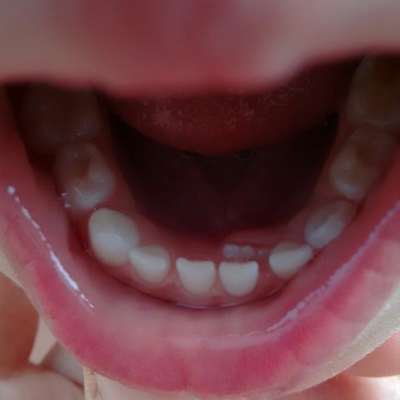
All about baby teeth in a child
The period of the appearance of teeth in babies is often not easy, causing sleepless nights, moods and other problems. And to help the baby, young parents should learn more about baby teeth, normal terms and the order of their appearance, possible problems and the period when they begin to change to permanent ones.
What is it?
Milk teeth are the first teeth that appear in early childhood. The complete set includes twenty milk teeth, represented by 8 incisors, 4 canines, and 8 milk molars. They need babies to bite off and chew food, as well as to form the jaw until the time when the eruption of teeth, called permanent or indigenous, begins. Besides, they are important for the development of masticatory muscles and speech.
Unlike regular dairy:
- Smaller size.
- More rounded.
- White with a slight blue tint.
- Grow vertically.
- More fragile.
- With wider and shorter roots.
We recommend to watch an interesting video about why the baby needs them:
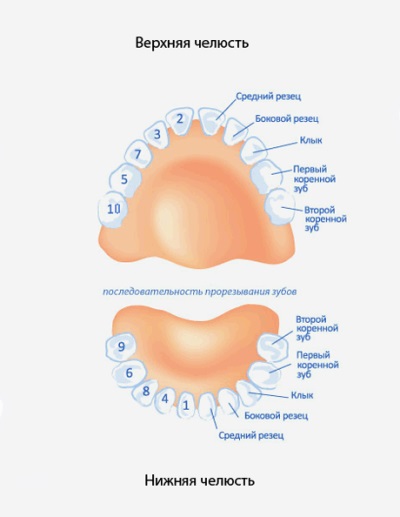
Counting the teeth of a child, start from the middle line and move outwards., as a result, a dental formula of 5 teeth is formed: “the central incisor — the lateral incisor — the canine — the first molar — the second molar”. Thus, "edinichkami" called the central incisors, "twos" - the lateral incisors. The canines occupy the third place and therefore are “troika”, and the molars, respectively, the “fours” and “fives”.
Dental biological age
Assessment of the child’s teeth is used to control the development of the child’s body, determining whether the child is developing normally, isn’t his development delayed, or is the baby ahead of its peers.
In babies, the number of teeth is counted and compared with average rates for their age. In children 2-6 years old, radiography is often used to assess the changes, since the external teeth do not change.
When milk teeth erupt?
Special features
- Baby teeth are often cut in pairs. If mom noticed one "spiked" tooth, soon we should expect the appearance of his "partner".
- In most cases, the process begins with the lower jaw. It is on it that the first central incisors, canines, and molars erupt, after which they appear on the upper jaw. At the top, only the lateral incisors erupt first.
- To count the normal number of teeth for a certain age of babies Doctors use the formula "taken in months of the crumbs minus 4".
First tooth
In most babies, the first tooth that has erupted is the lower central incisor. It is flat and small, located on the lower jaw, used for biting food. Its average term of appearance is called 6-8 months, although in some babies it appears a few months earlier, while in others, its eruption may linger until the age of one year.
Timing
A lot of factors influence the time of teething of children's teeth, among which the heredity, the state of health and nutritional features of the baby are called the main ones. All baby teeth, as a rule, erupt to 2.5-3 years of age. Approximate dates of occurrence, average for most babies, are displayed in the table:
|
Name of a pair of teeth |
Age in months |
|
Central incisors |
Bottom at 6-9 Upper in 7-10 |
|
Side cutters |
On the upper jaw at 9-11 Down at 11-14 |
|
First molars |
On the lower jaw at 12-18 Above at 13-20 |
|
Fangs |
Down at 16-22 Upper at 17-23 |
|
Second molars |
Bottom at 20-26 On the upper jaw at 26-33 |
Sequence
The order in which the milk teeth “hatch” is usually different for different children, but most of the children have this sequence:
- After the appearance of the lower central incisors Next, the same pair of teeth is cut on the upper jaw.
- Next, near the central upper incisors are cut lateral incisorsand then the opposite lateral incisors that appear on the lower jaw begin to cut.
- The following begin to erupt first molars. First, they are cut below, and then “pecked” on the upper jaw.
- Between the molars and the lateral incisors, the lower ones begin to erupt. fangs, and after them - fangs on the upper jaw.
- Complete the process of teething milk teeth. second molarswhich at first, as a rule, cut through below, and then on the upper jaw.
A few words about the sequence of cutting and said the famous Dr. E. Komarovsky:
Symptoms
As a rule, children with cutting milk teeth observe:
- Increased saliva production and discharge.
