dissolve, and only after that the teeth fall out, so they cannot remain in the gum.
When and why do x-rays?
In controversial situations, when it is difficult to determine if a baby tooth is already molar, an X-ray examination is recommended. For example, using this method of research, one can decide how to treat it or why its change to a permanent one is late. On the radiograph can be seen:
- The length of the roots that the milk teeth will be shorter.
- The presence or absence of tooth germs under the milk teeth.
- The location of the cutting molar (it affects the correctness of the position after eruption).