- Swelling and redness of the gums in the place where the tooth is cut.
- Decreased appetite.
- Bad sleep.
- Capricious and irritable behavior.
- The desire to gnaw a variety of items to reduce itching in the gums.
In some children during the period of teething milk teeth temperature rises (often not higher than + 37.5 ° C) and not for long the chair is liquefied due to saliva being swallowed. Also found the appearance of a mild wet cough and a weak rhinitis with clear discharge. Due to the annoying effect of saliva escaping from the mouth, it is possible the appearance of redness and rash on the chin and chest.
Why can hurt?
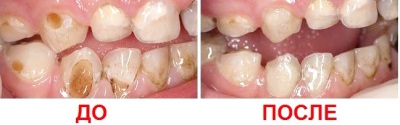
Milk teeth due to thinner enamel and increased vulnerability are affected by various diseases more often than permanent ones. They are most often affected by caries, but in the early stages no painful sensations arise from this disease.
If the infection penetrates deeper, the teeth begin to react with pain to some stimuli, for example, sour food or a sweet drink.
Temperatures can also cause soreness, and if the caries has become deep and complicated by pulpitis, pain also occurs when chewing.
In the presented video, a children's dentist gives some tips on how to avoid the development of caries:
Treatment
Although some parents think that milk teeth do not require as attentive care and treatment as permanent, they must be treated. Lack of treatment can lead to activation of the infection process, penetration deep into the dental tissues and pulp, as well as serious complications. The result is the loss of a tooth, which may cause a violation of the permanent bite.
A decayed baby tooth acts as a source of infection in the baby’s body and weakens its defenses.
The treatment uses the following methods:
- Fluoridation. The teeth are treated with solutions containing fluoride ions. The technique is often used to prevent caries, as well as during its initial manifestations in the form of white spots.
- Silvering. With this method, the teeth are treated with solutions with silver. As well as fluoridation, the technique is shown at initial caries or for its prevention. Its main disadvantage is the darkening of the teeth.
- Remineralization. The essence of this method is the processing of special compounds that fill the teeth with minerals, in particular, calcium, phosphorus and fluorine.
- Ozone treatment. This method is used to clean teeth from bacteria and disinfect.
- Fissure sealing. With this method, the teeth are covered with a special glass-like substance.
- Sealing. This technique involves the removal of infected tissue from the affected tooth and the installation of fillings.
Deletion
Milk teeth with their diseases, in most cases, try to save, so that they "hold a place" for the indigenous. However, there are situations forcing them to be removed, for example:
- His injury.
- Deep caries with the destruction of the roots.
- Increased mobility.
- Serious complications of caries, such as periodontitis.
- Violation of the term of loss.
To remove a baby tooth, as a rule, it is necessary to perform injection anesthesia, and in some cases it is impossible to do without general anesthesia.
Why fall out?
Baby teeth are temporary, as the child’s jaw grows and the load on it increases. They should be replaced by stronger and larger teeth, therefore, starting from the age of 5, their roots gradually dissolve.
For most children, they fall out at this age:
|
Name of a pair of teeth |
At what age fall out |
|
Central incisors |
In 6-8 years |
|
Side cutters |
From 7 to 8 years |
|
First molars |
At 9-11 years old |
|
Fangs |
From 9 to 12 years |
|
Second molars |
10-12 years old |
Change to indigenous
What is it
Indigenous - are permanent teeth, replacing dairy in the children's body. They are more durable and are represented in larger numbers - just 32 pieces are cut through a person, although the last four of them, which are called “wisdom teeth,” can cut through well after adolescence.
Unlike the milk bite, there are permanent teeth, called premolars. They cut between fangs and molars.
Dental intervals
Before the first milk teeth begin to fall out, parents will notice that the gaps between them have increased. This is absolutely normal evidence of the child's jaw growth process, because the size of the molar teeth is much larger, and by the time they erupt, the jaw is enlarged. If there are no gaps between the milk teeth by the age of six or seven, the child should be shown to the dentist.
First permanent
They are called “sixes” for their location, since they are cut behind the fifth milk teeth (second milk molars). Dentists call these permanent teeth the first permanent molars.
Their eruption is often observed up to the moment when a child has a loss of the first milk tooth. This most often occurs at the age of 5-6 years, that is, a 6-year-old child may experience a situation in which there are 24 teeth in the mouth, including twenty milk teeth and 4 permanent ones.
Timing
After the first permanent molars appeared and the milk incisors began to fall out, the molars are cut in this order:
| The name of the pair of teeth and their location | How many years are cut |
| Lateral incisors below | 7-8 |
| Lateral incisors on the upper jaw | 8-9 |
| Bottom fangs | 9-10 |
| Top canines | 11-12 |
| First premolars below | 10-11 |
| Upper first premolars | 10-12 |
| Second premolars above | 10-12 |
| Second premolars on the lower jaw | 11-12 |
| Lower second molars | 12-13 |
| Upper second molars | 12-13 |
| Third molars | after 17 |
You will learn more by watching Dr. Komarovsky’s program.